Instructions
VTOL to drive
Yaw to turn
Brake to brake
FireWeapons to fire main gun
FireGuns to fire MG
Switch to Gunner sight and aim with Camera
note : The speedometer was faulty at the time of measuring max speed for the second image above
Christie Suspension.
The Christie suspension is a type of vehicle suspension system that was developed in the early 20th century by American engineer J. Walter Christie. It is most notably associated with military tanks and armored vehicles.
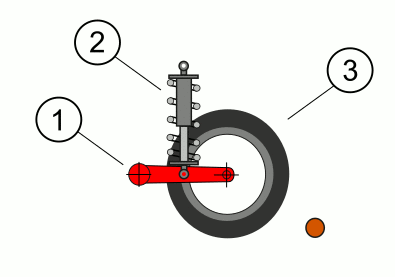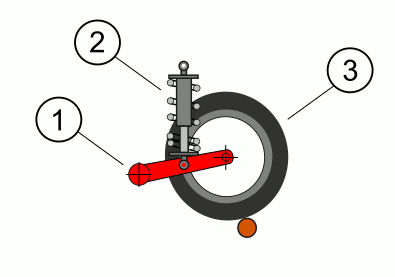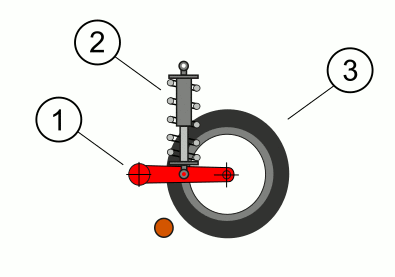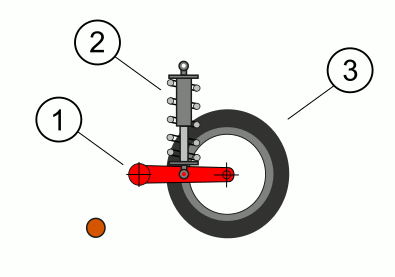
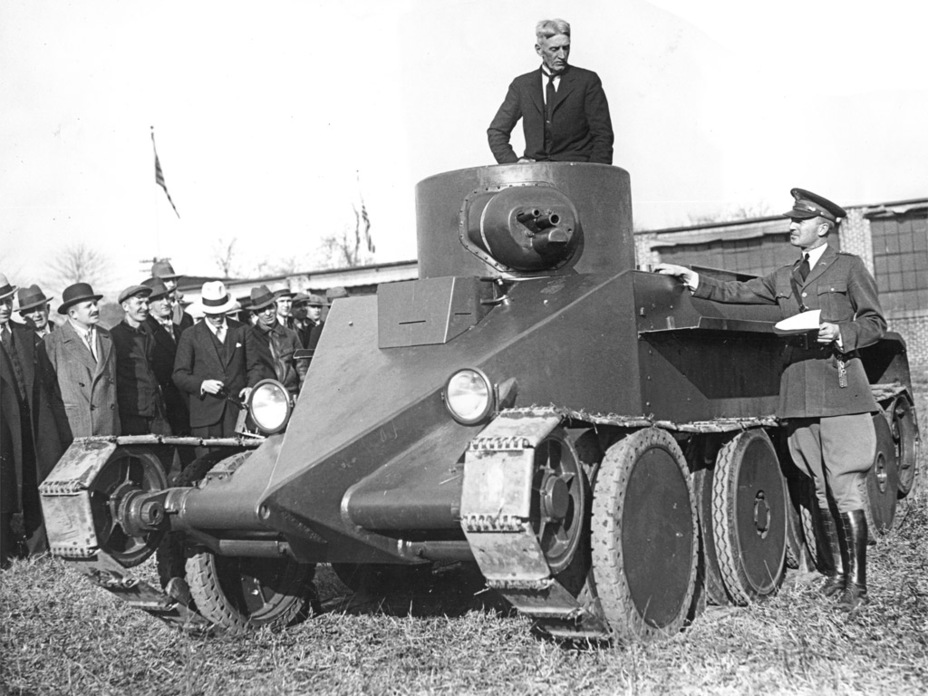
Christie's Tank
The Germans, constrained by the Treaty of Versailles which severely limited their ability to develop and produce military hardware, were nonetheless keenly interested in J. Walter Christie's innovative tank designs, particularly the Christie M1931. The treaty's restrictions forced Germany to be creative in their military advancements, often studying foreign technologies to circumvent direct prohibitions. Christie's tank, with its revolutionary suspension system and exceptional mobility, drew significant attention. Although Germany did not directly acquire Christie's tanks due to these restrictions, they closely monitored the advancements and performance of these vehicles through various means, including intelligence reports and international exhibitions. The high speed and superior cross-country capabilities of Christie's designs deeply impressed German military planners. This covert interest in advanced tank technology influenced the development of Germany's own armored vehicles during the interwar period and World War II, emphasizing the critical importance of mobility and innovative engineering in modern warfare.

