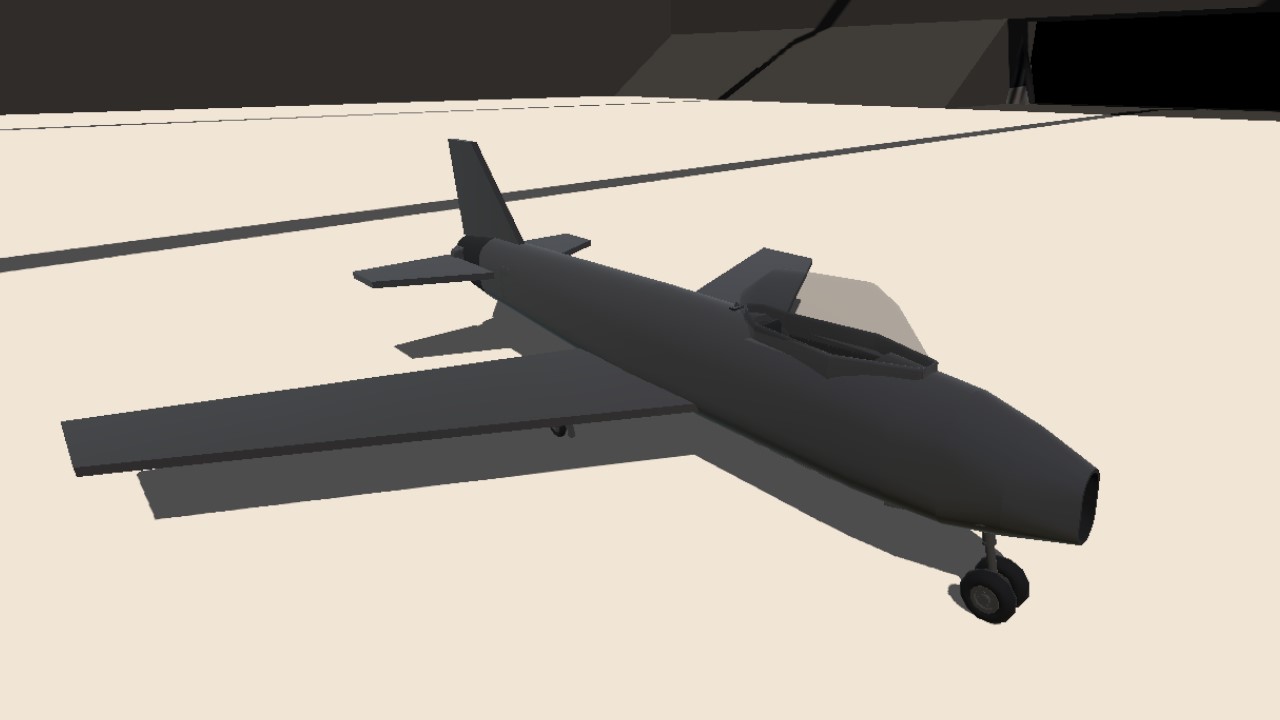
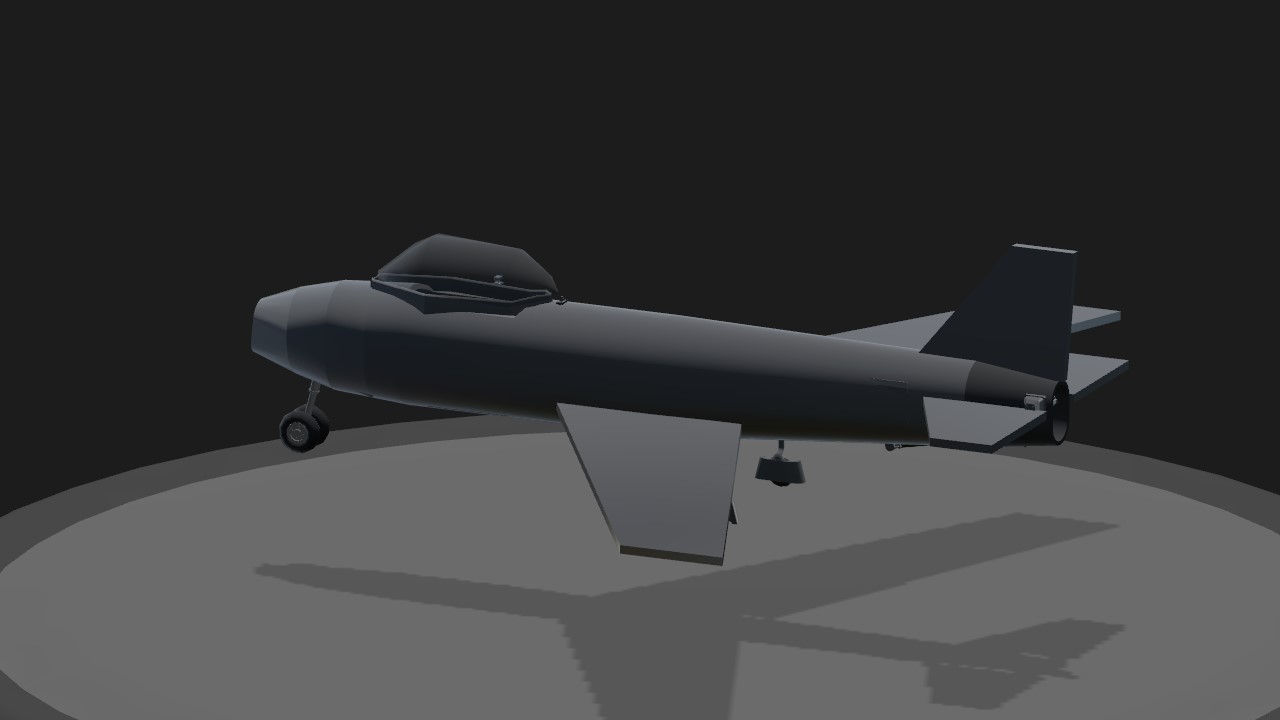
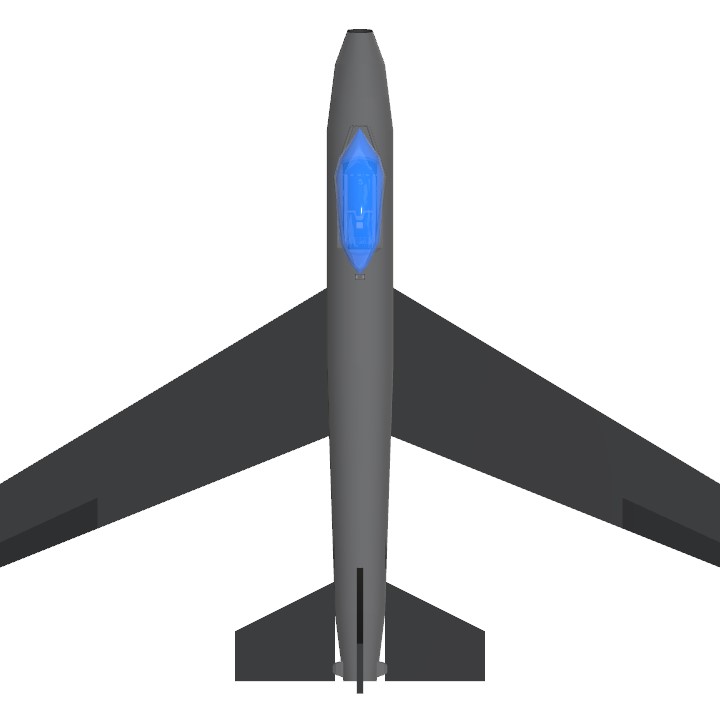
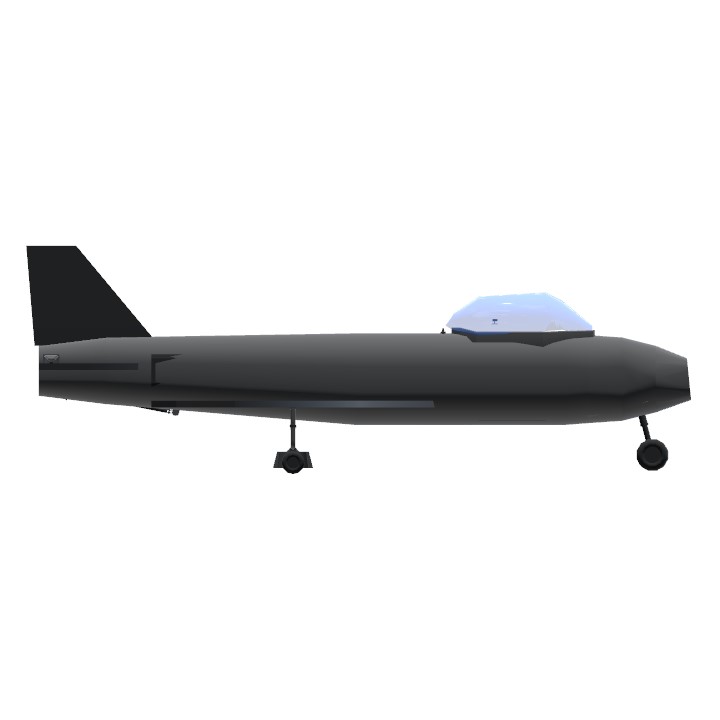
View The Instruions
AI Tested
HOW TO LAND:
1:Active AG4 For Airbrakes
2:Set Trim to None
3:Squeeze or Hold the Brake Button
4:Squeeze the AG3 into the parachutes
ACTIVATION GROUPS:
AG1:Open Capony
AG2:Hook Gear
AG3: Drag Kicks
AG4:Starting the Airbrakes
HISTORY:
The F-86 Sabre was a subsonic jet-powered day fighter developed by the North American Company in the United States from late 1944 onwards and became one of the most widely produced fighters in the Western world during the Cold War . It became famous for its involvement in the Korean War , where it successfully confronted its main opponent, the MiG-15 .
Although it was no longer a top-of-the-line aircraft by the end of 1950 , it remained in service for more than four decades until 1994, when the Bolivian Air Force finally withdrew it from service.
It was the most prominent second-generation fighter aircraft, which incorporated everything that had been most developed by North American designers in the design of jet aircraft and which also benefited from the advanced aerodynamic concepts developed by German scientists during the Second World War .
It was built in large numbers in the United States , Canada , Italy and Japan , in several of its versions and variants and operated by more than 35 air forces, representing an important role in the defense of the Western world in the early years of the Cold War .
Development
