( English version at the bottom of the page )
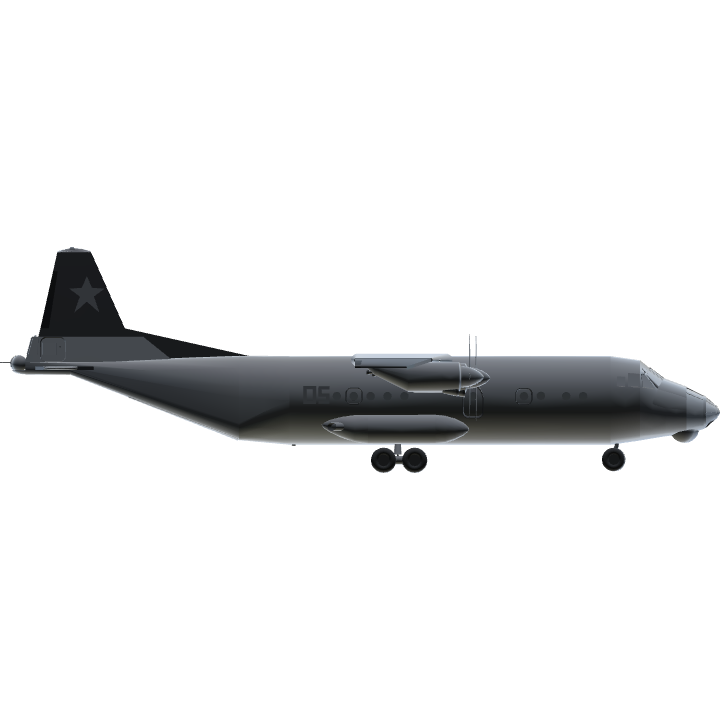
L'An-12 est la version cargo militaire de l'An-10 et fut développée parallèlement, après une demande
de la force aérienne soviétique pour un appareil de transport à turbopropulseurs en novembre 1955.
Il fut développé sous la dénomination "projet T" et une maquette fut approuvée par les autorités soviétiques le 22 juillet 1956.
2 prototypes furent construits à Irkoutsk, et le premier d'entre eux, codé 7900101, décolla pour la première fois
le 16 décembre 1957 avec Ya.I. Vernikov et G.I. Lysenko aux commandes. Il était propulsé par 4 Kuznetsov NK-4.
Ce premier prototype fut perdu par accident en février 1959. Les essais étatiques eurent lieu entre juillet 1958 et juin 1959.
L'An-12 était effectivement très proche de l'An-10 et partageait avec lui de nombreux composants, à 86%. En revanche, bien que
sa soute fut prévue pour, elle n'a jamais été pressurisée. Il semble aussi ne jamais avoir souffert des problèmes structurels
de son grand frère. La dérive, elle, accueillait à sa base un poste de tir vers l'arrière comprenant 2 canons AM-23 équipés
de 350 obus par canon, dans la grande tradition soviétique. Enfin, la partie arrière fut dessinée afin d'accueillir une rampe.
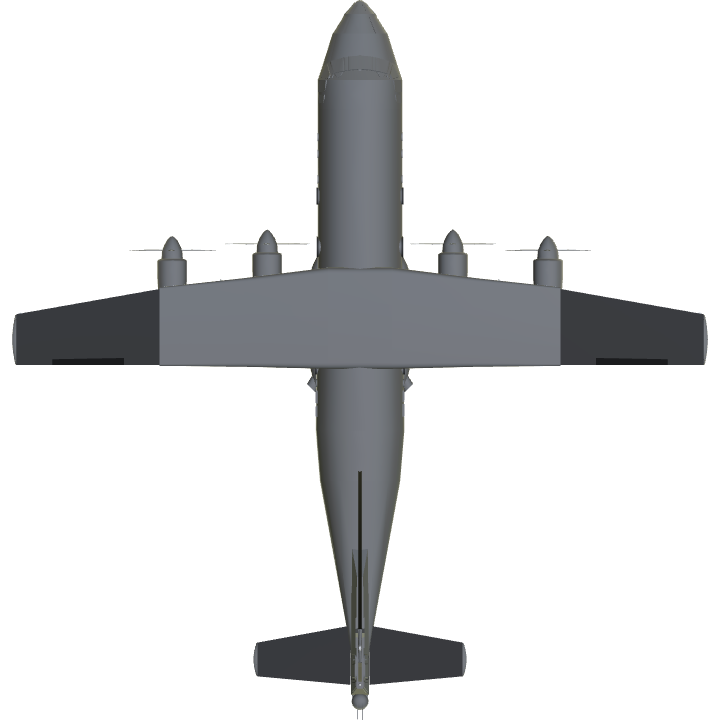
L'An-12 se distingue de l'An-10 par l'absence des deux quilles ventrales à l'arrière.
