also posted during vacations

(why it's raining too much during my vacations!?)
The Lockheed Martin X-59 Quesst ("Quiet SuperSonic Technology"), sometimes styled QueSST, is an American experimental supersonic aircraft under development by Skunk Works for NASA's Low-Boom Flight Demonstrator project.[2] Preliminary design started in February 2016, with the X-59 planned to begin flight testing in 2021. After delays, as of January 2024, it is planned to be delivered to NASA for flight testing in 2024. It is expected to cruise at Mach 1.42 (1,510 km/h; 937 mph) at an altitude of 55,000 ft (16,800 m), creating a low 75 effective perceived noise level (EPNdB) thump to evaluate supersonic transport acceptability.

desing :
The Low-Boom X-plane is 99.7 ft (30.4 m) long with a 29.5 ft (9.0 m) wingspan for a maximum takeoff weight of 32,300 lb (14,700 kg). Propelled by a General Electric F414 engine, it should reach a maximum speed of Mach 1.5 or 990 mph (1,590 km/h), and cruise at Mach 1.42 or 940 mph (1,510 km/h) at 55,000 ft (16,800 m).[27] The cockpit, ejection seat and canopy come from a Northrop T-38 and the landing gear from an F-16.[6] With afterburner, its engine will provide 22,000 lbf (98 kN) of thrust.[28]
As of 2017, the ground noise was expected to be around 60 dB(A), about 1/1000 as loud as current supersonic aircraft. This was to be achieved by using a long, narrow airframe and canards to keep the shock waves from coalescing.[5] A 2018 projection was that the aircraft would create a 75 EPNdB thump on ground, as loud as closing a car door, compared with 105-110 EPNdB for the Concorde.[6] The central engine has a top-mounted intake for low boom, but inlet flow distortion due to vortices is a concern.[12]
The flush cockpit means that the long and pointed nose-cone will obstruct all forward vision. The X-59 will use an enhanced flight vision system (EVS), consisting of a forward 4K camera with a 33° by 19° angle of view, which will compensate for the lack of forward visibility.[6][29]