In late 1944, North American was developing studies based on the NA-134 model, which gave rise to the US Navy 's FJ-1 Fury ; it was a conventional jet fighter with a right-angled wing and powered by an Allison TG-180 turbine . At about the same time, the United States Army Air Force ordered a similar aircraft, named project NA-140 , which would result in the F-86 . After the presentation of the model, which was approved, the manufacturer proposed the incorporation of a swept wing with an angle of 35º, based on studies carried out, in the meantime captured, by the Germans and which led to the Me-262 , which demonstrated the increase in speed without the need for a large increase in power. [ 1 ]
On October 1, 1947 , the XP-86A prototype flew for the first time , powered by a General Electric J35-C-3 turbine but produced by Chevrolet , later re-equipped with the more powerful J47-GE-3 and then designated YF-86A , due to the restructuring of the designations assigned to the USAF aircraft. Still during the construction phase of the three prototypes, the first 33 F-86As of final production were ordered of a phased total that reached 554 units, during their construction they were equipped with new engine upgrades: J47-GE-3 , J47-GE-7 , J47-GE-9 and J47-GE-13 This was followed by the F-86E , also a day interceptor, with clear improvements in performance with the introduction of improved engines. The F-86F was the most representative of the series and the one that had the most involvement and success during the conflict in the Korean Peninsula , constituting itself as the most capable opponent of the MiG-15 . It was also used as a fighter-bomber with success, although that was not its vocation; it introduced a wing optimized for high altitudes, by adding an extra 30 cm in length and the use of slats allowed greater stability at low altitude and low speed, necessary for bombing and/or ground attack. [ 3 ]
After the end of the Korean War , the F-86H fighter-bomber appeared , equipped with the more powerful General Electric J75 engine , greater fuel capacity, wider air intakes, stronger landing gear, hydraulically actuated airbrakes, electrically actuated flaps and a more reliable mechanism for ejecting external loads, and a clamshell canopy similar to that used on the F-86D . The internal armament was also revised, from the 116th example built, two 20 mm M-39 cannons were introduced , replacing the six 12.7 mm machine guns . [ 4 ]
The F-86D began as the F-95A, an all-weather interceptor day and night, armed only with a battery of 24 high-explosive rockets, AN/APG-36 search radar and powder engine. combustion J47-GE-17B later J47-GE-33 and was intended to intercept bomber formations penetrating North American airspace, if it encountered fighters it used the power of its engine to escape. As it was understood that it would be easier to obtain funds for its development if it was considered an evolution of an existing project and not a new model, it was decided to designate it F-86D . The F-86K was its export version, after solving some of the mechanical and electronic problems it suffered from. [ 5 ]
Chronology
Important dates, but not exhaustive, in the development of the F-86 SabreJet . [ 6 ] [ 7 ]
November 22 , 1944
North American begins studies on a straight-wing jet fighter for the United States Army Air Force .
