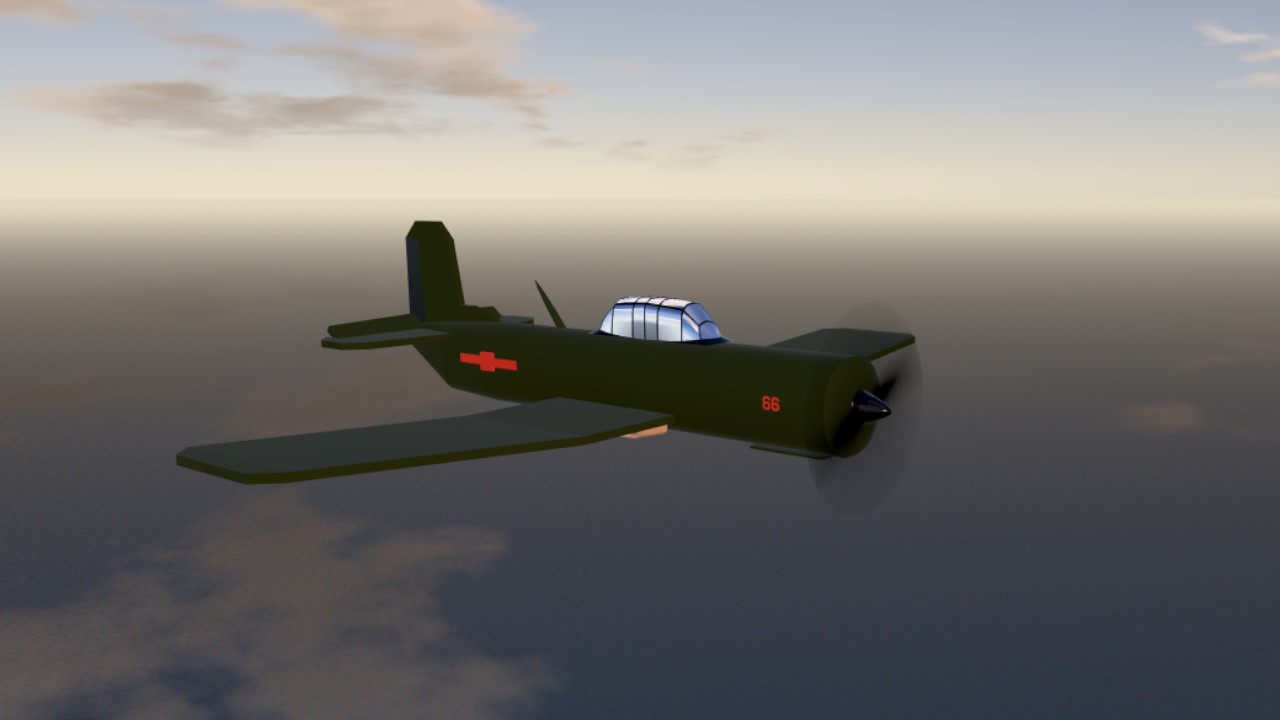
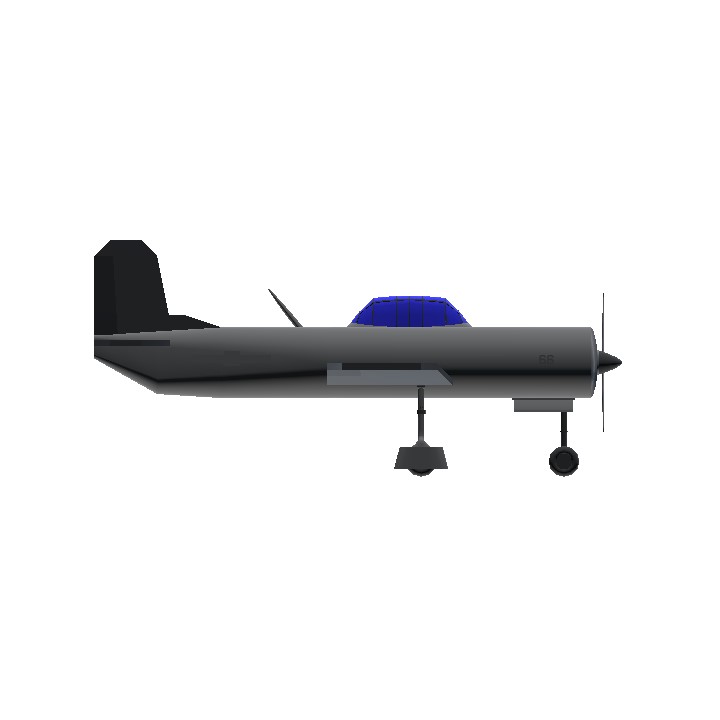
The CJ-6 (Chu Jiao ?? = Chuji Jiaolianji ????? = basic trainer aircraft) is an all-original Chinese design that is commonly mistaken for a Yak-18A. Its predecessor, the Nanchang CJ-5, was a licence-built version of the Yak-18. However, advancements in pilot training brought a need for a new aircraft with improved performance and a tricycle landing gear. When the Soviet Union developed the Yak-18A, PLAAF engineers decided that its performance and design would not suit China's needs.[1]
The aircraft was designed in 1958 by the Nanchang Aircraft Factory (now Hongdu Aviation). As the Shenyang Aircraft Factory already had experience building the Shenyang JJ-1 begun technical research for the CJ-6, more than 20 Shenyang designers were transferred to Nanchang, including chief designers Tu Jida and Lin Jiahua.[2] Xu Shunshou and Huang Zhiqian, then China's top aircraft designers, were also involved.[1]
During late 1957 Aeronautical Engineers Cheng Bushi and Lin Jiahua began work in Shenyang on a trainer design that addressed the shortcomings of the Yak-18A. The design they delivered featured an aluminum semi-monocoque fuselage, flush-riveted throughout, and introduced a modified Clark airfoil wing design with pronounced dihedral in the outer sections. The dihedral and an angular vertical tail distinguish it externally from the otherwise vaguely similar Yak-18A. Wind tunnel testing validated the design, and in May 1958 the program was transferred to the Nanchang Aircraft Manufacturing factory where Chief Engineer Gao Zhenning initiated production of the CJ-6. The first flight of the CJ-6 was completed on August 27, 1958, by Lu Maofan and He Yinxi.
