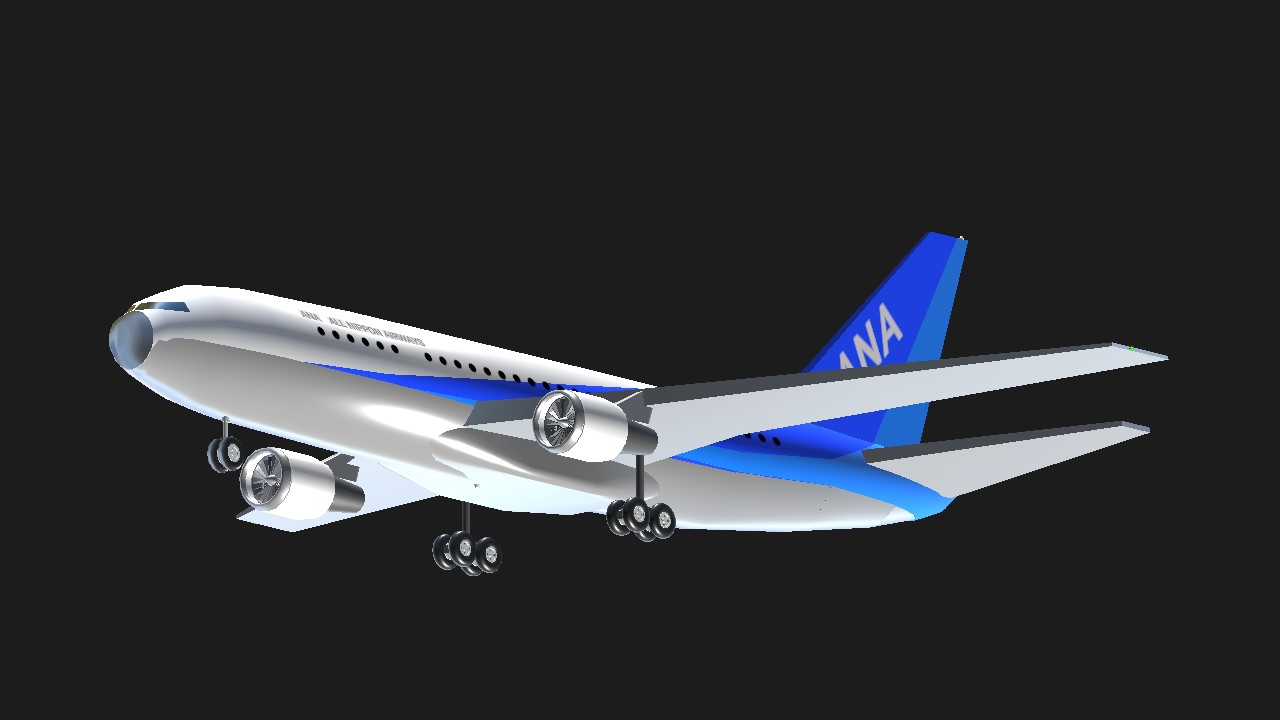
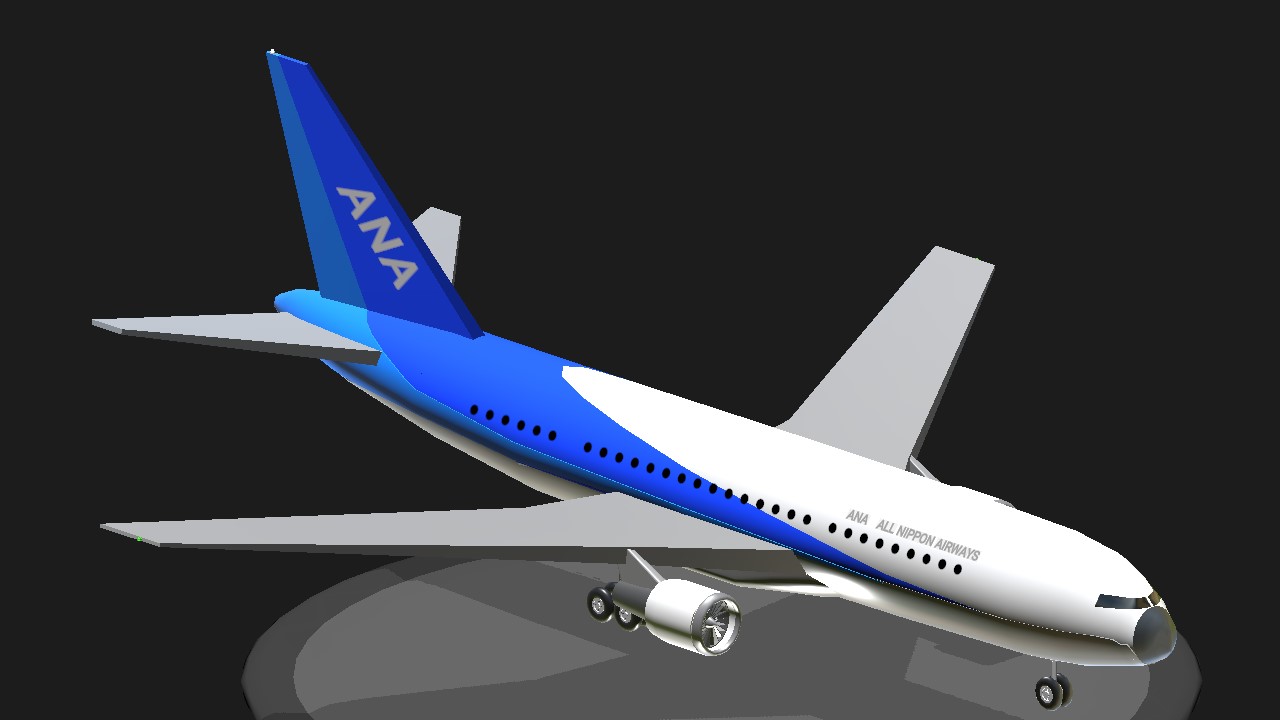
Airline :
All Nippon Airways Co., Ltd. (?????????, Zen Nippon Kuyu Kabushiki gaisha, ANA) is a Japanese airline headquartered in Minato, Tokyo. ANA operates services to both domestic and international destinations and is Japan's largest airline, ahead of its main rival flag carrier Japan Airlines.[6] As of April 2023, the airline has approximately 12,800 employees.[7] The airline joined as a Star Alliance member in October 1999

plane :
The 767-200ER was the first extended-range model and entered service with El Al in 1984.[45] The type's increased range is due to extra fuel capacity and higher maximum takeoff weight (MTOW) of up to 395,000 lb (179,000 kg).[42][134] The additional fuel capacity is accomplished by using the center tank's dry dock to carry fuel. The non-ER variant's center tank is what is called cheek tanks; two interconnected halves in each wing root with a dry dock in between. The center tank is also used on the -300ER and -400ER variants.[152]:?35?
This version was originally offered with the same engines as the 767-200, while more powerful Pratt & Whitney PW4000 and General Electric CF6 engines later became available.[42] The 767-200ER was the first 767 to complete a non-stop transatlantic journey, and broke the flying distance record for a twinjet airliner on April 17, 1988, with an Air Mauritius flight from Halifax, Nova Scotia to Port Louis, Mauritius, covering 8,727 nmi (16,200 km; 10,000 mi).[3] The 767-200ER has been acquired by international operators seeking smaller wide-body aircraft for long-haul routes such as New York to Beijing.