La production commença en 1958, dans l'usine N°39 à Irkoutsk, qui produisit 155 appareils jusqu'en décembre 1961.
Celle-ci fut transférée à l'usine 64 à Voronezh (258 exemplaires jusqu'en 1965) et à l'usine 84 de Tashkent en 1961 (830 appareils).
Il atteignit sa capacité opérationnelle initiale, au sein des VTA, fin 1959. Cependant, il fut victime d'accident à son entrée en
service et fut même cloué au sol jusqu'en juin 1960, le temps d'accomplir les modifications nécessaires.
L'OTAN l'appela tout d'abord "Cat-B" compte tenu de sa parenté avec l'An-10, puis finalement Cub.
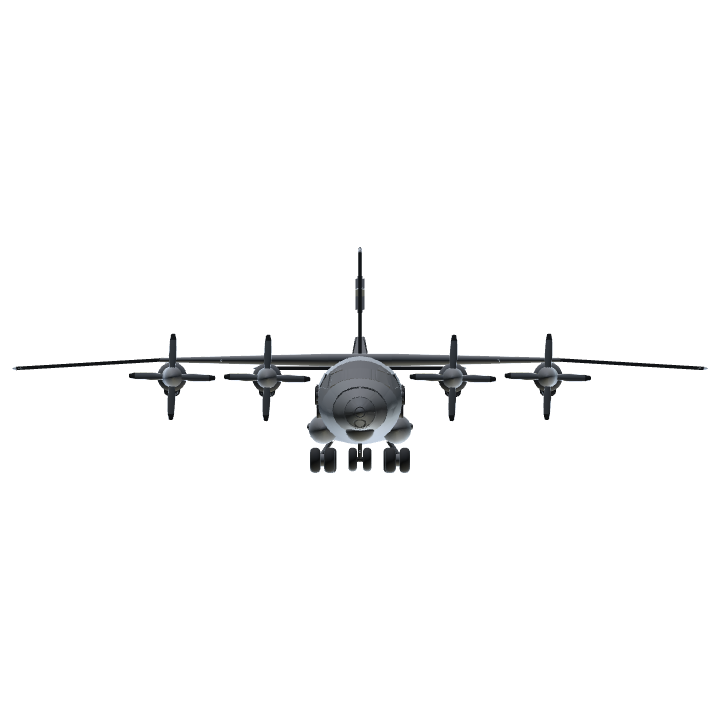
L'An-12 se présente comme un quadrimoteur, équipé de turbopropulseurs Ivchenko Al-20A de 4000 ch démarrés électriquement.
Seuls les prototypes et les 2 premiers appareils de présérie étaient propulsés par des NK-4. Son fuselage est circulaire et
de construction semi-monocoque. La plus grande partie de la structure est en alliage d'aluminium, avec quelques parties en alliage
de magnésium. Il est à ailes hautes et reprend le train d'atterrissage de l'An-10. Son équipage est de 6 personnes : un pilote, un
copilote, un mécanicien, un opérateur radio et radar, un navigateur, et un mitrailleur de queue (si nécessaire).
La cabine de l'équipage (poste du mitrailleur compris) est pressurisée, et le navigateur dispose de l'habituel poste vitré en avant.
Le cockpit est blindé, et dispose d'un viseur de bombardement et de caméras destinés à diriger les parachutages, d'un radar de
navigation RPB-2 (Toad Stool pour l'OTAN), d'un système de radio-navigation PDSP-2S Proton-M, d'un IFF entre autres.
Si le fuselage est circulaire, la soute est rectangulaire, avec les dimensions suivantes : 13,5 mètres de long et 3,5 mètres
de large sur 2,6 mètres de haut, soit un volume de 122,9 m3. Il peut emporter 58 parachutistes, 91 soldats, 85 blessés ou
20 tonnes de fret incluant des véhicules légèrement ou moyennement blindés (le GAZ-69 par exemple), des pièces d'artillerie, des
camions. Le manque de pressurisation implique de voler en-dessous du régime maximal des moteurs, d'où une perte d'autonomie.