Power for the prototype was provided by a Czech-built horizontally-opposed piston engine, but flight testing revealed the need for more power, so a locally manufactured version of the Soviet AI-14P 260 hp radial, the Huosai HS-6 (Chinese: ??-6), was substituted along with a matching propeller, and with that change the CJ-6 was approved for mass production. In 1965 the HS-6 engine was upgraded to 285 hp and redesignated the HS-6A, and the aircraft equipped with the new power plant were designated the CJ-6A.
A total production run estimated at more than 3,000 aircraft supplied CJ-6 aircraft for PLAAF training, as well as for export (as the PT-6) to countries including Albania, Bangladesh, Cambodia, North Korea, Tanzania, and Sri Lanka.
It is expected Hongdu/Yakovlev joint developed CJ-7 Trainer (L-7) primary trainer will replace CJ-6s in PLAAF.
CJ-6 attained its civil aviation type certificate on February 28, 2019, more than 60 years after it entered military service in China.
Specifications
General Characteristics
- Created On Mac
- Wingspan 37.5ft (11.4m)
- Length 27.7ft (8.4m)
- Height 12.2ft (3.7m)
- Empty Weight 5,443lbs (2,469kg)
- Loaded Weight 6,910lbs (3,134kg)
Performance
- Horse Power/Weight Ratio 0.144
- Wing Loading 25.3lbs/ft2 (123.4kg/m2)
- Wing Area 273.5ft2 (25.4m2)
- Drag Points 2239
Parts
- Number of Parts 36
- Control Surfaces 5
- Performance Cost 223