Is this the another one of pioneering a 'world's first' literal multirole fighter aircraft, just because so much beloved among RAF fighter pilots?~
Supermarine Spitfire
- About the aircraft
The Supermarine Spitfire is a British single-seat fighter aircraft used by the Royal Air Force and other Allied countries before, during, and after World War II. It was the only British fighter produced continuously throughout the war. The Spitfire remains popular among enthusiasts. Around 70 remain airworthy, and many more are static exhibits in aviation museums throughout the world.
The Spitfire was designed as a short-range, high-performance interceptor aircraft by R. J. Mitchell, chief designer at Supermarine Aviation Works, which operated as a subsidiary of Vickers-Armstrong from 1928. Mitchell developed the Spitfire's distinctive elliptical wing (designed by Beverley Shenstone) with innovative sunken rivets to have the thinnest possible cross-section, achieving a potential top speed greater than that of several contemporary fighter aircraft, including the Hawker Hurricane. Mitchell continued to refine the design until his death in 1937, whereupon his colleague Joseph Smith took over as chief designer.
Smith oversaw the Spitfire's development through many variants, from the Mk 1 to the Rolls-Royce Griffon-engined Mk 24, using several wing configurations and guns. The original airframe was designed to be powered by a Rolls-Royce Merlin engine producing 1,030 hp (768 kW). It was strong enough and adaptable enough to use increasingly powerful Merlins, and in later marks, Rolls-Royce Griffon engines producing up to 2,340 hp (1,745 kW). As a result, the Spitfire's performance and capabilities improved over the course of its service life.
During the Battle of Britain (July–October 1940), the more numerous Hurricane flew more sorties resisting the Luftwaffe, but the Spitfire captured the public's imagination as the main RAF fighter, in part because the Spitfire was generally a better fighter aircraft than the Hurricane. Spitfire units had a lower attrition rate and a higher victory-to-loss ratio than Hurricanes, most likely due to the Spitfire's higher performance. During the battle, Spitfires generally engaged Luftwaffe fighters—mainly Messerschmitt Bf 109E–series aircraft, which were a close match for them.
After the Battle of Britain, the Spitfire superseded the Hurricane as the principal aircraft of RAF Fighter Command, and it was used in the European, Mediterranean, Pacific, and South-East Asian theatres.
Much loved by its pilots, the Spitfire operated in several roles, including interceptor, photo-reconnaissance, fighter-bomber, and trainer, and it continued to do so until the 1950s. The Seafire was an aircraft carrier–based adaptation of the Spitfire, used in the Fleet Air Arm from 1942 until the mid-1950s.
The Spitfire was designed as a short-range, high-performance interceptor aircraft by R. J. Mitchell, chief designer at Supermarine Aviation Works, which operated as a subsidiary of Vickers-Armstrong from 1928. Mitchell developed the Spitfire's distinctive elliptical wing (designed by Beverley Shenstone) with innovative sunken rivets to have the thinnest possible cross-section, achieving a potential top speed greater than that of several contemporary fighter aircraft, including the Hawker Hurricane. Mitchell continued to refine the design until his death in 1937, whereupon his colleague Joseph Smith took over as chief designer.
Smith oversaw the Spitfire's development through many variants, from the Mk 1 to the Rolls-Royce Griffon-engined Mk 24, using several wing configurations and guns. The original airframe was designed to be powered by a Rolls-Royce Merlin engine producing 1,030 hp (768 kW). It was strong enough and adaptable enough to use increasingly powerful Merlins, and in later marks, Rolls-Royce Griffon engines producing up to 2,340 hp (1,745 kW). As a result, the Spitfire's performance and capabilities improved over the course of its service life.
During the Battle of Britain (July–October 1940), the more numerous Hurricane flew more sorties resisting the Luftwaffe, but the Spitfire captured the public's imagination as the main RAF fighter, in part because the Spitfire was generally a better fighter aircraft than the Hurricane. Spitfire units had a lower attrition rate and a higher victory-to-loss ratio than Hurricanes, most likely due to the Spitfire's higher performance. During the battle, Spitfires generally engaged Luftwaffe fighters—mainly Messerschmitt Bf 109E–series aircraft, which were a close match for them.
After the Battle of Britain, the Spitfire superseded the Hurricane as the principal aircraft of RAF Fighter Command, and it was used in the European, Mediterranean, Pacific, and South-East Asian theatres.
Much loved by its pilots, the Spitfire operated in several roles, including interceptor, photo-reconnaissance, fighter-bomber, and trainer, and it continued to do so until the 1950s. The Seafire was an aircraft carrier–based adaptation of the Spitfire, used in the Fleet Air Arm from 1942 until the mid-1950s.