DEVELOPMENT LORE
To circumvent the restrictive terms of the Treaty of Versailles, which prohibited the development and production of military tanks, the Germans ingeniously devised a subterfuge by labeling their interest in J. Walter Christie's innovative tank as a project for "tracked all-terrain racing vehicles." This clever ruse allowed them to explore advanced armored vehicle technologies under the guise of civilian racing and engineering research. By promoting the Christie M1931 as a high-speed, all-terrain vehicle for competitive racing, the Germans were able to discreetly import and study its groundbreaking suspension system and mobility features without attracting suspicion from the Allies. This subversive strategy enabled German engineers to gain invaluable insights into advanced tank design, The PzSpWg I Ausf. A.

Gun
The development of the PaK 38 (Panzerabwehrkanone 38) was initiated by Germany in 1938 as a response to the increasing armor of contemporary tanks, particularly those seen in the early stages of World War II. Designed by Rheinmetall-Borsig, the PaK 38 was a 50 mm anti-tank gun that offered a significant upgrade over its predecessors, such as the 37 mm PaK 36. Officially entering service in 1940, the PaK 38 featured a longer barrel and higher muzzle velocity, enabling it to penetrate thicker armor at greater distances. Its deployment became crucial during the invasion of the Soviet Union in 1941, where it proved effective against the lightly armored Soviet tanks. However, as the war progressed and tanks with even heavier armor appeared on the battlefield, the PaK 38 eventually became less effective, leading to the development of more powerful anti-tank guns. Nonetheless, its role during the critical early years of the war highlighted the importance of continuous innovation in anti-tank warfare.
Actual development
In 1941, amidst the relentless demands of World War II, German engineers are developing a new lightweight combat and scout tank incorporating the innovative Christie suspension and the formidable 50 mm PaK 38 anti-tank gun. This new design aims to combine speed, agility, and firepower, leveraging the Christie suspension's superior cross-country mobility and high-speed capabilities. The tank's lightweight construction ensures rapid maneuverability, making it ideal for reconnaissance missions and quick strikes against enemy positions. Armed with the PaK 38, it can effectively engage and destroy a range of enemy armor, providing a versatile tool for the Wehrmacht. This combination of advanced suspension technology and powerful armament is expected to enhance the operational effectiveness of German scouting units, allowing them to gather crucial intelligence and deliver decisive blows with unprecedented efficiency.
Tactics
German tactical ingenuity on the Eastern Front involved the strategic use of conventional tanks as bait to lure heavier Soviet tanks, such as the KV series, into vulnerable positions. This tactic exploited the Soviet tanks' slower speed and maneuverability. Meanwhile, the Panzerspähwagen I Ausf. A (PzSpWg I Ausf. A), a light armored scout vehicle armed with a 50mm PaK 38 anti-tank gun, was employed to flank and engage these heavier adversaries from unexpected angles. Its speed and agility allowed it to swiftly maneuver around the battlefield, exploiting gaps in enemy defenses and targeting weak points on the heavily armored Soviet tanks. This asymmetrical warfare tactic highlighted the German Army's ability to maximize the strengths of their lighter, more agile vehicles against the superior armor of their opponents, contributing significantly to their successes in countering Soviet armor on the battlefield.
