This livery horizontal stabilizer took me 2 days to research 💀
Credit @UziDoorman for the plane
About British Aerospace 146 (Avro RJ)
The British Aerospace 146 (also BAe 146) is a short-haul and regional airliner that was manufactured in the United Kingdom by British Aerospace, later part of BAE Systems. Production ran from 1983 until 2001. Avro International Aerospace manufactured an improved version known as the Avro RJ. Production for the Avro RJ version began in 1992. Later on, a further-improved version with new engines, the Avro RJX, was announced in 1997, but only two prototypes and one production aircraft were built before production ceased in 2001. With 387 aircraft produced, the Avro RJ/BAe 146 is the most successful British civil jet airliner program.
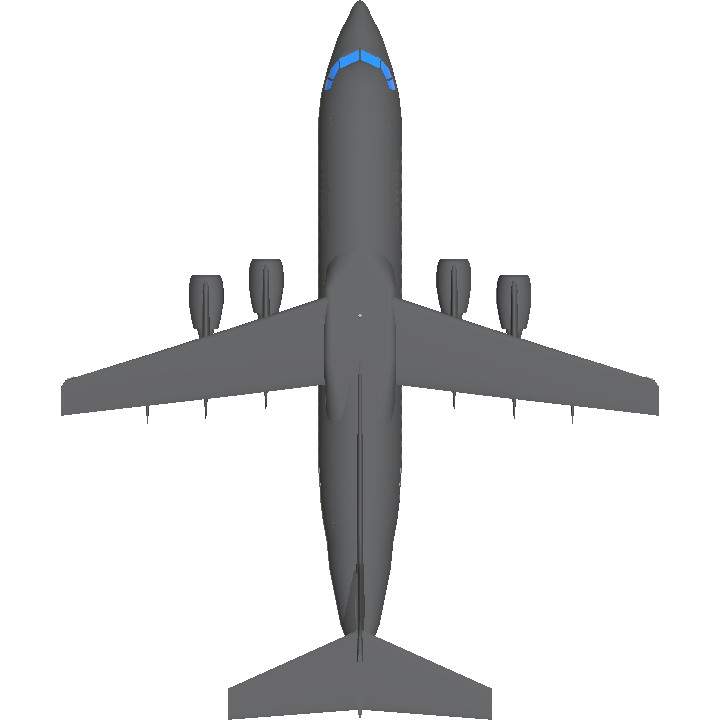
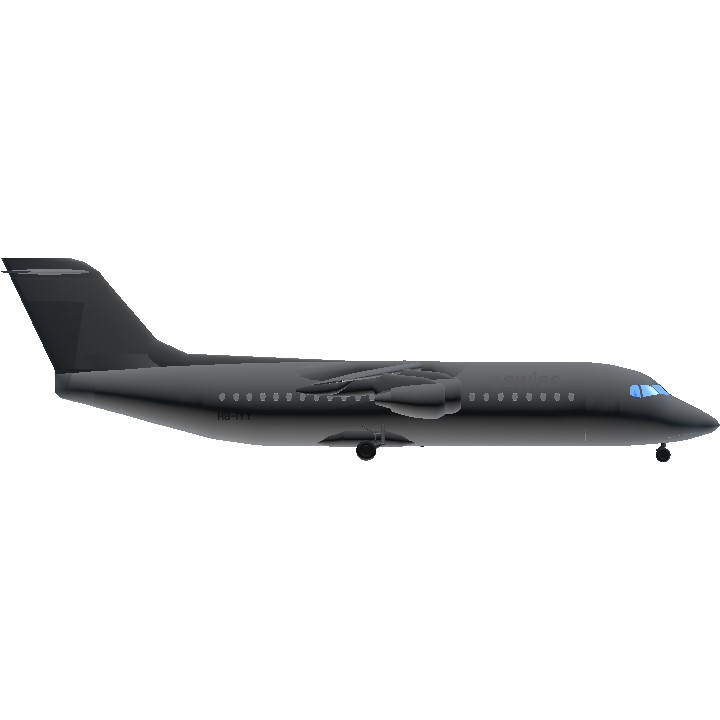
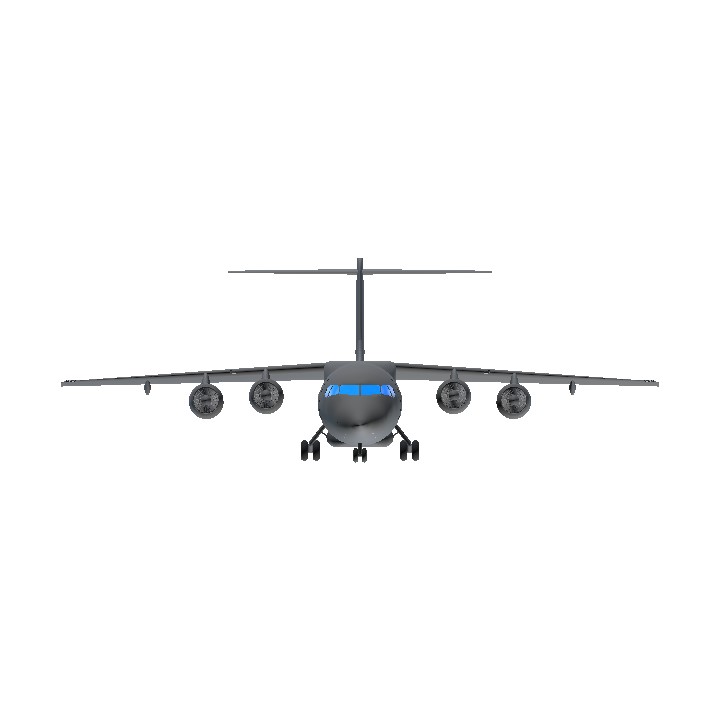
The BAe 146/Avro RJ is a high-wing cantilever monoplane with a T-tail. It has four geared turbofan engines mounted on pylons underneath the wings, and has a retractable tricycle landing gear. The aircraft operates very quietly, and as such has been marketed under the name Whisperjet. It sees wide usage at small, city-based airports such as London City Airport. In its primary role, it serves as a regional jet, short-haul airliner, or regional airliner, while examples of the type are also in use as private jets.
The BAe 146 was produced in -100, -200 and -300 models. The equivalent Avro RJ versions are designated RJ70, RJ85, and RJ100. The freight-carrying version carries the designation "QT" (Quiet Trader), and a convertible passenger-or-freight model is designated as "QC" (Quick Change). A "gravel kit" can be fitted to aircraft to enable operations from rough, unprepared airstrips.