May 18 , 1945
Authorization for the construction of three NA-140/XP-86A prototypesThis was followed by the F-86E , also a day interceptor, with clear improvements in performance with the introduction of improved engines. The F-86F was the most representative of the series and the one that had the most involvement and success during the conflict in the Korean Peninsula , constituting itself as the most capable opponent of the MiG-15 . It was also used as a fighter-bomber with success, although that was not its vocation; it introduced a wing optimized for high altitudes, by adding an extra 30 cm in length and the use of slats allowed greater stability at low altitude and low speed, necessary for bombing and/or ground attack. [ 3 ]
After the end of the Korean War , the F-86H fighter-bomber appeared , equipped with the more powerful General Electric J75 engine , greater fuel capacity, wider air intakes, stronger landing gear, hydraulically actuated airbrakes, electrically actuated flaps and a more reliable mechanism for ejecting external loads, and a clamshell canopy similar to that used on the F-86D . The internal armament was also revised, from the 116th example built, two 20 mm M-39 cannons were introduced , replacing the six 12.7 mm machine guns . [ 4 ]
The F-86D began as the F-95A, an all-weather interceptor day and night, armed only with a battery of 24 high-explosive rockets, AN/APG-36 search radar and powder engine. combustion J47-GE-17B later J47-GE-33 and was intended to intercept bomber formations penetrating North American airspace, if it encountered fighters it used the power of its engine to escape. As it was understood that it would be easier to obtain funds for its development if it was considered an evolution of an existing project and not a new model, it was decided to designate it F-86D . The F-86K was its export version, after solving some of the mechanical and electronic problems it suffered from. [ 5 ]
Chronology
Important dates, but not exhaustive, in the development of the F-86 SabreJet . [ 6 ] [ 7 ]
November 22 , 1944
North American begins studies on a straight-wing jet fighter for the United States Army Air Force .
May 18 , 1945
Authorization for the construction of three NA-140/XP-86A prototypes
This was followed by the F-86E , also a day interceptor, with clear improvements in performance with the introduction of improved engines. The F-86F was the most representative of the series and the one that had the most involvement and success during the conflict in the Korean Peninsula , constituting itself as the most capable opponent of the MiG-15 . It was also used as a fighter-bomber with success, although that was not its vocation; it introduced a wing optimized for high altitudes, by adding an extra 30 cm in length and the use of slats allowed greater stability at low altitude and low speed, necessary for bombing and/or ground attack. [ 3 ]
After the end of the Korean War , the F-86H fighter-bomber appeared , equipped with the more powerful General Electric J75 engine , greater fuel capacity, wider air intakes, stronger landing gear, hydraulically actuated airbrakes, electrically actuated flaps and a more reliable mechanism for ejecting external loads, and a clamshell canopy similar to that used on the F-86D . The internal armament was also revised, from the 116th example built, two 20 mm M-39 cannons were introduced , replacing the six 12.7 mm machine guns . [ 4 ]
The F-86D began as the F-95A, an all-weather interceptor day and night, armed only with a battery of 24 high-explosive rockets, AN/APG-36 search radar and powder engine. combustion J47-GE-17B later J47-GE-33 and was intended to intercept bomber formations penetrating North American airspace, if it encountered fighters it used the power of its engine to escape. As it was understood that it would be easier to obtain funds for its development if it was considered an evolution of an existing project and not a new model, it was decided to designate it F-86D . The F-86K was its export version, after solving some of the mechanical and electronic problems it suffered from. [ 5 ]
Chronology
Important dates, but not exhaustive, in the development of the F-86 SabreJet . [ 6 ] [ 7 ]
November 22 , 1944
North American begins studies on a straight-wing jet fighter for the United States Army Air Force .
