new warthunder vehicle update leak 2024 🥵🥵
INSTRUCTIONS
-AG-1: Engine & Electronics Start [Enable Engine]
-AG-2: Detach Trailer
-AG-3: Headlights (PS: I messed up, Headlights is now part ofAG-1, i forgot to change it.)
-AG-4: Travel Lock
-AG-5: Open Side Armor
-AG-6/AG-7: Hydropneumatic suspension
~6= Back
~7= Front
-Pitch&Roll: Forward/Reverse & Left/Right
-VTOL: Gun Elevation/Depression
-Trim: Turret Traverse
?PS:LandingGearis to lower the retractable legs for when stationary.
Some few lines of FT codes in this vehicle are not mine. Though i don't remember who made it since it's been a long time since. I apologize in advance to anyone who might find it an inconvenience.
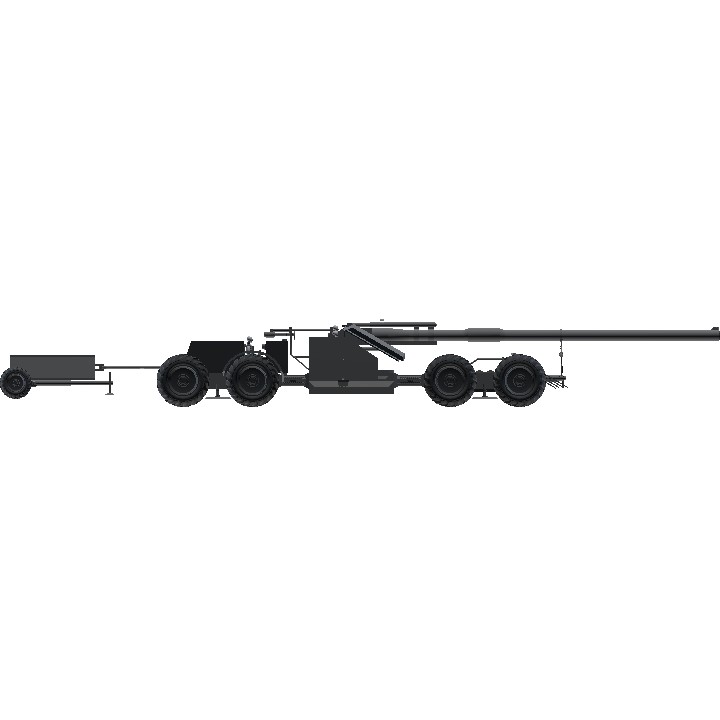
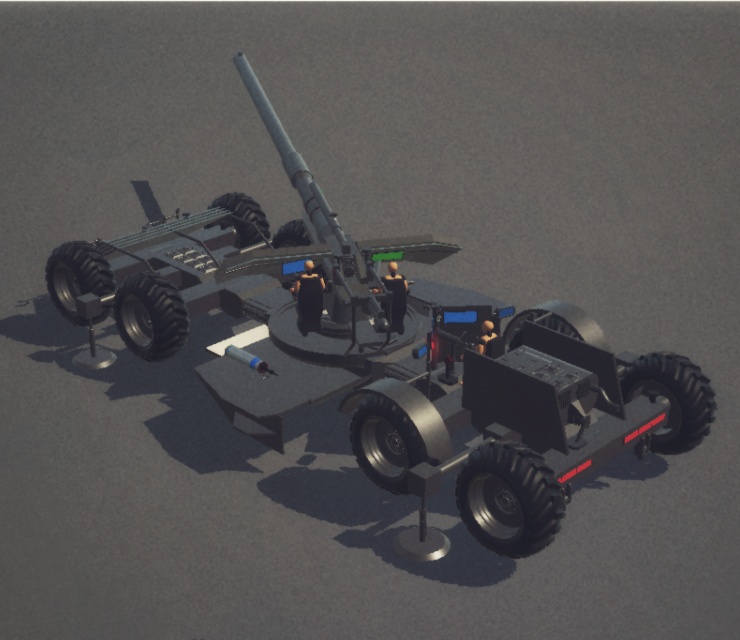
This vehicle is basically a 12.8cm PAK 44 on steroids.
(In other words, a modern and old design mix)
I tried to make it a 1:1 scale using the cannon size as reference for it.
The rest of this post is basically a Wikipedia-like article of the vehicle.
(Description generated by ChatGPT; modified by me)
Thumbnail and photos made and edited in ibisPaintX and Snapseed.
nothing is impossible with an engineer that has incentives and high monthly paycheck
17.5cm SL.FR. FPAK 82
The 17.5cm Selbstfahrende-Feldpanzerabwehrkanone 82 (English: Self-propelled field anti-tank cannon 82), also known as the 17.5cm SL.FR. FPAK 82 or simply FPAK 82, was a West German self-propelled anti-tank gun developed during the Cold War in 1982. Designed to counter the formidable Soviet armor of the era, the FPAK 82 combined advanced armor technology with a powerful 175mm cannon, drawing inspiration from the World War II-era 12.8cm PAK 44. This vehicle represents a unique blend of mobility, protection, and firepower, encapsulating the strategic needs and technological capabilities of the Bundeswehr during the late Cold War period.