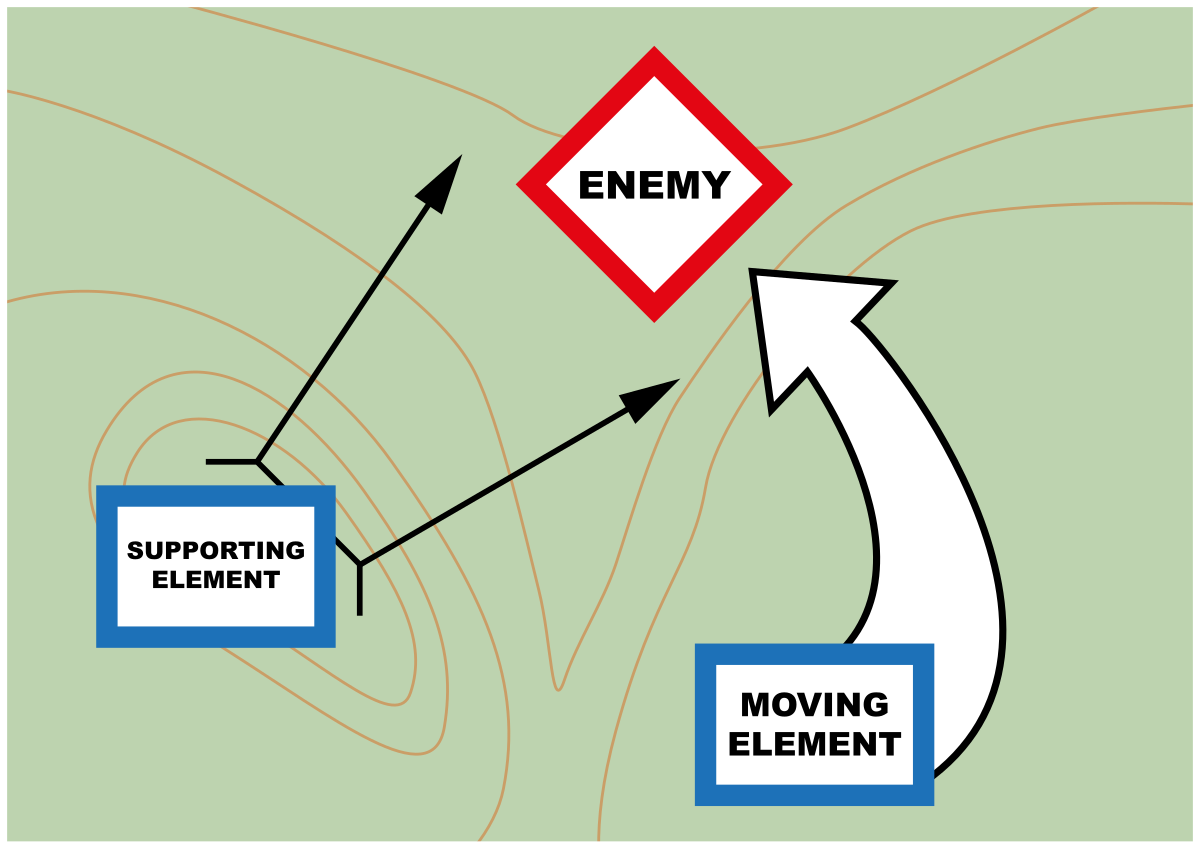

The Trade Off
the vehicle's lack of armor made it vulnerable to enemy fire, especially in close engagements. The high-speed maneuvers required a skilled crew to operate effectively, and inexperienced personnel often struggled to handle the vehicle's rapid movements and complex battlefield tactics. Tragically, mistakes made by inexperienced crews sometimes resulted in fatal consequences, as the vehicle's speed could lead to accidents or leave it exposed to enemy ambushes. Only a few crews managed to master the PzSpWg I Ausf. A and use it effectively, relying on superior training and tactical awareness to capitalize on its strengths while minimizing its vulnerabilities in combat situations.
