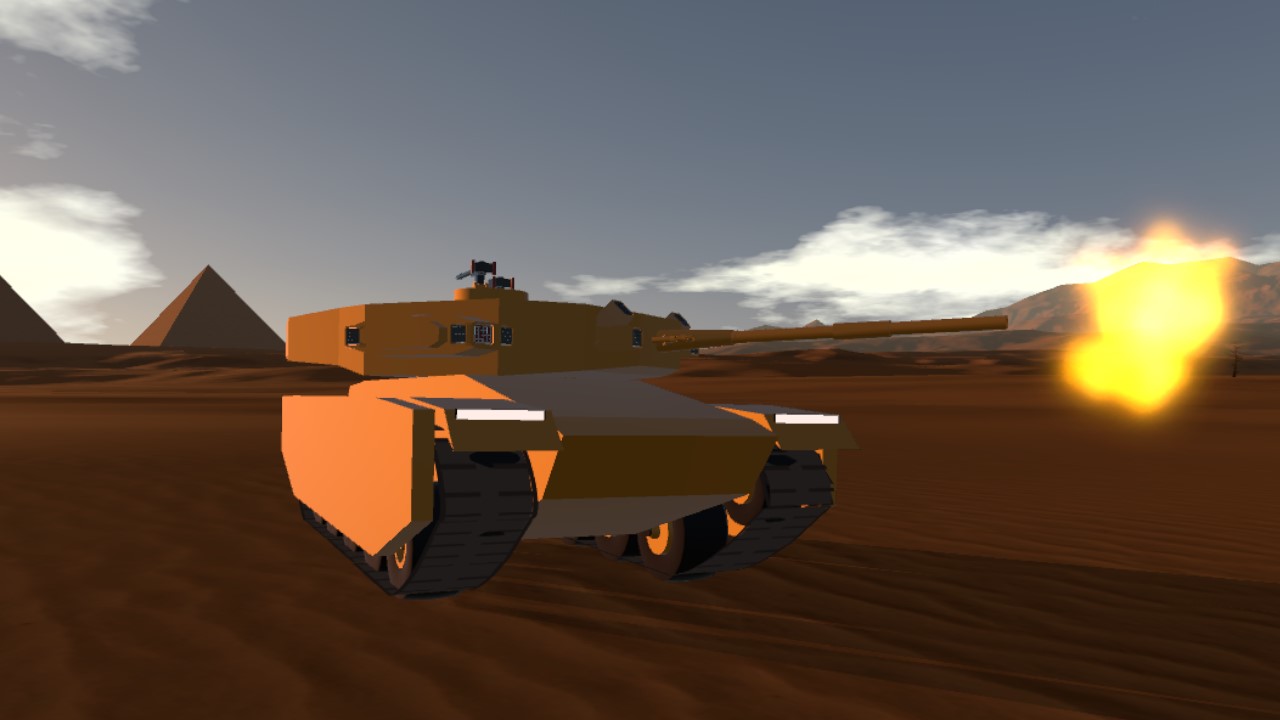
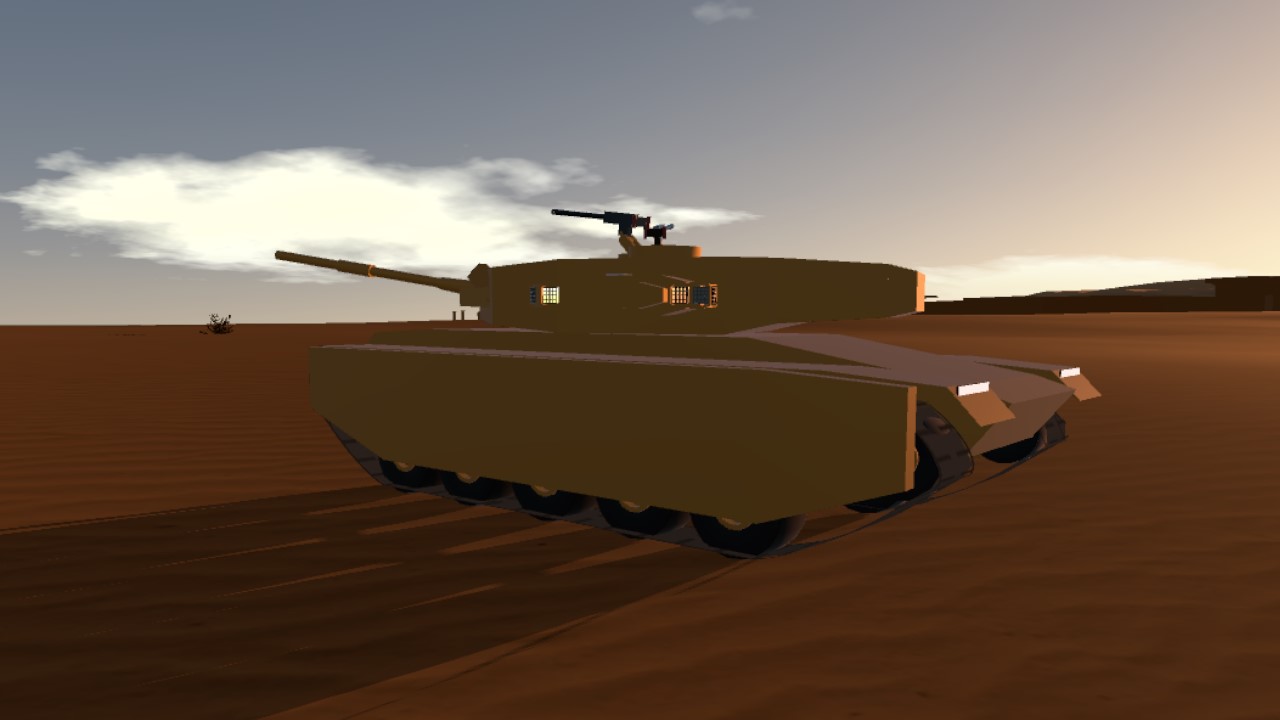
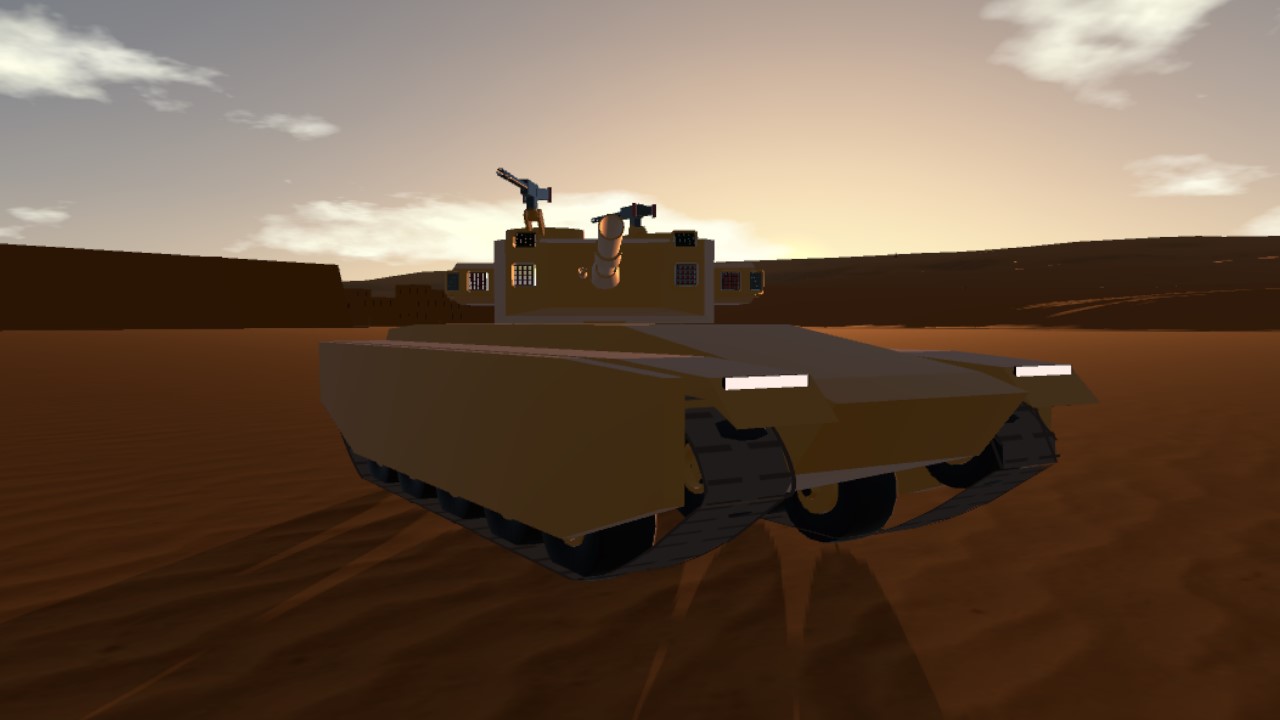
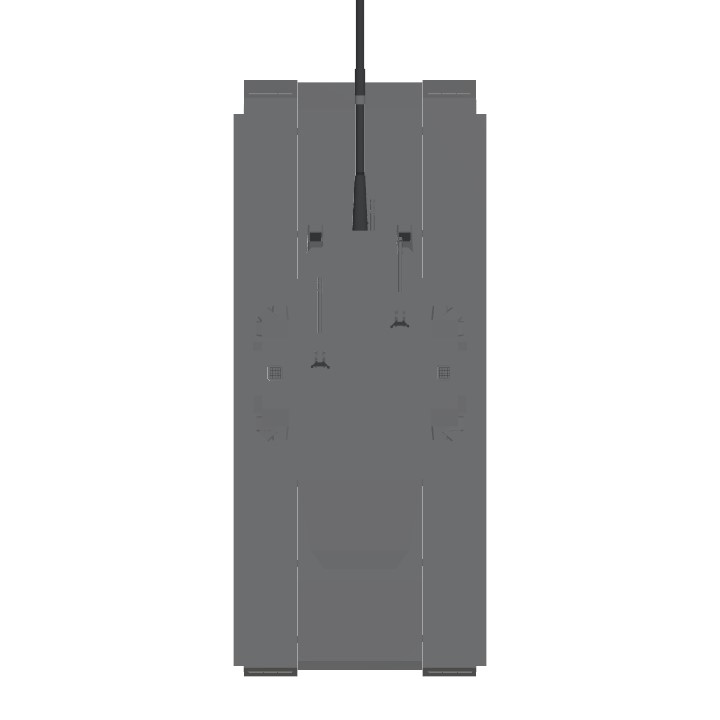
The Type 74 Ha-Go (74-gata shiki-sensha Ha-go) is a main battle tank used by the Japanese Imperial Army Corps during the latter years of the Cold War era, replacing the earlier Type 57 main battle tanks that had served both army and marines during the earlier years. The tank, similarly to it's predecssor, sported a 100mm cannon, however it was smoothbore as opposed to rifled on the Type 57. The tank, despite being developed from more or less the same basic chassis as the Type 72 fielded by the Marine Corps, was developed for the Army Corps and thus around the 100mm guns that the Army fielded as standard. The 100mm shells proved impractical to mount within a carosel autoloader without significantly compromising survivability, one major roadblock in the tank's development, and thus the autoloader had to be changed to a bustle titing-arm autoloader. While the tank would use the same powerplant and optics suite as the Type 72, in further addition, the turret ring had to be redesigned and moved further back to accomodate the larger turret housing the 100mm, the tank was heavier, thus requiring a redesigned transmission, factors which delayed it's introduction within the Army Corps for a good two years. Production would not fully commence untill well into October 1973, nearly two years later than the Marine Corps's Type 72. The first battalions of Type 74s came online in late 1974.