- About the variant
A constant flow of modifications were made as production progressed. A "blown" cockpit hood, manufactured by Malcolm, was introduced in an effort to further increase the pilot's head-room and visibility. Many mid to late production Vbs – and all Vcs – used the modified, improved windscreen assembly with the integral bullet resistant centre panel and flat side screens introduced with the Mk III. Because the rear frame of this windscreen was taller than that of the earlier model the cockpit hoods were not interchangeable and could be distinguished by the wider rear framing on the hood used with the late-style windscreen.
C O N T R O L S
Trim : Flaps, cruising 'rotate' adjuster
VTOL : Further flaps
Specifications
General Characteristics
- Created On Android
- Wingspan 37.4ft (11.4m)
- Length 31.3ft (9.6m)
- Height 11.4ft (3.5m)
- Empty Weight 4,358lbs (1,977kg)
- Loaded Weight 6,363lbs (2,886kg)
Performance
- Power/Weight Ratio 0.126
- Horse Power/Weight Ratio 0.268
- Wing Loading 13.1lbs/ft2 (64.1kg/m2)
- Wing Area 485.0ft2 (45.1m2)
- Drag Points 1432
Parts
- Number of Parts 69
- Control Surfaces 7
- Performance Cost 476
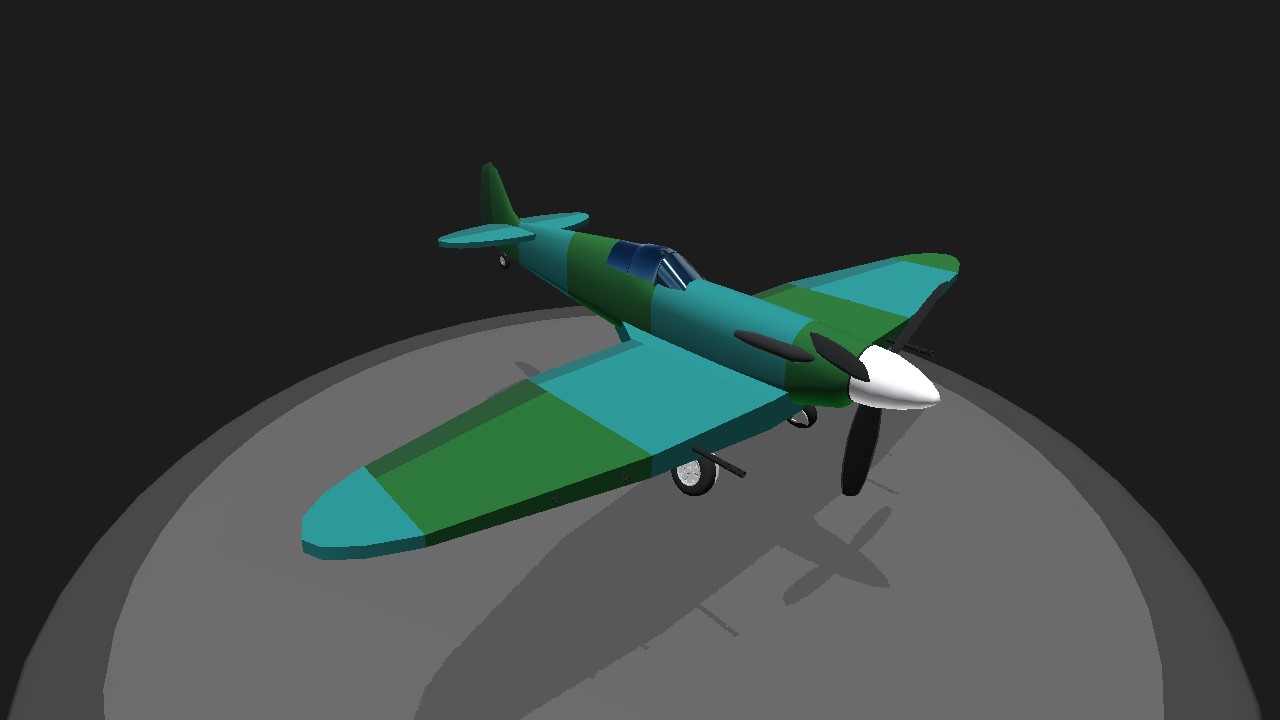
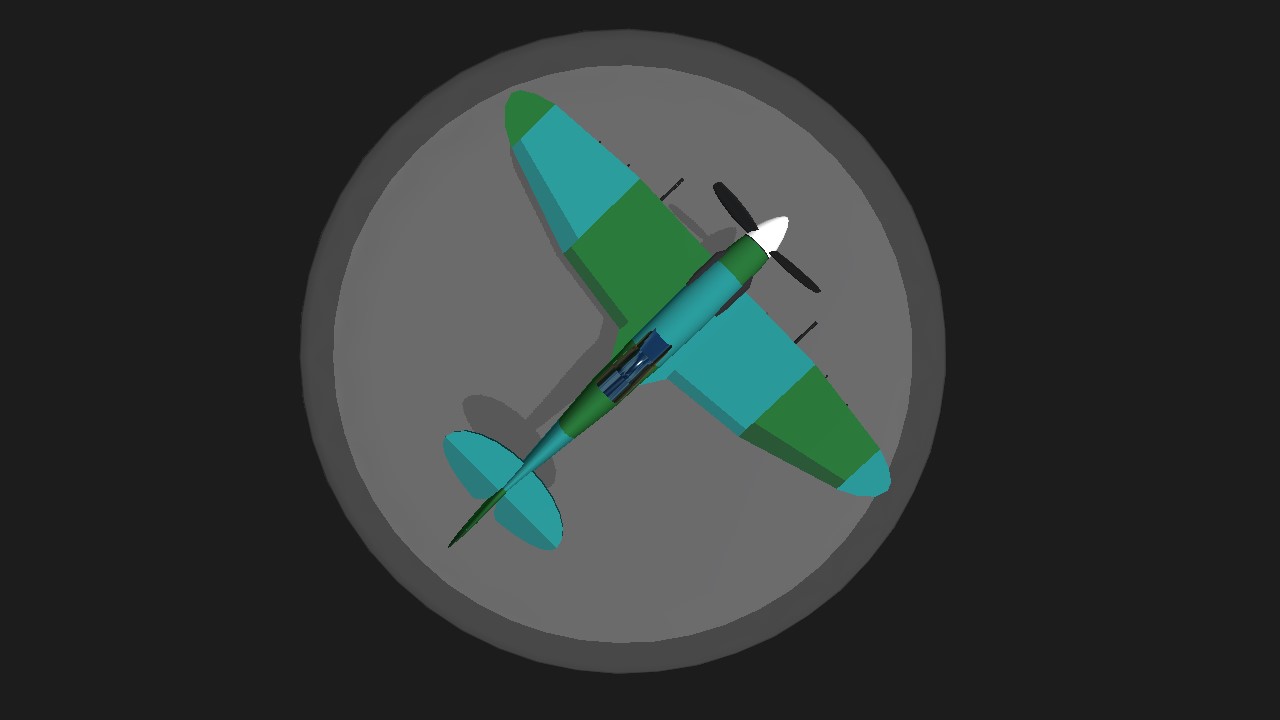
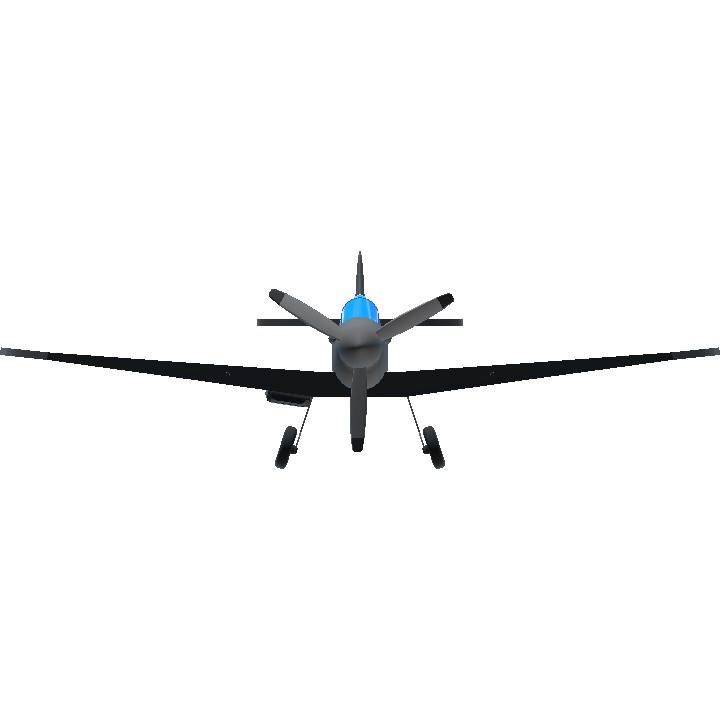





@LunarEclipseSP YES. 🇬🇧🇬🇧🇬🇧🇬🇧🇬🇧🇬🇧
@MoriSamaSP you should add tags so people can see this in the future, it's a very nice plane
@LunarEclipseSP eww… America 4 ever
BRITAIN FOREVEEEEERRR!!!