Captain Hauptmann Karl Schneider
Hauptmann Karl Schneider was a renowned German tank ace who commanded the Panzerspähwagen I Ausf. A with the 7th Panzer Division during World War II. Schneider's combat exploits were marked by his exceptional skill and tactical acumen. His most memorable moment came during a pivotal engagement where he single-handedly destroyed five Soviet tanks in a single day, earning him the title of "ace in a day." Operating under the callsign "312," Schneider demonstrated extraordinary bravery and precision, exploiting the speed and firepower of his lightly armored vehicle to outmaneuver and ambush larger enemy tanks. His actions not only bolstered the morale of his unit but also showcased the effectiveness of the Panzerspähwagen I Ausf. A in reconnaissance and offensive operations. Schneider's leadership and combat prowess made him a legend among his comrades and a formidable adversary to the Soviet forces on the Eastern Front.

Hatches
the commander and gunner typically had top hatches located on the turret. These hatches allowed them quick access to observe the battlefield and operate their respective positions. However, unlike the commander and gunner, the driver often had to enter and exit the tank through front doors, similar to the Soviet T-34 tank design. This design feature required the driver to expose himself to potential dangers when entering or leaving the tank, contrasting with the relative safety of the top turret hatches used by the commander and gunner for observation and firing positions. Such differences in hatch placement reflected varying priorities in crew functionality, protection, and tactical efficiency among different tank designs of the era.

Future plans
The engineers tasked with upgrading the tank faced the challenge of integrating several improvements without compromising its performance. Their plans included adding extra armor to enhance protection against enemy fire, particularly on the frontal glacis and turret sides. A bigger gun, such as the powerful PaK 40 anti-tank gun, was proposed to improve firepower and ensure the tank could effectively engage heavier enemy armor at longer ranges. To accommodate these enhancements and the increased weight, stronger engines were under consideration to maintain or improve mobility. Additionally, wider tracks were planned to distribute the weight more effectively over the terrain, reducing ground pressure and enhancing traction. These upgrades were part of a comprehensive effort to modernize the tank, balancing increased defensive capability with improved offensive prowess and maneuverability on the battlefield.

Kill Rings
also known as kill rings and stripes, were a notable tradition among tank crews during World War II and beyond. These painted rings or stripes on the barrel of a tank's main gun served as a visual representation of the crew's combat achievements, specifically the number of enemy tanks or vehicles they had successfully destroyed in battle. Each ring symbolized a confirmed kill, making the barrel stripes not only a record of the crew's effectiveness in combat but also a source of pride and camaraderie within their unit. Beyond their practical function of tallying kills, these markings became symbols of bravery and skill under fire, highlighting the courage and proficiency of tank crews facing formidable adversaries on the front lines. The tradition of kill rings continues to be observed in modern armored units, honoring the legacy and sacrifices of those who served in armored warfare.
Major flaw
One of the Panzerspähwagen I Ausf. A's notable design features was the placement of its ammo rack on the sides of the turret, allowing for quick crew access and efficient use of interior space. This positioning facilitated faster reloading during intense engagements, crucial for maintaining combat effectiveness. However, this configuration also posed a significant flaw: the ammo rack's location made the vehicle vulnerable to catastrophic ammunition detonations when hit by enemy fire. This vulnerability was a critical concern as any penetration near the ammo rack could lead to devastating explosions, endangering the crew and potentially immobilizing the vehicle. Despite its advantage of expedited reloading, the inherent risk of being easily ammoracked underscored the trade-offs in tank design between operational efficiency and crew safety during combat operations. The PzSpWg I Ausf. B will try to fix that issue.