In January 2019, RTX Corporation subsidiary Collins Aerospace was selected to supply its Pro Line Fusion Cockpit avionics, displaying[clarification needed] the boom on the ground, and EVS with long-wave infrared sensors.[30] The Collins EVS-3600 multispectral imaging system, beneath the nose, is used for landing, while the NASA external vision system (XVS), in front of the cockpit, gives a forward view
Specifications
General Characteristics
- Created On Android
- Wingspan 32.1ft (9.8m)
- Length 113.9ft (34.7m)
- Height 16.7ft (5.1m)
- Empty Weight 21,058lbs (9,551kg)
- Loaded Weight 38,788lbs (17,594kg)
Performance
- Power/Weight Ratio 1.013
- Wing Loading 39.3lbs/ft2 (192.0kg/m2)
- Wing Area 986.2ft2 (91.6m2)
- Drag Points 3847
Parts
- Number of Parts 79
- Control Surfaces 5
- Performance Cost 406
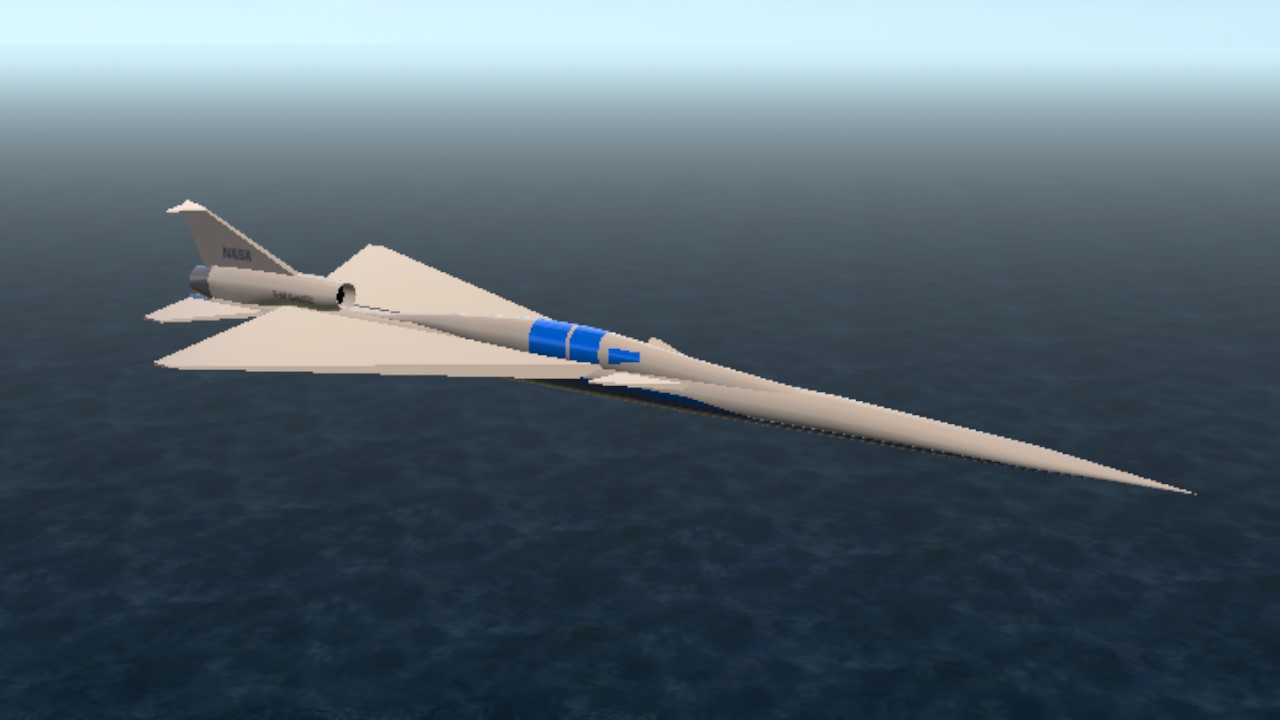
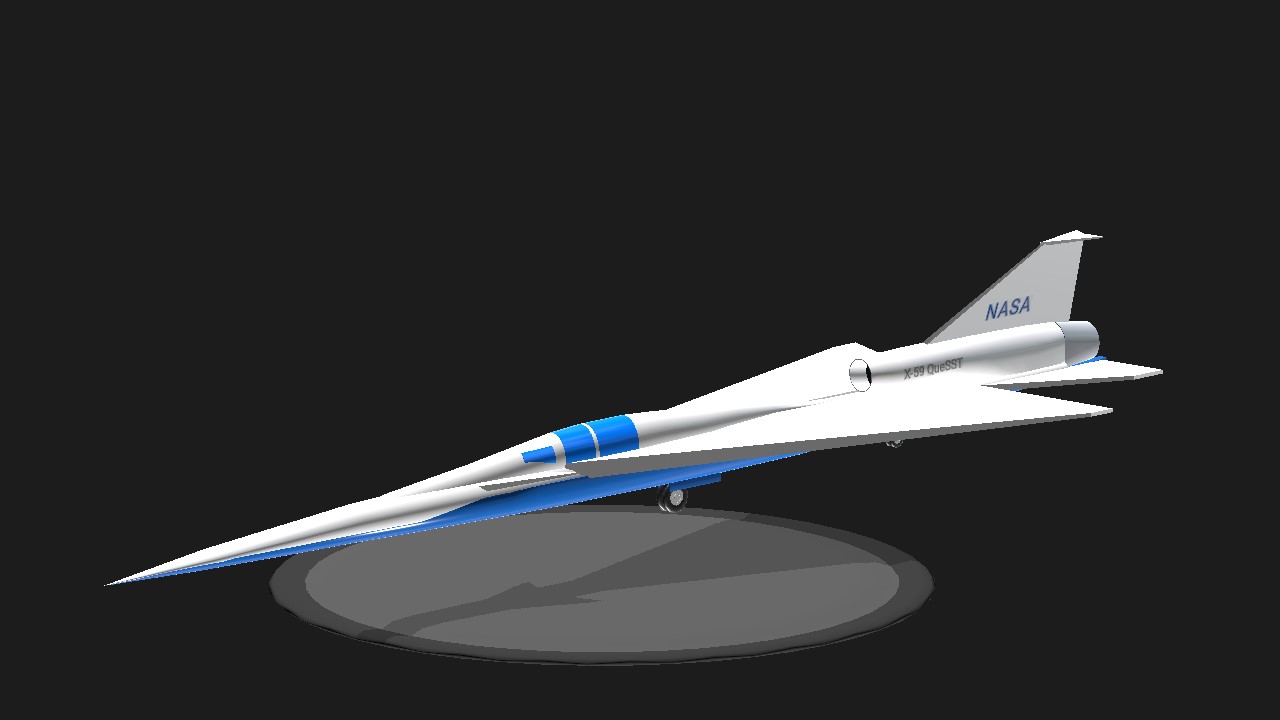
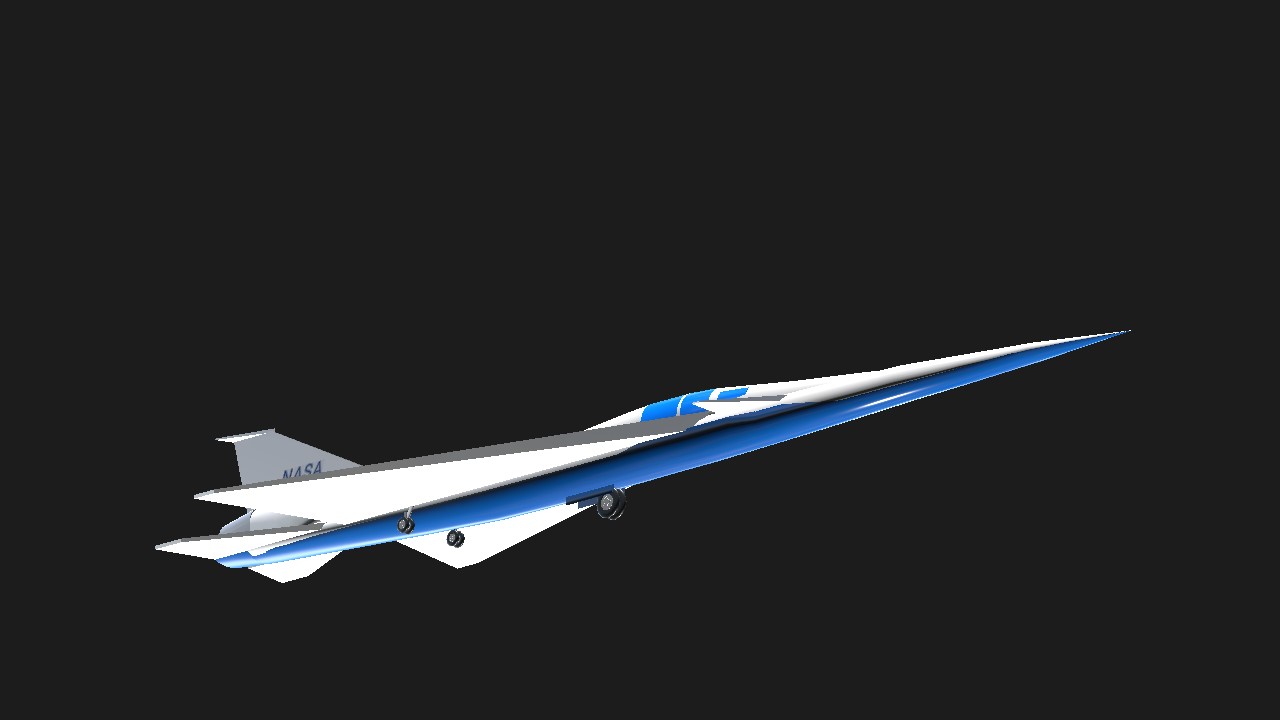






Really nice! Suprisingly easy to land with that strange landing gear arrangement too!
Nice build with 79 parts . I love it.