Lufthansa Avro RJ85 (BAe 146-200)
BAe 146-300 (Avro RJ100) variant
British Aerospace announced its initial proposals for the -300 at the 1984 Farnborough Air Show. The aircraft's fuselage was to be stretched by 3.2 metres (10 ft 6 in) compared with the -200, allowing 122 passengers to be carried at 32-inch seat pitch and 134 at 29-inch seat pitch. More powerful (33 kilonewtons (7,500 lbf)) ALF 502R-7 engines would be used, and winglets were to be fitted to the aircraft's wingtips. However, due to airlines favouring a lower initial price rather than minimising seat-mile costs, the definitive 146-300 emerged as a less extreme development. Ultimately, the fuselage was stretched by 2.34 metres (7 ft 8 in), giving a capacity of 100 passengers seated five-abreast at a 31-inch seat pitch, without winglets or the proposed ALF 502R-7. Deliveries began in December 1988. A modified BAe 146-301 is used as the UK's Facility for Airborne Atmospheric Measurements. The BAe 146-300QC (Quick Change) is the convertible passenger/freight version and the BAe 146-300QT (Quiet Trader) is the freighter version.
The Avro RJ version of the 146-300, the second such development of the 146 product line, became the Avro RJ100. It shared the fuselage of the 146 version, but with interior, engine, and avionics improvements. The most common configuration in the RJ100 seats 100 passengers. An RJ115 variant, the same physical size, but with an increased MTOW and different emergency exits, was marketed, but never entered production; it seated 116 as standard or up to a maximum of 128 in a high-density layout.
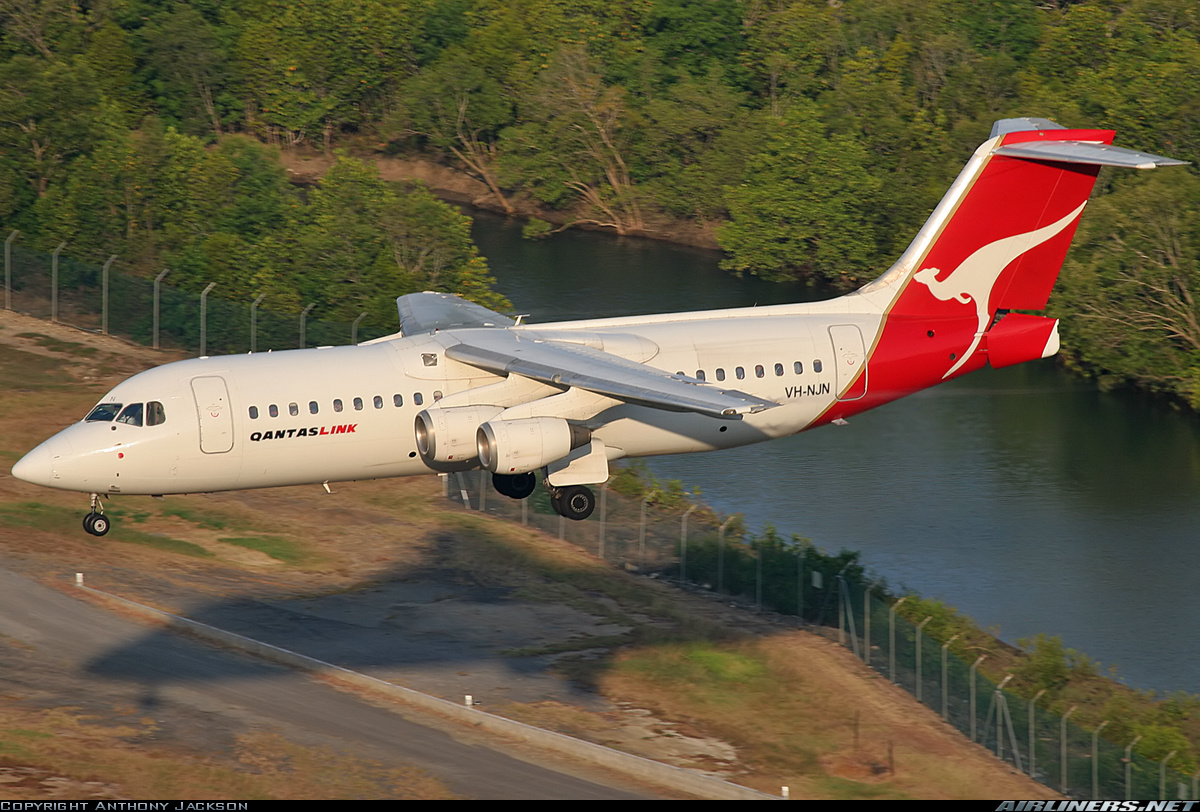

