The FA-18B Hornet is a two-seat, twin-engine multirole fighter aircraft used primarily by the United States Navy and Marine Corps, along with several other military forces worldwide. It is part of the broader McDonnell Douglas F/A-18 Hornet family, which was designed to provide both fighter and attack capabilities. The FA-18B is a variant of the F/A-18A, equipped with an additional seat for a second crew member, typically a weapons system officer or a pilot undergoing training. Here’s a detailed overview of the FA-18B:
1. Development History
- The F/A-18 Hornet was developed in the 1970s as a carrier-capable multirole aircraft for the U.S. Navy to replace the aging F-4 Phantom II and A-7 Corsair II.
- The FA-18B variant was developed as an advanced, two-seat trainer aircraft, which allowed for training without compromising combat capabilities.
- It first entered service in the early 1980s, with the FA-18B becoming a common aircraft for training and operational roles.
- The FA-18B served as a bridge before the more advanced FA-18C/D and Super Hornet variants entered service.
2. Key Features
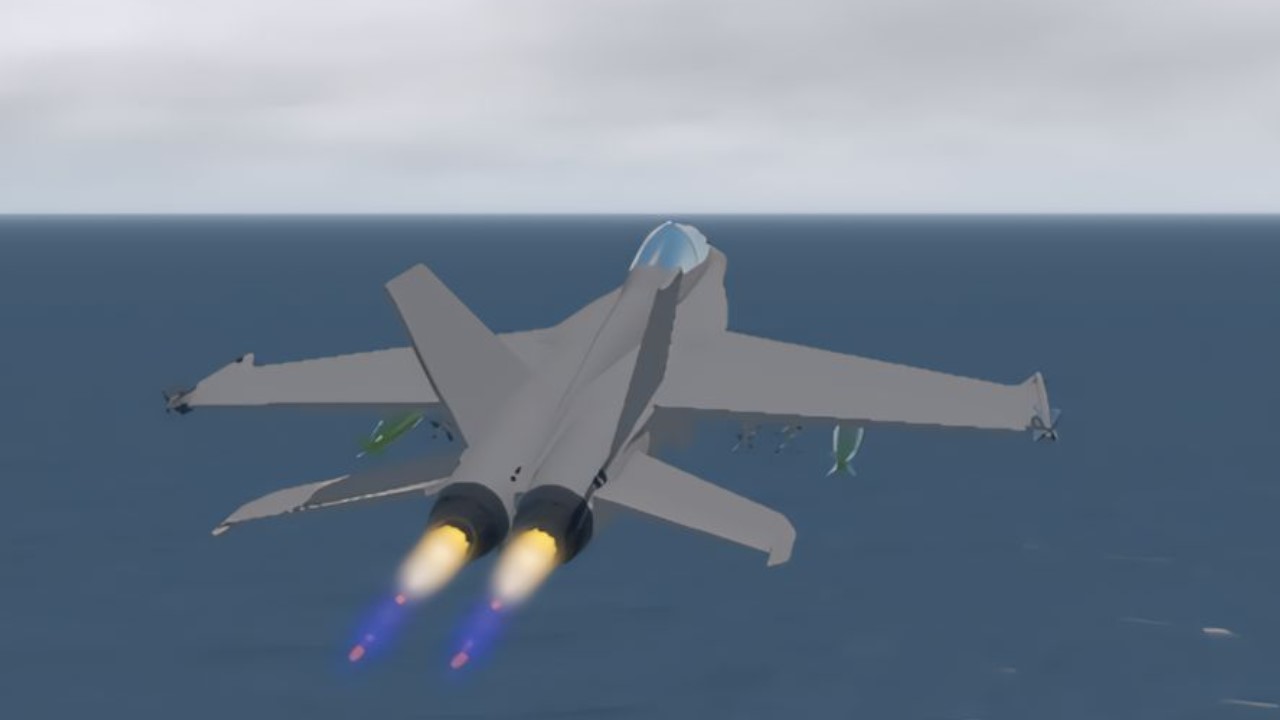
- Twin-Engine Design: Powered by two F404-GE-402 turbofan engines made by General Electric, the FA-18B offers a reliable thrust-to-weight ratio and can achieve speeds up to Mach 1.8.