Overview
17.5cm Selbstfahrende-Feldpanzerabwehrkanone 82
German FPAK 82 in Baumholder Training Area in 1981
- Type: Self-propelled anti-tank gun
- Place of origin: West Germany
- In Service: 1983–1991
- Used by: Germany
- Wars: None
- Designer: Rheinmetall
- Designed: 1978–1982
- Manufacturer: Krauss-Maffei
- Produced: 1982–1986
- Number built: 250
- Weight: 37,202 kg (empty), 38,459 kg (loaded)
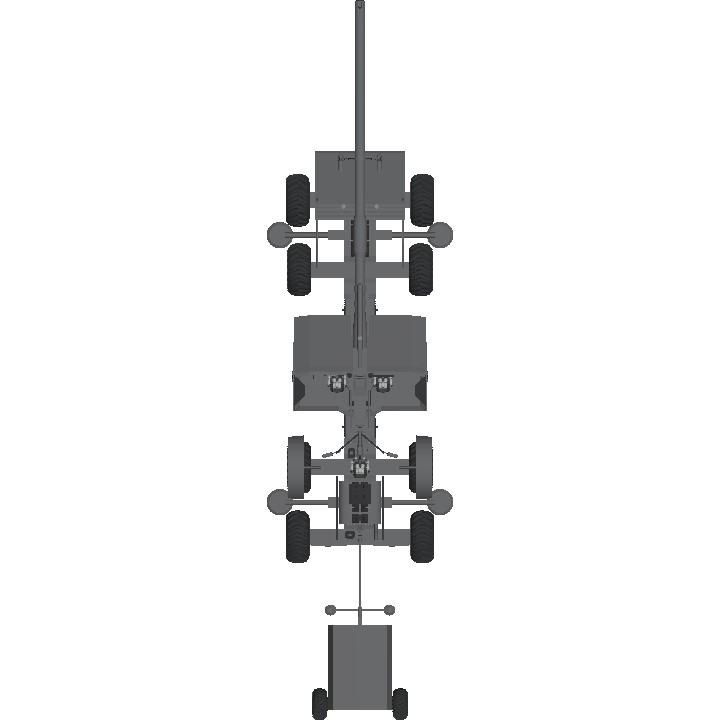
- Length: 13.2 m (16.8 m with towed shell trailer)
- Width: 4.4 m
- Height: 2.0 m
- Crew: 6 (driver, commander, gunner, loader, 2 assistant loaders)
- Unit Cost: DM 2.7 million ($3.85 million, €3.53 million as of July 2024)
Development
The development of the FPAK 82 was initiated in response to the increasing threat posed by Soviet armored units, such as the T-72 and T-80 tanks. The Bundeswehr recognized the need for a new anti-tank platform capable of delivering high-velocity, armor-piercing rounds at long ranges. Rheinmetall was tasked with designing a weapon system that would meet these requirements, while Krauss-Maffei was responsible for the vehicle's chassis and overall construction.
The project began in 1978, drawing heavily on historical designs like the 12.8cm PAK 44 but incorporating modern technologies such as composite armor and a smoothbore cannon. The vehicle was designed to offer a high level of protection and firepower while maintaining mobility and ease of deployment.
Design
Armament
Rheinmetall immediately went to work on making a new high-calibre smoothbore cannon that could penetrate any Soviet armor the Bundeswehr could encounter, in case of any potential conflict with the Soviet Union in the near future. That cannon was to be mounted onto the turret of the new FPAK 82 platform designed by Krauss-Maffei. They came up with a newly designed 17.5cm RH-175 smoothbore cannon, capable of firing an enormous 175mm APFSDS round. The cannon, weighing 2.9 tons and measuring 13 meters in length, had a muzzle velocity of 1250 m/s, enabling it to penetrate the most advanced Soviet armor at significant distances.
Armor
The vehicle featured an armor system designed to maximize protection while minimizing weight. The turret was protected by 130mm composite armor with a 30mm spall-liner, both sloped at 60 degrees. The hull was equipped with four welded spaced armor plates, each 80mm thick and angled at 60 degrees. The sides featured folding armor panels ranging from 60 to 90mm thick, which provided additional protection when locked and served as a platform for the crew when unfolded.
Mobility
The FPAK 82 was built on an 8x8 chassis with a hydropneumatic suspension system that allowed the crew to adjust the height of the vehicle's front or back. This feature provided tactical advantages, such as improved maneuverability on uneven terrain and enhanced gun elevation and depression angles in various combat situations.
The vehicle was powered by three engines: a primary engine at the front, an electric engine in the middle, and a secondary engine at the rear. This configuration allowed for a maximum speed of 72 km/h on flat terrain and an average speed of 58 km/h. The vehicle had a fuel capacity of 87 liters, with an additional 100 liters available through extra fuel tanks.