Qantas Link BAe 146-300 (Arvo RJ100)
About Swiss International Air Lines

Swiss International Air Lines AG, stylized as SWISS, is the flag carrier of Switzerland and a subsidiary of the Lufthansa Group, as well as a Star Alliance member. It operates scheduled services in Europe and to North America, South America, Africa and Asia. Zurich Airport serves as its main hub and Geneva Airport as its secondary hub.
Its headquarters are at Kloten (near Zurich Airport), Switzerland, and an office at Zurich Airport in Kloten, Switzerland. The company's registered office is in Basel.
The airline was formed following the bankruptcy in 2002 of Swissair, Switzerland's then-flag carrier. The new airline was built around what had been Swissair's regional subsidiary, Crossair. Swiss retains Crossair's IATA code LX (Swissair's code was SR). It assumed Swissair's old ICAO code of SWR (Crossair's was CRX), to maintain international traffic rights.

Swiss International Air Lines Boeing 777
History of HB-IYY
The aircraft was first delivered to Crossair in December 1998 with registration number HB-IYY.

This aircraft was then operated by the following airlines:
- Swiss International Air Lines and Swiss Gobal Air lines from March 2002 to April 2017 with registration number HB-IYY.

- Tronos with registration number T7-IYY.

- Aerovías DAP and Antarctic Airways with registration number CC-ATI.

This aircraft is currently operated by Antarctic Airways.
Specifications
Spotlights
- GalacticaAsia 7 days ago
- Aviationguy24 7 days ago
General Characteristics
- Predecessor BAE146-200
- Successors 1 airplane(s)
- Created On Android
- Wingspan 86.1ft (26.2m)
- Length 103.7ft (31.6m)
- Height 29.5ft (9.0m)
- Empty Weight N/A
- Loaded Weight 78,885lbs (35,781kg)
Performance
- Power/Weight Ratio 0.256
- Horse Power/Weight Ratio 0.076
- Wing Loading 41.7lbs/ft2 (203.6kg/m2)
- Wing Area 1,891.6ft2 (175.7m2)
- Drag Points 9609
Parts
- Number of Parts 500
- Control Surfaces 9
- Performance Cost 3,324







woah