Sukhoi dreamed of Soviet squadrons using twin-engine fighters to escort bombers to their targets and back. In January 1943, he proposed two escort fighter designs with general similarities; just in case one failed, he would have a back-up design.
AG-1 - 23mm VYa-23 cannons
AG-2 - Nose .50 cal UB machine guns
AG-3 - Dorsal .50 cal UBT machine gun
AG-4 - Ventral .50 cal UBT machine gun
History:
It is known that the leadership of the SC Air Force, basically, considered twin-engine fighters as escort fighters. Therefore, OKB P. O. Sukhoi led work in this direction. The outline design of a two-seat twin-engine escort fighter (in two designs) with two Shvetsov M-71F radial engines with four TK-3 turbochargers was completed in January 1943. In the spring, the draft of the first variant was presented for consideration by the Air Force Research Institute. The project was rejected with the motivation "... as unsatisfying with the requirements of air combat with enemy fighters and having insufficient range ...", without specifying which airplanes are involved. Even before the approval of the Conclusion, materials on the draft project, at the request of P. O. Sukhoi, were returned to the OKB. By its designation, it was "a fighter escorting bombers at high altitudes operating within a radius of up to 1000 km."
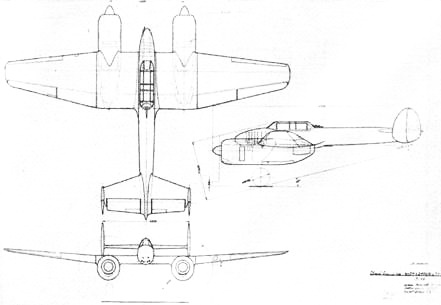
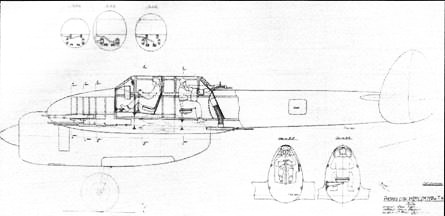
The aircraft was a low-glider mixed design with a twin tail unit and retractable landing gear. By its design, the fighter was not much different from the IOP-2AM-37 (This one will show up later). The exception was the fuselage, which had a metal nose and a wooden tail. The power plant included two air-cooled engines M-71F (Nbsp = 2,200 hp), each had two TK-3 turbochargers. The output of the air coolant was regulated by the bonnet flaps of the engines. Oil-radiators were located in the engine compartment under the hood, in the tunnel under the engine reducer. Tested fuel tanks at 787.5 kg were located in the tail sections of the nacelles. Germo-axles and tanks filled with inert gas. Armament included a stationary battery in the forward part of the fuselage and two machine-guns for firing at the rear hemisphere. The central battery included two Volkov-Yartsev VYa-23 cannons with a total ammunition capacity of 400 shells and four .50 cal Berezin UB machine guns with a total ammunition capacity of 1,600 rounds. The upper flexible installation is .50 cal UBT machine gun with 200 rounds of ammunition, the lower one - .50 cal UBT with 150 rounds. In the transshipment variant, it was possible to suspend 200 kg of bombs in the cargo compartment under the pilot's cabin.
Original OKB drawing of I-2M-71F (Option 1)
Inboard profile
Specifications
General Characteristics
- Created On iOS
- Wingspan 60.0ft (18.3m)
- Length 44.5ft (13.6m)
- Height 13.6ft (4.2m)
- Empty Weight 9,675lbs (4,388kg)
- Loaded Weight 19,404lbs (8,801kg)
Performance
- Horse Power/Weight Ratio 0.206
- Wing Loading 34.4lbs/ft2 (168.1kg/m2)
- Wing Area 563.8ft2 (52.4m2)
- Drag Points 4948
Parts
- Number of Parts 77
- Control Surfaces 10
- Performance Cost 391






@AircraftoftheRedStar you're welcome!
Thanks! @Trainzo
Cool replica . Nice joob .
Thank you! @Razor3278
Thank you for the upvote! @DerekSP