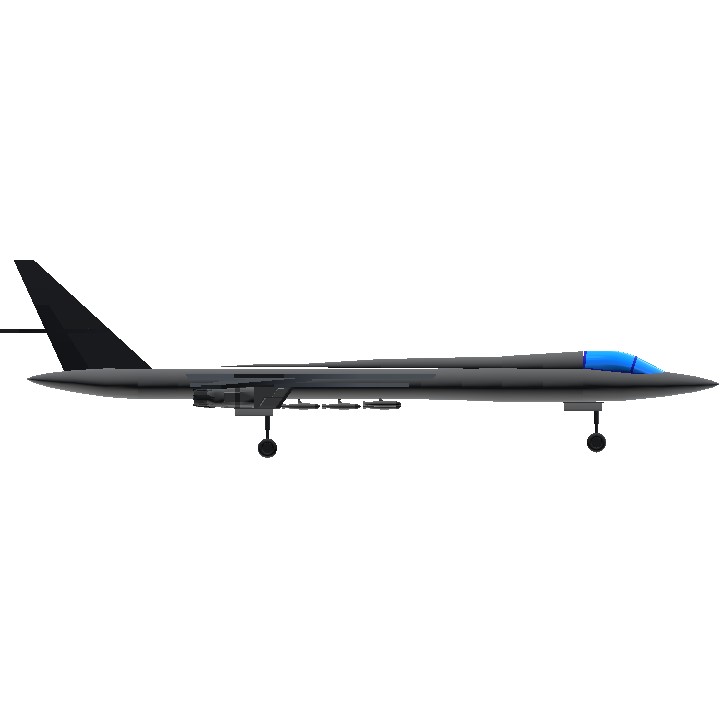
The Rockwell B-1 Lancer is a supersonic variable-sweep wing, heavy bomber used by the United States Air Force. It is commonly called the "Bone" (from "B-One"). It is one of three strategic bombers serving in the U.S. Air Force fleet along with the B-2 Spirit and the B-52 Stratofortress as of 2022.
The B-1 was first envisioned in the 1960s as a platform that would combine the Mach 2 speed of the B-58 Hustler with the range and payload of the B-52, and was meant to ultimately replace both bombers. After a long series of studies, Rockwell International (now part of Boeing) won the design contest for what emerged as the B-1A. This version had a top speed of Mach 2.2 at high altitude and the capability of flying for long distances at Mach 0.85 at very low altitudes. The combination of the high cost of the aircraft, the introduction of the AGM-86 cruise missile that flew the same basic speed and distance, and early work on the stealth bomber all significantly reduced the need for the B-1. This led to the program being canceled in 1977, after the B-1A prototypes had been built.
Variable sweep wing control- VTOL
group 7 to lunch all bombs together
Have fun!
Specifications
General Characteristics
- Created On Android
- Wingspan 53.0ft (16.2m)
- Length 58.3ft (17.8m)
- Height 15.9ft (4.9m)
- Empty Weight 16,145lbs (7,323kg)
- Loaded Weight 18,223lbs (8,265kg)
Performance
- Power/Weight Ratio 2.219
- Wing Loading 36.8lbs/ft2 (179.8kg/m2)
- Wing Area 494.8ft2 (46.0m2)
- Drag Points 3535
Parts
- Number of Parts 76
- Control Surfaces 5
- Performance Cost 592