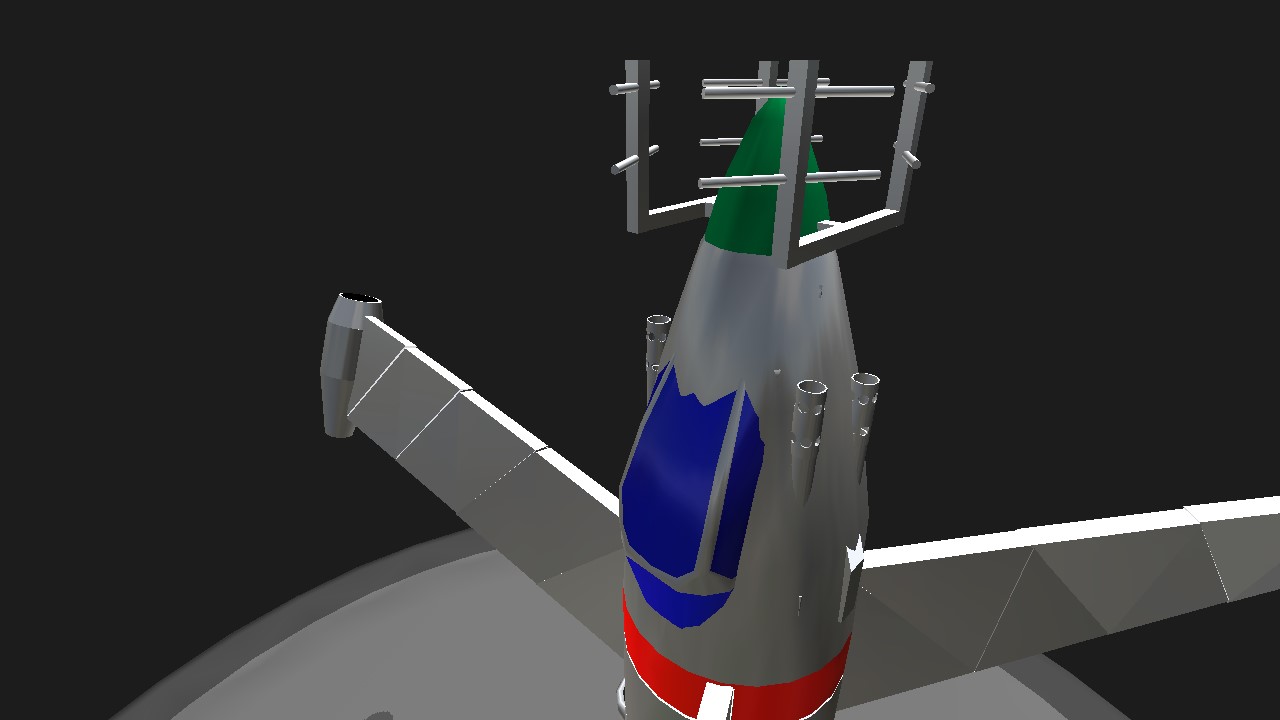
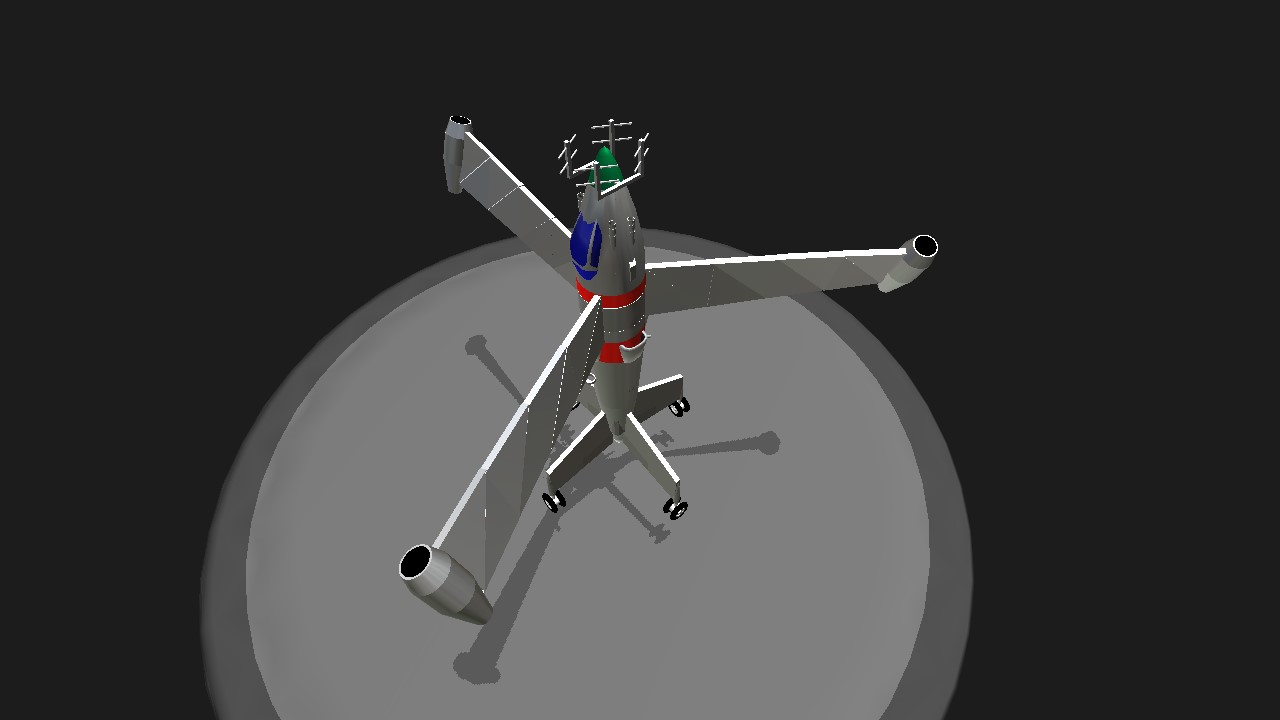
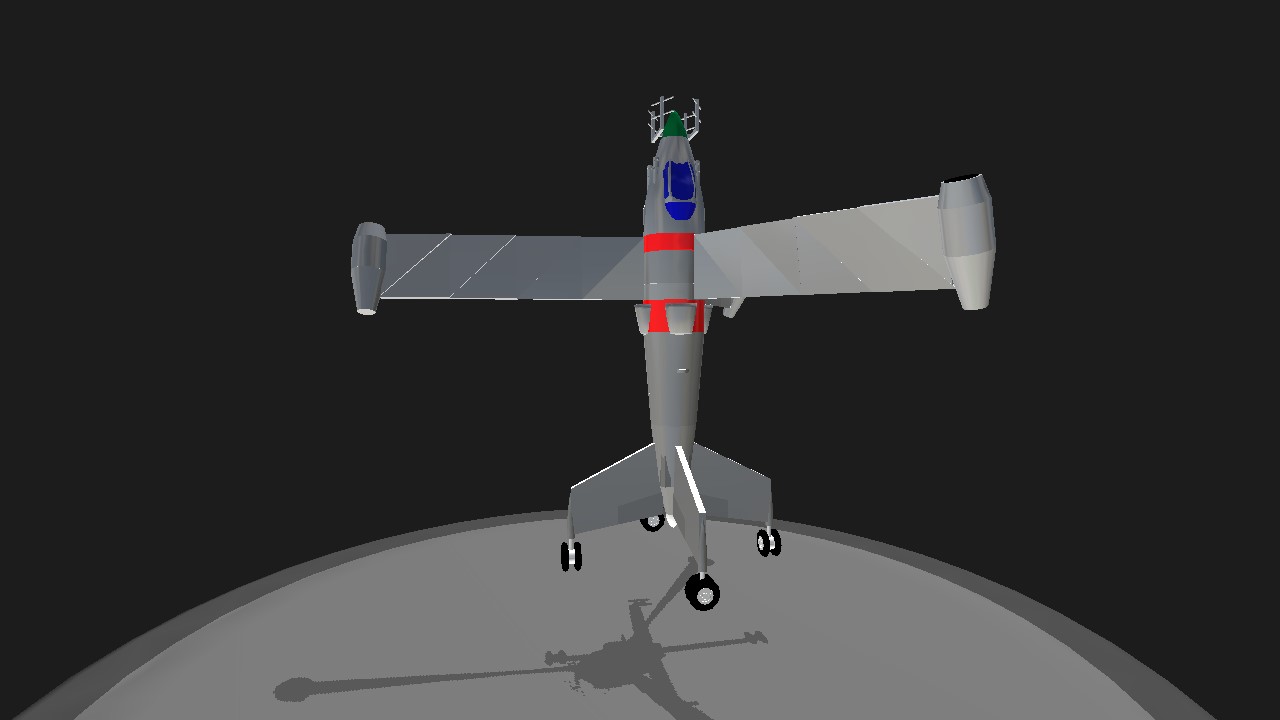
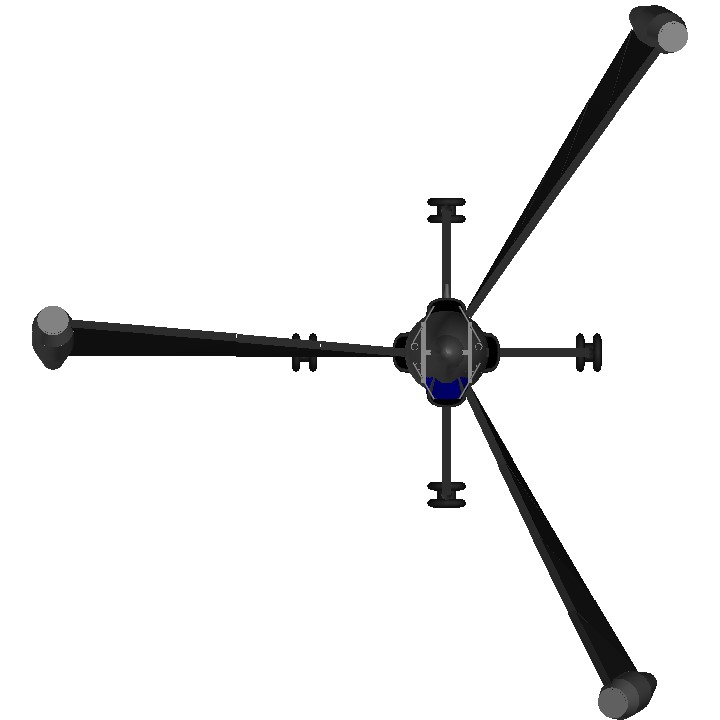
The Focke-Wulf plant completed development of this design in September 1944 and conducted control tests of its model in a wind tunnel at speeds up to Mach 0.9, but not a single prototype was ever built. the aircraft was a highly efficient vertical takeoff and landing interceptor fighter powered by a ramjet engine. Its three wings were mounted on a rotating ring just behind the cockpit and powered by a Pabos jet engine, which was accelerated to operational speed with a small solid-propellant rocket. During takeoff and landing, the wings acted like the propellers of a helicopter, and in level flight, they worked like a huge propeller. The tribflugel belonged to the tail landing apparatus and was equipped with one central tail wheel, as well as four stabilizing outrigger wheels mounted at the ends of each vertical stabilizer. During the flight, the wheels were closed with streamlined grab flaps.
Specifications
General Characteristics
- Predecessor Focke-Wulf Triebflugel
- Created On Android
- Wingspan 25.6ft (7.8m)
- Length 28.1ft (8.6m)
- Height 24.6ft (7.5m)
- Empty Weight 9,385lbs (4,257kg)
- Loaded Weight 11,353lbs (5,150kg)
Performance
- Power/Weight Ratio 1.187
- Wing Loading 47.8lbs/ft2 (233.4kg/m2)
- Wing Area 237.5ft2 (22.1m2)
- Drag Points 7943
Parts
- Number of Parts 102
- Control Surfaces 4
- Performance Cost 413