Specifications
Spotlights
- Kerbango 5 months ago
- SILVERPANZER 5 months ago
- Zhixunlin23 5 months ago
- dabestsock 5 months ago
General Characteristics
- Created On Android
- Wingspan 9.0ft (2.8m)
- Length 19.2ft (5.8m)
- Height 15.6ft (4.8m)
- Empty Weight 12,636lbs (5,731kg)
- Loaded Weight 30,359lbs (13,770kg)
Performance
- Wing Loading N/A
- Wing Area 0.0ft2 (0.0m2)
- Drag Points 5274
Parts
- Number of Parts 290
- Control Surfaces 0
- Performance Cost 1,576
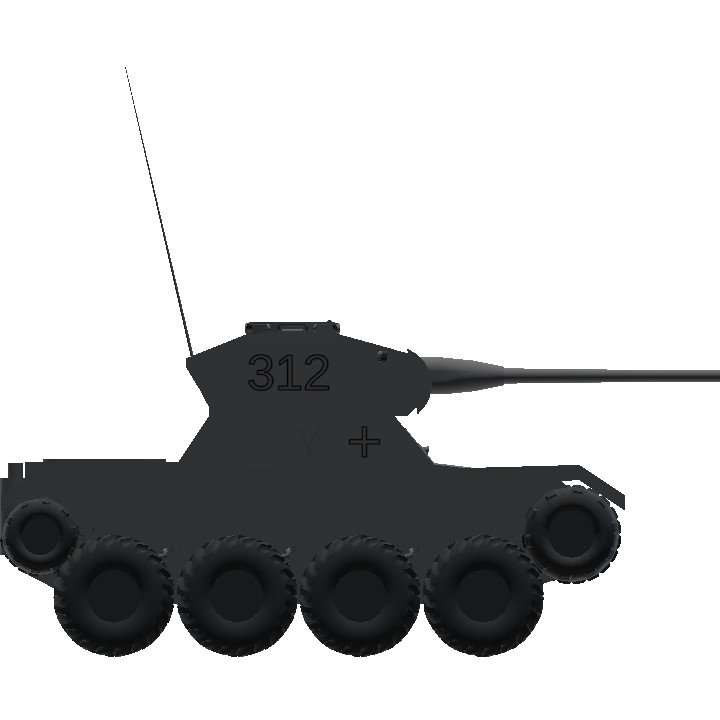
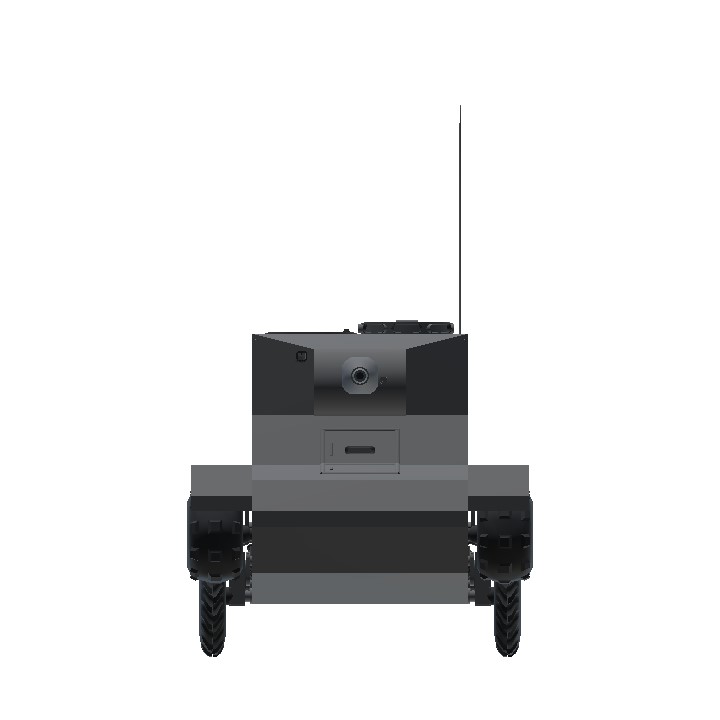






I was bored so I made shit up (lore/story)
This tank features a semi functional interior, that I half-assed
Wow nice
@Kerbango keep at it, have a good day m8
@NicholasMaximum Your statement is my life... Just look at my posts.