Overview
Type: Main battle tank
Origin: Japan
Manufacturer: Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
Operators: see Operators
Developed from: Mitubishi Type 57
Produced: 1973-current
Specifications
Mass: 44 tons standard load
Width: 11.7ft (3.6m)
Length: 33.2ft (10.1m)
Height: 10.9ft (3.3m)
Crew: 3 (commander, gunner and driver)
Armor
Japan Steel Works tungsten carbide/steel-ceramic composite, effective protection equal to 6x RHA
- 100mm front, angled 60-80 degrees from vertical
- 50mm sides and rear, vertical
- 150mm frontal turret, angled 45 degrees from vertical
- 75mm turret sides and rear, vertical
- 37mm turret roof, horizontal
Armament
1x Enoshima Type 70 100mm/65 high-velocity smoothbore cannon (88 rounds)
3x Type 93 heavy machine gun (1 coaxial, 2 turret)
General characteristics
Autoloader: Revolving breech, revolving arm, rear bustle (rate of fire: 20 rounds/min)
Engine: 1x Mitsubishi Sakae 14-cylinder air-cooled single-turbo radial diesel engine, 1,100hp, 2,100rpm
Transmission: 5-speed sequential automatic torsion shifter transmission, 2 secondary reverse clutches
Suspension: Torsion spring
Top speed: 72km/h (44mph) forwards, 72km/h (44mph) backwards
Operational range: 700km
Countermeasures
