Lockheed Martin F-22 Raptor

The Lockheed Martin F-22 Raptor is an air dominance fighter aircraft manufactured in the United States by Lockheed Martin . It was the first fifth-generation fighter to enter service. Its primary mission is to maintain air superiority on the battlefield, but it also has a secondary ground attack capability.
The high cost of the aircraft development program (US$66.7 billion [ 9 ] ), delays in the development of the Russian and Chinese fifth-generation fighter programs , the export ban, and the development of the more versatile F-35 eventually ended the F-22 production program. [ 10 ] Today the U.S. Air Force has 187 of these aircraft in active service, with the last F-22 delivered in 2012.
As a secondary weapon, the F-22 uses a 20 mm M61A2 Vulcan cannon with 480 rounds. As for its main armament, the Raptor can be armed with two AIM-9 short-range air-to-air missiles and up to six AIM-120 AMRAAMs medium- and long-range air-to-air missiles . For air-to-ground combat, the F-22 can be armed with two 1,000-pound GBU-32 JDAMs and two AIM-120 missiles . [ 1 ]
Chronology

Proposal
October 1985 the US Air Force proposes the Advanced Tactical Fighter . [ 11 ]
Decision
April 23, 1991, U.S. Air Force selects F-22 as next air superiority aircraft . [ 11 ]
Start
December 8, 1993, Boeing manufactures the first part of the first Raptor. [ 12 ]
First flight
September 7, 1997, from Dobbins Air Reserve Base , chief test pilot Paul Metz begins the maiden flight, reaching approximately 4,572 m altitude in 3 minutes. [ 13 ]
Program cancellation
On April 6, 2009, the U.S. Department of Defense decided to cancel new contracts and projects related to the F-22 because of its high production cost. It was also due to delays in the development of the fifth-generation fighter program in Russia and China and due to the export ban. In addition, the F-35 fighter became more interesting because its manufacturing cost was lower and it is more versatile because it can take off and land vertically like a helicopter.
Problems in mission
On March 25, 2010, an F-22 crashed near Edwards Air Force Base in the Mojave Desert in southern California . The crash occurred at around 10:00 a.m. local time (2:00 p.m. ET) on a training mission, approximately 30 miles (50 km) northwest of the base . [ citation needed ]
On November 6, 2010, an F-22 lost communication with Alaska Air Traffic Control and crashed. The pilot, Captain Jeffre Haney, did not survive. The American pilots of the fighter decided not to fly in snowy areas. [ citation needed ]
On 22 March 2011, problems with unspecified electronic equipment left some F-22 fighters out of the NATO operation in Libya , being replaced by F/A-18 fighters
History

Origin
In 1981, the United States Air Force (USAF) developed a requirement for a new air superiority fighter , the Advanced Tactical Fighter (ATF), to replace the F-15 Eagle . The ATF was a demonstration and validation program undertaken by the USAF to develop the next generation of air superiority fighters to counter emerging threats worldwide, including the development and proliferation of the Soviet-era Sukhoi Su-27 . It was envisioned that the ATF would incorporate emerging technologies, including advanced alloys and composite materials, fly-by-wire flight control systems, more advanced propulsion systems, and radar stealth technology .
A request for proposals was issued in July 1986, and two contract teams, Lockheed / Boeing / General Dynamics and Northrop / McDonnell Douglas were selected in October 1986 to conduct a demonstration within 50 months, culminating in the flight testing of two prototypes, the YF-22 and YF-23 , respectively.
During the development process in the 1980s , the expected growth of the ATF, increasing takeoff weight, and rising cost excluded some features. IRST was downgraded from multi-color to single-color, then eliminated (although the infrared/ultraviolet missile warning system would function as an IRST system in a future software update), the side-scan radar was deleted, and the requirement for an ejection seat was downgraded so that it would not be able to cover the "flight envelope" (a term for a number of factors that can interfere with flight) completely, which would later result in one fatality during flight testing. [ 14 ]
On April 23, 1991, the Lockheed YF-22 was announced as the winner of the ATF contest. [ 15 ]
Starting production