May 18 , 1945
Authorization for the construction of three NA-140/XP-86A prototypesThis was followed by the F-86E , also a day interceptor, with clear improvements in performance with the introduction of improved engines. The F-86F was the most representative of the series and the one that had the most involvement and success during the conflict in the Korean Peninsula , constituting itself as the most capable opponent of the MiG-15 . It was also used as a fighter-bomber with success, although that was not its vocation; it introduced a wing optimized for high altitudes, by adding an extra 30 cm in length and the use of slats allowed greater stability at low altitude and low speed, necessary for bombing and/or ground attack. [ 3 ]
After the end of the Korean War , the F-86H fighter-bomber appeared , equipped with the more powerful General Electric J75 engine , greater fuel capacity, wider air intakes, stronger landing gear, hydraulically actuated airbrakes, electrically actuated flaps and a more reliable mechanism for ejecting external loads, and a clamshell canopy similar to that used on the F-86D . The internal armament was also revised, from the 116th example built, two 20 mm M-39 cannons were introduced , replacing the six 12.7 mm machine guns . [ 4 ]
The F-86D began as the F-95A, an all-weather interceptor day and night, armed only with a battery of 24 high-explosive rockets, AN/APG-36 search radar and powder engine. combustion J47-GE-17B later J47-GE-33 and was intended to intercept bomber formations penetrating North American airspace, if it encountered fighters it used the power of its engine to escape. As it was understood that it would be easier to obtain funds for its development if it was considered an evolution of an existing project and not a new model, it was decided to designate it F-86D . The F-86K was its export version, after solving some of the mechanical and electronic problems it suffered from. [ 5 ]
Chronology
Important dates, but not exhaustive, in the development of the F-86 SabreJet . [ 6 ] [ 7 ]
November 22 , 1944
North American begins studies on a straight-wing jet fighter for the United States Army Air Force .
May 18 , 1945
Authorization for the construction of three NA-140/XP-86A prototypesThis was followed by the F-86E , also a day interceptor, with clear improvements in performance with the introduction of improved engines. The F-86F was the most representative of the series and the one that had the most involvement and success during the conflict in the Korean Peninsula , constituting itself as the most capable opponent of the MiG-15 . It was also used as a fighter-bomber with success, although that was not its vocation; it introduced a wing optimized for high altitudes, by adding an extra 30 cm in length and the use of slats allowed greater stability at low altitude and low speed, necessary for bombing and/or ground attack. [ 3 ]
After the end of the Korean War , the F-86H fighter-bomber appeared , equipped with the more powerful General Electric J75 engine , greater fuel capacity, wider air intakes, stronger landing gear, hydraulically actuated airbrakes, electrically actuated flaps and a more reliable mechanism for ejecting external loads, and a clamshell canopy similar to that used on the F-86D . The internal armament was also revised, from the 116th example built, two 20 mm M-39 cannons were introduced , replacing the six 12.7 mm machine guns . [ 4 ]
The F-86D began as the F-95A, an all-weather interceptor day and night, armed only with a battery of 24 high-explosive rockets, AN/APG-36 search radar and powder engine. combustion J47-GE-17B later J47-GE-33 and was intended to intercept bomber formations penetrating North American airspace, if it encountered fighters it used the power of its engine to escape. As it was understood that it would be easier to obtain funds for its development if it was considered an evolution of an existing project and not a new model, it was decided to designate it F-86D . The F-86K was its export version, after solving some of the mechanical and electronic problems it suffered from. [ 5 ]
Chronology
Important dates, but not exhaustive, in the development of the F-86 SabreJet . [ 6 ] [ 7 ]
November 22 , 1944
North American begins studies on a straight-wing jet fighter for the United States Army Air Force .
May 18 , 1945
Authorization for the construction of three NA-140/XP-86A prototypes
Specifications
Spotlights
- HudDistance 1.1 years ago
General Characteristics
- Created On Windows
- Wingspan 35.4ft (10.8m)
- Length 32.6ft (9.9m)
- Height 11.0ft (3.3m)
- Empty Weight 5,285lbs (2,397kg)
- Loaded Weight 7,585lbs (3,440kg)
Performance
- Power/Weight Ratio 2.221
- Wing Loading 30.8lbs/ft2 (150.6kg/m2)
- Wing Area 245.9ft2 (22.8m2)
- Drag Points 678
Parts
- Number of Parts 82
- Control Surfaces 2
- Performance Cost 577