2x Type 80 active protection systems
4x Type 57 flare launchers
Optics and targeting equipment
Mikasa Mi-70 day/night vision optical sight
Mikasa Mi-69 gyro-stabilized tank fire-control system
Aichi Kokuki Ai-71 infared laser rangefinder
- backup secondary open ring iron sights and coincidence rangefinder
Operators
Japan (Japanese Imperial Army Corps): 24,000 tanks across eight regiments within the Army Corps's four divisions.
Obelia (Obelia Imperial Army): 30 tanks, presumably for support roles
Controls
AG1: Night Vision
AG2 + FireGuns: APS
WASD: Driving the mechanical abnomination
IMPORTANT: Within the list of weapons, there is one titled '13.2mm coaxial heavy machine gun'. This weapon serves no other purpuse than to toggle the fire control system into aiming for the coaxial wing gun that has gravityless bullet paths as opposed to the dropping trajectories of the 100mm smoothbore.
Specifications
General Characteristics
- Predecessor Mitsubishi Type 72 Ni-Go main battle tank
- Successors 2 airplane(s) +14 bonus
- Created On Windows
- Wingspan 11.7ft (3.6m)
- Length 33.2ft (10.1m)
- Height 10.9ft (3.3m)
- Empty Weight 80,078lbs (36,323kg)
- Loaded Weight 97,166lbs (44,074kg)
Performance
- Horse Power/Weight Ratio 0.02
- Wing Loading 22,220.5lbs/ft2 (108,489.9kg/m2)
- Wing Area 4.4ft2 (0.4m2)
- Drag Points 5491
Parts
- Number of Parts 177
- Control Surfaces 0
- Performance Cost 1,588