The YF-22 was modified for the production F-22. Differences between the YF-22 and F-22 include the relocation of the cockpit, structural changes, and many other minor changes. [ 16 ]
Production of the F-22 began on April 9, 1997, at Lockheed Georgia Co., Marietta, Georgia . It first flew on September 7, 1997.
The first batch of F-22s was delivered to Nellis AFB, Nevada , on 14 January 2003 and dedicated initial test and evaluation began on 27 October 2003. By 2004, 51 Raptors had been delivered.
In 2006, the Raptor development team, comprised of Lockheed Martin and more than 1,000 other companies, plus the United States Air Force (USAF), won the Collier Trophy, the most prestigious award in American aviation .
In 2006, the USAF intended to acquire 381 F-22s to be divided among the seven active combat squadrons and three fighters to integrate with the Air Force Reserve Command and Air National Guard fighter squadrons. [ 17 ]
Contracts
Originally the idea was for the USAF to buy 750 aircraft , but due to the high costs the Pentagon changed the plan to only 183 units. [ 17 ]
On July 31, 2007, Lockheed Martin was awarded a multi-year contract for 60 F-22s worth a total of $7.3 billion. [ 18 ] [ 19 ] In 2009, future purchases were canceled in favor of the F-35 fighter . [ 10 ]
Features
The F-22 Raptor is a fifth-generation fighter aircraft . Its twin afterburning- capable Pratt & Whitney F119-PW-100 turbofan engines are capable of firing at 35,000 lbf (156 kN) per engine. [ 20 ] Maximum speed, without external weapons, is estimated at Mach 1.82 in supercruise mode , as demonstrated by General John P. Jumper, the former Chief of Staff of the United States Air Force (USAF), when his Raptor exceeded Mach 1.7 without afterburner on January 13, 2005. [ 21 ] With afterburner , according to Lockheed Martin , it can reach speeds in excess of Mach 2.0, and the Raptor can still exceed speed limits, particularly at low altitudes.
The F-22 has eight internal fuel tanks with a combined capacity of 8,200 kg. With this fuel volume, the F-22 has a range of 3,219 km, or a combat radius of 759 km. This capacity is considerably greater than that of its predecessor, the F-15 Eagle, which requires external fuel tanks to match this performance. The F-22 could have further increased these numbers by installing up to four external fuel tanks in the underwing pylons, but at the expense of its stealth capability. [ 22 ]
The electronic suite installed in the F-22 represents the state of the art in systems and sensors in the United States industry. Its radar is the Nothrop Grumman AN/APG-77 AESA (Active Electronically Scanned Array ) type . This radar has 1,500 small devices, like cells, called transmission and reception modules (TRM) that emit radar beams in several directions simultaneously and receive the reflections of these emissions, allowing a 120º scan without gaps, as occurs with mechanical scanning radars that emit only one beam from their antenna that keeps moving to track the entire frontal area of ??the fighter. This makes the target location much more accurate, and, as a bonus, there is a greater ability to track targets with a small radar signature. [ 23 ]
Cockpit