[3][134] Deliveries of the type totaled 121 with no unfilled orders.[2] As of July 2018, 21 examples of passenger and freighter conversion versions were in airline service.[147] The type's main competitors of the time included the Airbus A300-600R and the A310-300.[43]
767-300
The 767-300, the first stretched version of the aircraft, entered service with Japan Airlines in 1986.[45] The type features a 21.1-foot (6.43 m) fuselage extension over the 767-200, achieved by additional sections inserted before and after the wings, for an overall length of 180.25 ft (54.9 m).[42] Reflecting the growth potential built into the original 767 design, the wings, engines, and most systems were largely unchanged on the 767-300.[42] An optional mid-cabin exit door is positioned ahead of the wings on the left,[25] while more powerful Pratt & Whitney PW4000 and Rolls-Royce RB211 engines later became available.[43] The 767-300's increased capacity has been used on high-density routes within Asia and Europe.[153] The 767-300 was produced from 1986 until 2000. Deliveries for the type totaled 104 aircraft with no unfilled orders remaining.[2] The type's

Specifications
General Characteristics
- Predecessor [AI] Boeing 767-300
- Created On Android
- Wingspan 69.8ft (21.3m)
- Length 75.2ft (22.9m)
- Height 25.1ft (7.6m)
- Empty Weight 55,184lbs (25,031kg)
- Loaded Weight 226,588lbs (102,778kg)
Performance
- Power/Weight Ratio 0.297
- Wing Loading 64.4lbs/ft2 (314.2kg/m2)
- Wing Area 3,521.1ft2 (327.1m2)
- Drag Points 4415
Parts
- Number of Parts 111
- Control Surfaces 9
- Performance Cost 640