Crew and Layout
The vehicle was operated by a crew of six: a driver, commander, gunner, loader, and two assistant loaders. The driver's compartment was small and half-exposed, located at the rear behind the turret. The design included adequate storage space near the crew and a towed shell carriage capable of storing at least 18 rounds, depending on the layout used.
Shell
The FPAK 82's primary ammunition was the 175mm APFSDS round, designed for maximum penetration against heavily armored targets. Each shell weighed 87 kg and measured 1.8 meters in length, with a diameter of 0.175 meters. The penetrator was 1.5 meters long with a diameter of 0.130 meters (0.150 meters if including fins). This design allowed for optimal aerodynamics and penetration capability, ensuring effectiveness against the latest Soviet tank armor.
The towed shell carriage provided the necessary logistics for carrying additional ammunition, allowing the vehicle to sustain prolonged engagements without the immediate need for resupply. The carriage was designed to accommodate various shell layouts, offering flexibility in operational planning and engagement strategies.
Production and Testing
Production of the FPAK 82 began in 1982 at Krauss-Maffei's manufacturing facilities. A total of 250 units were produced between 1982 and 1986. The vehicle underwent extensive testing at the Baumholder Military Training Area.
Testing revealed that the FPAK 82 could effectively penetrate Soviet main battle tanks, reinforcing its role as a deterrent against armored advances. However, the vehicle's size and weight posed challenges in terms of strategic mobility and air transportability.
Combat History
Although the FPAK 82 was never deployed in combat, it played a crucial role in NATO's defensive strategy during the Cold War. Its presence in the Bundeswehr's arsenal served as a powerful psychological deterrent against potential Warsaw Pact aggression, contributing to the overall balance of power in Europe.
Feedback and Drawbacks
Feedback from the Bundeswehr highlighted the FPAK 82's exceptional firepower and protection levels. The advanced hydropneumatic suspension system was praised for providing excellent maneuverability in varied terrains, giving the vehicle a tactical edge in positioning and firing angles.
However, the FPAK 82's large size and weight limited its deployment in certain terrains, making it less suitable for rapid redeployment. The complex logistics required for its operation, including the maintenance of its three-engine configuration, were seen as potential drawbacks. Additionally, the vehicle's high fuel consumption was noted as a challenge, particularly for extended operations without resupply.
Variants
Several variants of the FPAK 82 were proposed, though very few were produced:
- FPAK 82A1: A variant with enhanced electronics and targeting systems for improved accuracy and engagement range.
- FPAK 82B1: An upgraded model featuring additional armor and an autoloader system, reducing crew size to five.
- FPAK 82C1: A command and control variant equipped with advanced communication systems for battlefield coordination.
Fate and Legacy
With the end of the Cold War and the Reunification of Germany, the FPAK 82 was gradually phased out of service. By 1991, most units had been retired, with some preserved in military museums as a testament to their role in Cold War history.
The FPAK 82's design influenced subsequent generations of armored vehicles, particularly in the areas of composite armor technology and large-caliber smoothbore cannons. Its legacy lives on in the continued development of anti-tank platforms and the strategic emphasis on combining firepower, mobility, and protection.
Comparable Vehicles
- FV4005 Stage II: A British self-propelled anti-tank gun developed during the Cold War with a similar emphasis on firepower and protection.
- Type 89 (PTZ-89): A Chinese self-propelled gun that balances firepower and mobility, comparable in its operational philosophy.
- 2S7 Pion: A Soviet self-propelled artillery piece with a focus on long-range engagement and firepower.
- Strv 103: A Swedish tank known for its innovative design and emphasis on anti-tank capabilities.
See Also
- Rheinmetall
- Krauss-Maffei
- Cold War armored fighting vehicles
- APFSDS ammunition
- List of Cold War military equipment of West Germany
- Tank Development and Design
- Self-Propelled Gun
- Tank Destroyer
Sources (that i made tf up)
- "Rheinmetall RH-175: Innovations in Large-Caliber Artillery," Military Technology Review, 1983.
- "Krauss-Maffei's Cold War Contributions: The FPAK 82 and Beyond," Armored Vehicle Journal, 1991.
- Bundeswehr Archives, "Development and Deployment of Anti-Tank Systems, 1980-1990."
External Links
This is all made up and not real, i repeat 🙏🙏
(Also, feel free to modify it if you're feeling it. Maybe turn it into a ballistic missile launcher, or just simply change its stats or whatever, i don't know.)
Specifications
Spotlights
- Zhixunlin23 1.5 years ago
- PAULO1236 1.5 years ago
- tetozz 1.5 years ago
General Characteristics
- Created On Android
- Wingspan 14.4ft (4.4m)
- Length 55.3ft (16.8m)
- Height 7.2ft (2.2m)
- Empty Weight 83,772lbs (37,998kg)
- Loaded Weight 84,063lbs (38,130kg)
Performance
- Wing Loading 1,983.4lbs/ft2 (9,684.0kg/m2)
- Wing Area 42.4ft2 (3.9m2)
- Drag Points 6871
Parts
- Number of Parts 344
- Control Surfaces 0
- Performance Cost 1,671