The F-22 is equipped with a glass cockpit with fully digital flight instruments. The monochrome head-up display (HUD) provides a wide field of view and serves as the primary flight instrument ; information is also displayed on a six-color LCD panel . [ 24 ] The primary flight controls are force-sensitive side-stick controls and a pair of throttles. The United States Air Force initially wanted to implement direct voice input (DVI) controls, but this was deemed too technically risky and was abandoned. [ 25 ] The canopy's dimensions are approximately 14 in (355 cm) long, 45 in (115 cm) wide, and 27 in (69 cm) high, with a weight of 345 lb (163 kg). [ 26 ] The canopy was redesigned after the original design lasted an average of 331 hours instead of the required 800 hours. [ 27 ]
The F-22 has integrated radio functionality, and the signal processing systems are virtualized rather than a separate hardware module. [ 28 ] The integrated control panel (ICP) is a keyboard-based system for inputting communications, navigation, and autopilot data. Two 3 × 4 in (7.6 cm × 10.2 cm) forward-facing displays located around the ICP are used to display integrated warning/caution warning (ICAW) data, CNI data, and also serve as a standby flight instrument cluster and fuel quantity indicator. [ 29 ] The standby flight cluster displays an artificial horizon , for instrument meteorological conditions . The 8 × 8 in (20 cm × 20 cm) primary multifunction display (PMFD) is located below the ICP and is used for navigation and situational awareness. Three 6 × 6 in (15.9 cm × 15.9 cm) secondary multifunction displays are located around the PMFD for tactical information and stockpile management. [ 30 ]
Analysis
The F-22 Raptor is a milestone in the United States Air Force's air combat capability, revolutionizing air combat in the 21st century, and was conceived as an icon of American air power for many years to come. [ 31 ]
Costs
The United States Air Force initially planned to purchase 750 of the aircraft at a cost of $44.3 billion and a proxy cost of $26.2 billion in fiscal year 1985, with production beginning in 1994. In 1990, Secretary of Defense Dick Cheney reduced the order to 648, with deliveries beginning in 1996. In 1997, a defense budget cut resulted in a reduction in the order to 339, which was then further reduced to 277 in 2003. [ 32 ] In 2004, the Department of Defense further reduced the order, this time to 183 active-duty aircraft, despite the Air Force's preference for 381. [ 33 ] [ 34 ] A multi-year acquisition plan was implemented in 2006 to save $15 billion, with a total program cost of $62 billion for 183 F-22s to be fielded across seven combat squadrons. [ 35 ] In 2008, Congress passed a defense spending bill that brought the total production aircraft orders to 187. [ 36 ] [ 37 ]
Initially, the F-22 had several technological features that substantially increased its cost and caused development delays. [ 38 ] Many features were removed for post-service upgrades, reducing the initial cost but increasing the overall cost of the program. [ 39 ] As production was curtailed in 2011, the total cost of the program was around $67.3 billion, with $32.4 billion spent on research, development, test, and evaluation (RDT&E) and $34.9 billion on procurement and military construction dollars per year. The incremental cost for additional F-22 units was estimated at $138 million in 2009, per unit. [ 40 ] [ 41 ] As of 2020, the unit cost was around $330 million per aircraft. [ 2 ]
Division of labor
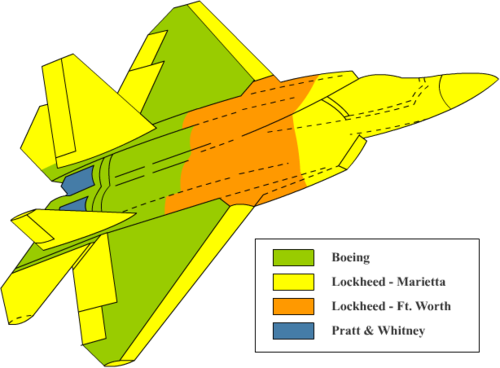
Lockheed Martin Aeronautics Company em Fort Worth, Texas[42]
Develops and builds the mid-fuselage and armament;
Provides INEWS , CNI , the provision management system and the inertial navigation system;
Develops the support system.
Lockheed Martin Aeronautics Company em Marietta, Georgia[42]
Oversees the entire integrated weapons system.
Develops and builds the forward fuselage , including the cockpit; vertical stabilizers; wings and tail leading edge, flaps , ailerons and landing gear .
Develops the spearheading avionics architecture ( cutting-edge avionics architecture , navigation protocol system, for example), as well as the displays, controls and the data and aperture system
Final meeting and test flight of the aircraft .
Boeing em Seattle, Washington[42]
Builds the wings, aft fuselage , structures for installing the engine, nozzles and auxiliary power unit;
Operar o Avionics System Integration Laboratory e o 757 Avionics Flying Laboratory
Develops the training system;
Pratt & Whitney, East Hartford, Connecticut.[3]
Builds the engines.
Operational history


Despite its high costs, the F-22 was not used in combat for many years. This led to criticism from many analysts, who said the aircraft would be a waste of money. Since the early 2000s, aircraft of this type have been deployed to several US military bases, especially in Asia and Europe. In September 2014, F-22 fighters participated in an air offensive against Syria, which was experiencing a civil war . This was the first combat mission in the aircraft's history. [ 44 ]
In August 2015, the United States dispatched a squadron of four F-22 fighter jets to Spangdahlem Air Base in Germany to reinforce the American military presence in Europe against a possible Russian threat . [ 45 ]
In November 2017, F-22s operating alongside B-52s bombed opium production and storage facilities in Taliban- controlled areas of Afghanistan . [ 46 ] In 2019, the operating cost of an F-22 per flight hour was $35,000. [ 47 ]
On February 4, 2023, an F-22 belonging to the 1st Fighter Wing shot down a Chinese spy balloon within visual range off the coast of South Carolina . [ 48 ] The F-22 fired an AIM-9X Sidewinder missile that hit the balloon between 60,000 (18.2 km) and 65,000 ft (19.8 km) high. The wreckage fell approximately 6 miles (9.65 km) offshore and was subsequently secured by United States Navy and Coast Guard vessels . [ 49 ]
On February 10, 2023, an F-22 shot down a high-altitude object near the coast of Alaska. [ 50 ] The object was shot down using an AIM-9X Sidewinder , marking the fighter's second air-to-air kill. [ 51 ] The following day, another American F-22 shot down yet another unidentified object flying over Yukon , also using the Sidewinder , marking the fighter's third aerial victory in its history. [ 52 ]
Specifications
Spotlights
- IAmSteve one month ago
General Characteristics
- Created On Windows
- Wingspan 40.7ft (12.4m)
- Length 54.6ft (16.6m)
- Height 16.4ft (5.0m)
- Empty Weight 16,043lbs (7,277kg)
- Loaded Weight 25,317lbs (11,483kg)
Performance
- Power/Weight Ratio 6.923
- Wing Loading 39.4lbs/ft2 (192.4kg/m2)
- Wing Area 642.3ft2 (59.7m2)
- Drag Points 6863
Parts
- Number of Parts 136
- Control Surfaces 4
- Performance Cost 711





This is actually really good
Good!