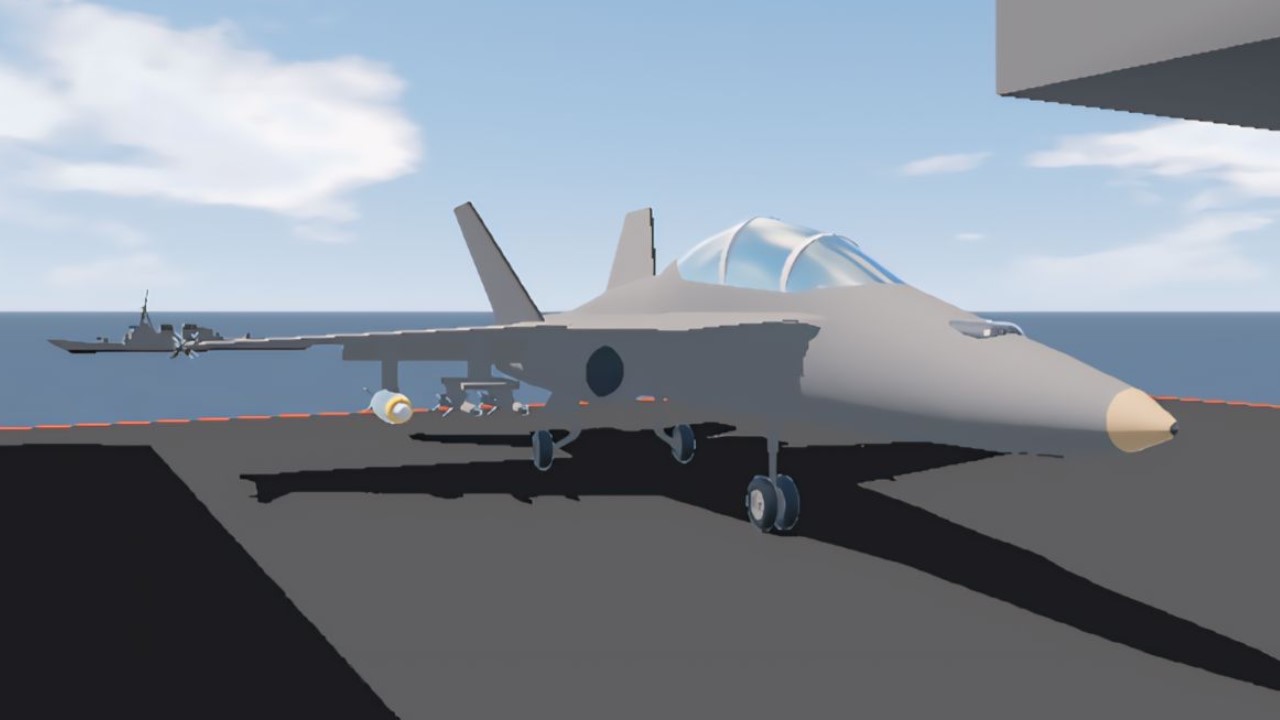
- Carrier-Capable: Designed for carrier operations, the FA-18B can take off and land on aircraft carriers using tailhooks and reinforced landing gear.
- Multirole Capability: It can perform a variety of missions, including air superiority, ground attack, reconnaissance, and close air support, thanks to its versatility in carrying different types of ordnance.
3. Avionics and Sensors
- Radar: The FA-18B is equipped with the AN/APG-65 radar, which provides a solid radar system for detecting and tracking targets in both air-to-air and air-to-ground modes.
- Cockpit: The two-seat configuration includes an advanced avionics suite for the pilot and the weapons system officer (WSO), with both seats featuring multi-function displays and hands-on throttle and stick (HOTAS) controls.
- Weapons: It can carry a wide variety of weapons, including air-to-air missiles (like the AIM-7 Sparrow and AIM-120 AMRAAM), air-to-ground missiles, bombs (including precision-guided munitions), and gun pods. The aircraft has seven hardpoints for various configurations.
- Countermeasures: The FA-18B is equipped with electronic warfare equipment, including chaff and flare dispensers for evading radar-guided and infrared-guided threats.
4. Training Role
- The FA-18B is primarily used for pilot training in the U.S. Navy and Marine Corps, where it helps new pilots gain experience in the multirole capabilities of the F/A-18 system.
- It allows for joint training with a pilot and a weapons officer, teaching complex tactics and coordination.
- The additional seat for a second crew member makes it ideal for instructional and operational training scenarios, where new pilots can receive feedback from experienced instructors.
5. Performance
- Speed: The FA-18B has a top speed of about Mach 1.8 (approximately 1,190 mph or 1,915 km/h).
- Range: It has a combat radius of around 400 nautical miles (740 km), with a ferry range of up to 2,000 nautical miles (3,700 km) depending on configuration and fuel tanks.
- Service Ceiling: Its service ceiling is about 50,000 feet (15,240 meters), offering superior high-altitude performance.
- Maneuverability: The aircraft is known for its exceptional agility, with a low radar cross-section and a highly maneuverable airframe, allowing it to excel in both air-to-air and air-to-ground combat scenarios.
6. Operational Use
- Although originally a trainer aircraft, the FA-18B has also been used in operational settings for combat, reconnaissance, and other missions.
- The U.S. Navy used the FA-18B in various conflicts, including the Gulf War, Bosnian War, and the Kosovo War.
- It has also been exported to several other countries, including Canada, Australia, and Spain, who use the FA-18B for both training and operational purposes.
7. Legacy and Successor
- The FA-18B was eventually succeeded by the FA-18C/D (with a focus on more advanced avionics and systems), and later the F/A-18E/F Super Hornet, which offers increased range, payload, and advanced systems.
