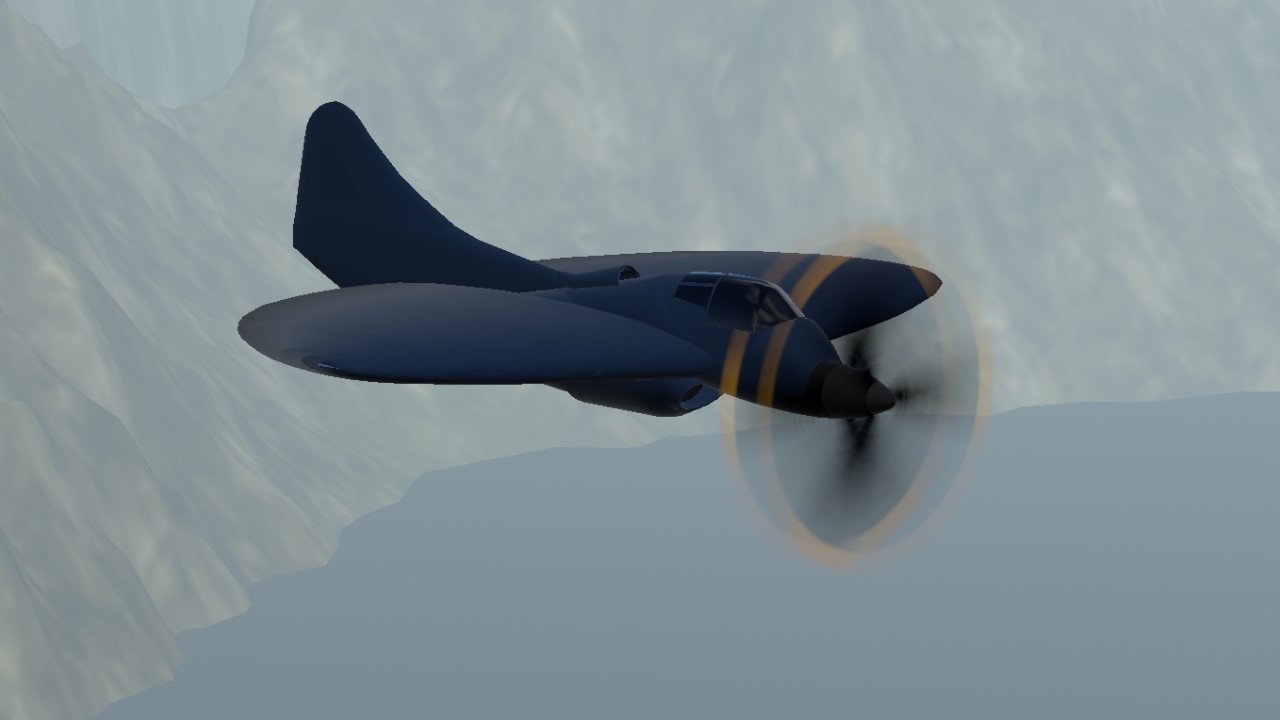
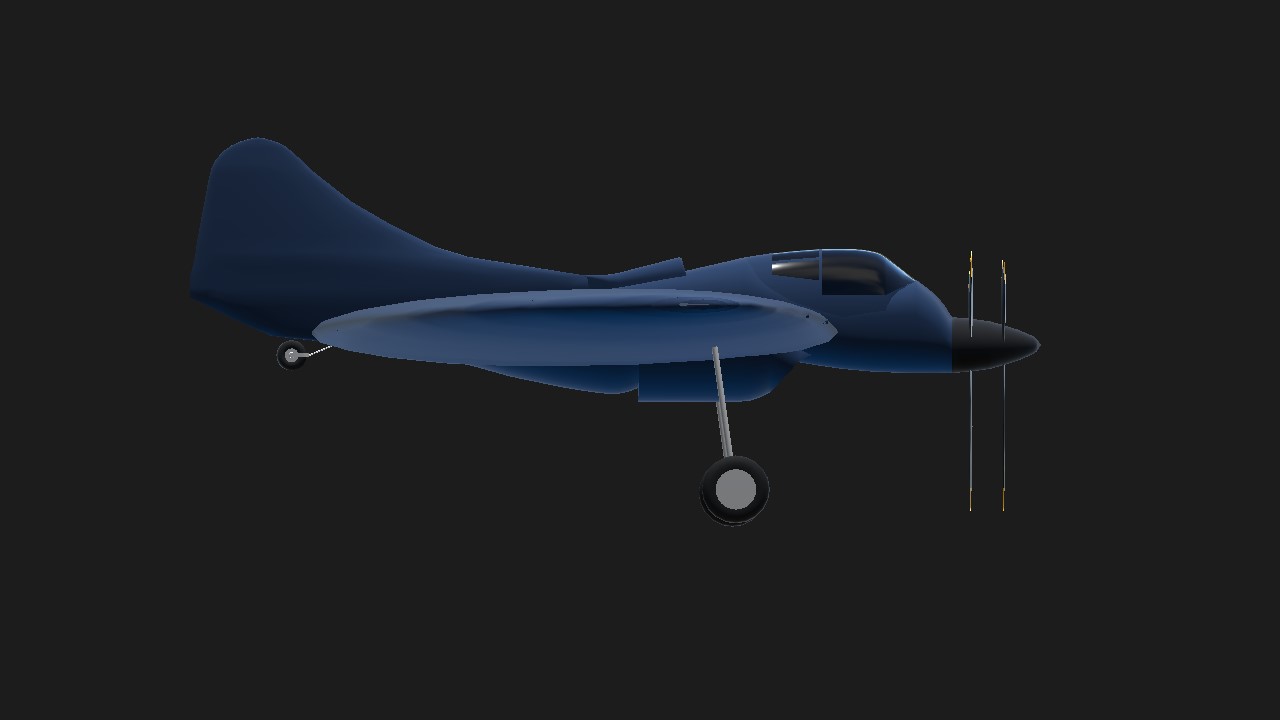
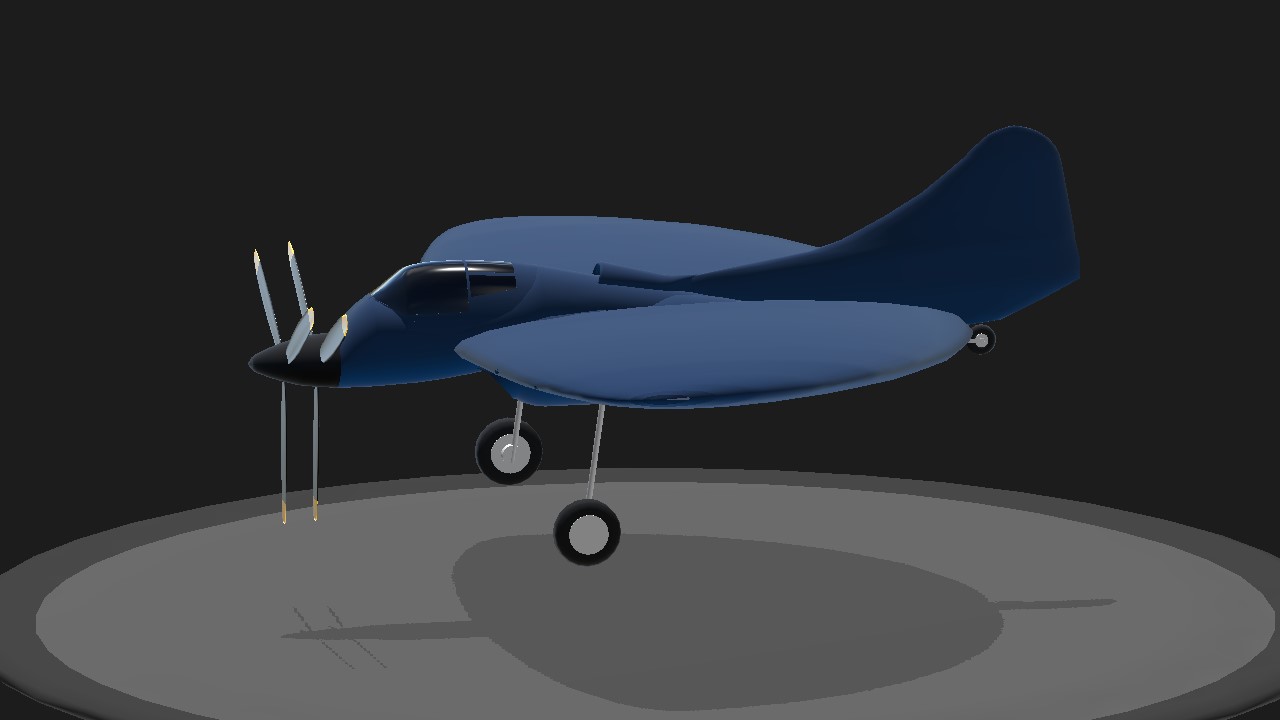
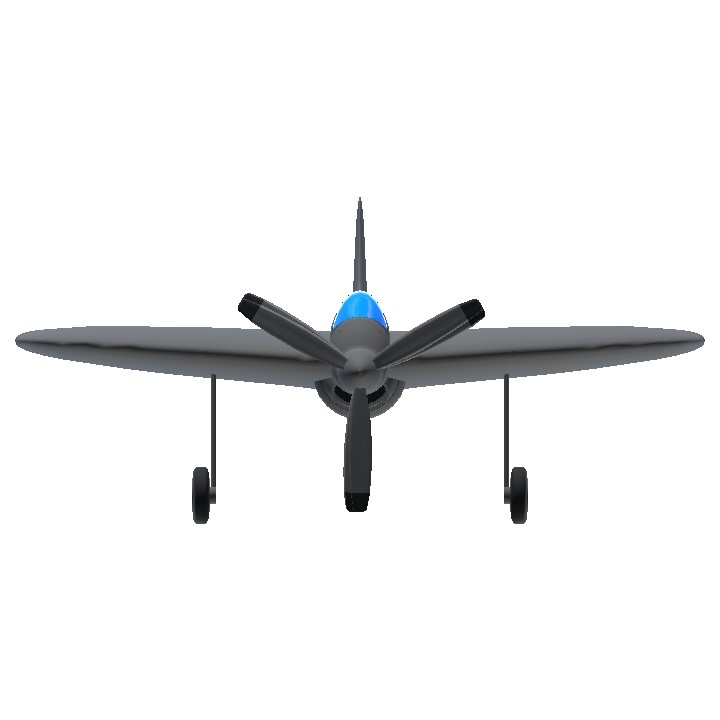
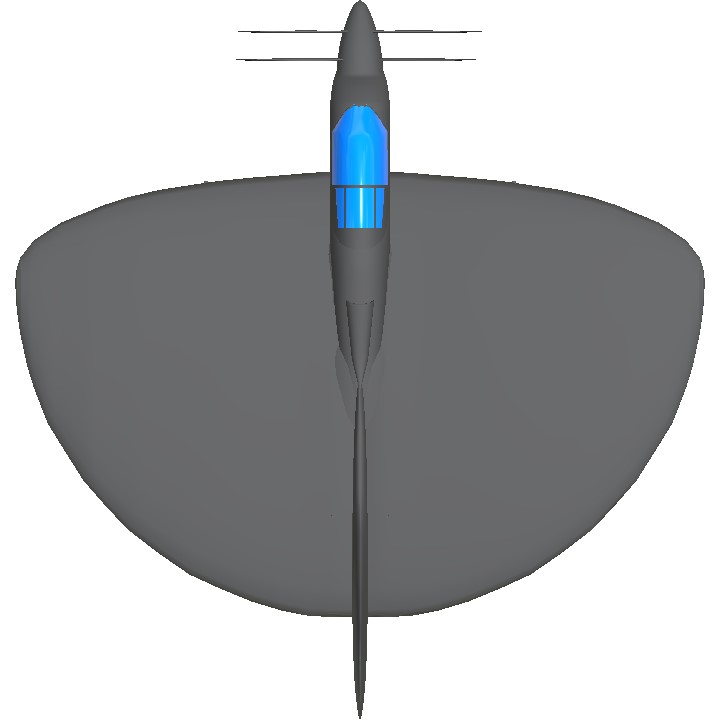
The Boeing model 390 was a project for a naval fighter with a circular wing form.
In mid-1940s Boeing engineers designed prototypes for a circular winged aircraft. These are models 390, 392 and the testbed 396. Unlike its counterpart, the Vought XF5U that has engine nacelles on its wing, the model 390's engine is rooted on the mid-section with an air duct protruding on its undersides. Moreover, it uses a tailless design that which its counterpart does not utilize.
Designation: Naval aircraft/Fighter
Pros:
Can outrun most aircraft of the preceding years and some on its era
Excellent climb rate
Decent maneuvrability
Cons:
Hard landing, braking on ground causes propeller damage
Subpar armament
Performance
Maximum speed: 712 km/h at 2,000 meters
Cruise speed:
Climb rate:
Armament:
x4 .50 calibre MG
Specifications
General Characteristics
- Created On Android
- Wingspan 33.0ft (10.1m)
- Length 34.5ft (10.5m)
- Height 15.7ft (4.8m)
- Empty Weight 8,061lbs (3,656kg)
- Loaded Weight 13,002lbs (5,897kg)
Performance
- Horse Power/Weight Ratio 0.23
- Wing Loading 22.4lbs/ft2 (109.6kg/m2)
- Wing Area 579.2ft2 (53.8m2)
- Drag Points 2783
Parts
- Number of Parts 160
- Control Surfaces 5
- Performance Cost 697