- Despite being replaced in front-line combat by newer models, the FA-18B continues to serve in training roles and remains a symbol of the Hornet's success in naval aviation.
8. Conclusion
- The FA-18B Hornet was a vital part of the U.S. Navy and Marine Corps for many years, offering unmatched versatility in both training and combat.
- Its adaptability, speed, and range make it an enduring model in the history of military aviation. While newer variants like the Super Hornet have largely replaced it in combat roles, the FA-18B remains an important asset for training the next generation of naval aviators and weapons officers.
Specifications
Spotlights
- StopBreathingMyAir 3 months ago
- SPsidearm 3 months ago
- MosquitowithaMachineGun 3 months ago
General Characteristics
- Created On Android
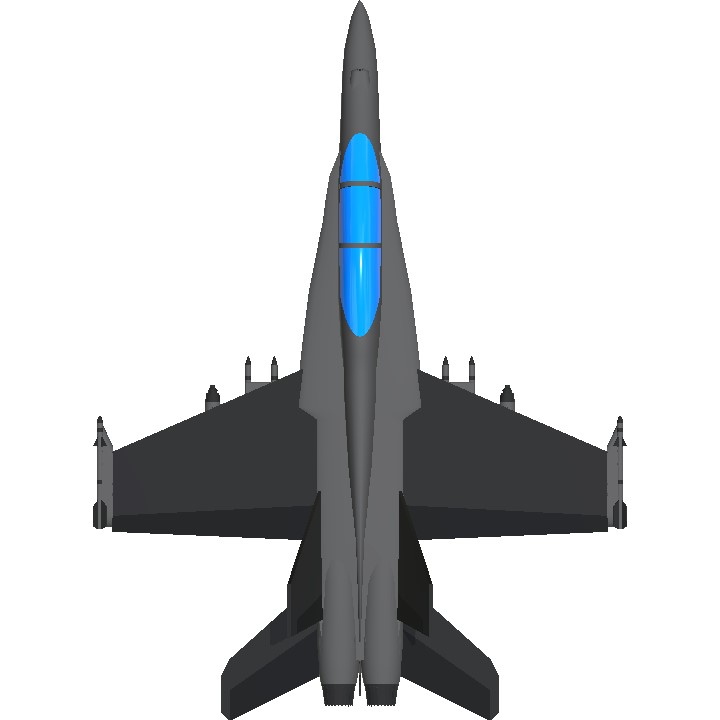
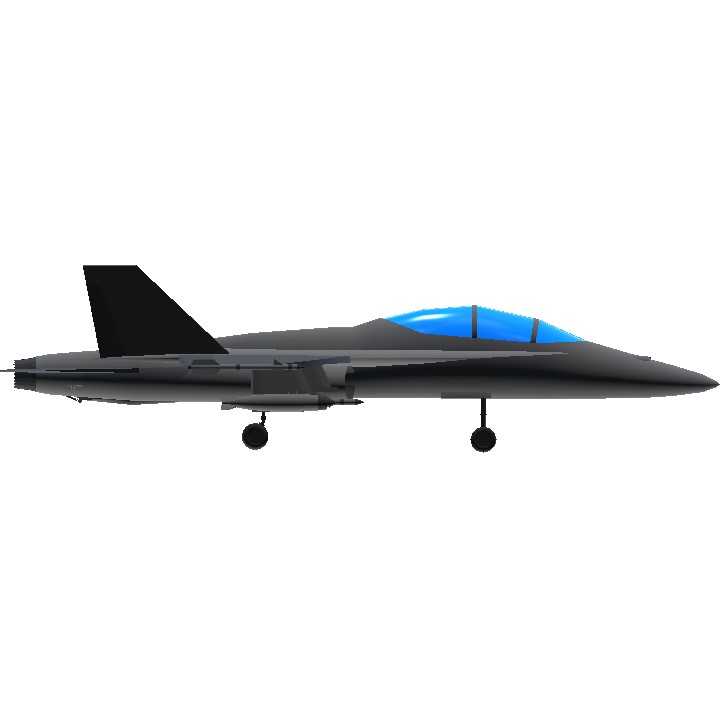
- Wingspan 48.6ft (14.8m)
- Length 66.4ft (20.2m)
- Height 17.1ft (5.2m)
- Empty Weight 28,770lbs (13,050kg)
- Loaded Weight 47,031lbs (21,333kg)
Performance
- Power/Weight Ratio 5.017
- Wing Loading 64.2lbs/ft2 (313.3kg/m2)
- Wing Area 733.0ft2 (68.1m2)
- Drag Points 5983
Parts
- Number of Parts 90
- Control Surfaces 8
- Performance Cost 631





cool
F/A-18D when
4: @Eagleman101SP
1: @MiGFOXHOUND31BSM26
2: @cooldude321
3: @spsidearm