Parmi les très nombreuses versions, 7 ou 8 An-12 furent construits avec un second APU, qui servait à alimenter des équipements
électroniques. On ignore de quoi il s'agissait, peut-être servirent-ils de relais de communication.
1245 An-12 furent produits jusqu'en 1973 (avec les 2 prototypes), et furent les principaux avions de transport
de l'Union Soviétique jusqu'à la fin des années 1970. Les An-12 furent déployés pour la première fois en 1968, lors de
l'intervention soviétique en Tchécoslovaquie, afin de parachuter des soldats. Il fut lourdement impliqué en Afghanistan
dans les années 1980, et plusieurs appareils furent perdus à cause des missiles Stinger.
Les An-12 furent alors équipés de lance-leurres (30 cartouches). Ils furent également utilisés lors des conflits en Tchétchénie.
L'An-12 a depuis été remplacé en grande partie par l'Il-76.
Décollage avec deux crans de volets . Vol en palier avec un cran de Trim .
Je remercie " BogdanX " pour la création de l'avant de l'appareil .
- Moteur : touche 1 2 3 4 .
- Feux de navigation : touche 5 .
- Feu d'atterrissage : touche 6 .
- Fumées moteurs : touche 8 .
- Volet : vtol .
- Trim : Trim .
English version .
The An-12 is the military cargo version of the An-10 and was developed in parallel, after a request
of the Soviet Air Force for a turboprop aircraft in November 1955.
It was developed under the name "Project T" and a model was approved by the Soviet authorities on July 22, 1956.
2 prototypes were built in Irkutsk, and the first one, coded 7900101, took off for the first time
December 16, 1957 with Ya.I. Vernikov and G.I. Lysenko at the controls. He was powered by 4 Kuznetsov NK-4.
This first prototype was lost by accident in February 1959. State tests took place between July 1958 and June 1959.
The An-12 was indeed very close to the An-10 and shared with him many components, 86%. On the other hand, although
her hold was planned for, she was never pressurized. He also seems to have never suffered from structural problems
of his big brother. The drift, it, hosted at its base a rear firing station with 2 AM-23 guns equipped
350 shells per barrel, in the great Soviet tradition. Finally, the rear part was designed to accommodate a ramp.
The An-12 differs from the An-10 in the absence of the two ventral pins at the rear.
Production began in 1958 at Irkutsk factory No. 39, which produced 155 aircraft until December 1961.
This was transferred to the Voronezh factory (258 copies until 1965) and to the Tashkent plant 84 in 1961 (830 units).
He reached his initial operational capacity within the VTAs at the end of 1959. However, he suffered an accident when he entered
service and was even grounded until June 1960, the time to make the necessary changes.
NATO called it "Cat-B" first because of its relationship with the An-10, and finally Cub.
The An-12 comes as a four-engine, equipped with Ivchenko Al-20A turboprop engines of 4000 hp started electrically.
Only the prototypes and the first 2 pre-production units were powered by NK-4s. Its fuselage is circular and
semi-monocoque construction. Most of the structure is aluminum alloy, with some alloy parts
magnesium. It is high-winged and resumes the landing gear of the An-10. Its crew is 6 people: a pilot, a
co-pilot, a mechanic, a radio and radar operator, a navigator, and a rear gunner (if necessary).
The crew cabin (including the gunner's post) is pressurized, and the navigator has the usual glazed position forward.
The cockpit is shielded, and has a bombing sight and cameras to direct the airdrops, a radar of
RPB-2 navigation (Toad Stool for NATO), a Proton-M PDSP-2S radio navigation system, an IFF among others.
If the fuselage is circular, the cargo hold is rectangular, with the following dimensions: 13.5 meters long and 3.5 meters
2.6 meters high, a volume of 122.9 m3. It can carry 58 paratroopers, 91 soldiers, 85 wounded or
20 tonnes of freight including lightly or medium-armored vehicles (GAZ-69 for example), artillery
trucks. The lack of pressurization involves flying below the maximum speed of the engines, resulting in a loss of autonomy.
Among the many versions, 7 or 8 An-12 were built with a second APU, which was used to power equipment
e. We do not know what it was, maybe they served as communication relays.
1245 An-12 were produced until 1973 (with the two prototypes), and were the main transport aircraft
of the Soviet Union until the late 1970s. The An-12s were first deployed in 1968, when
Soviet intervention in Czechoslovakia, to parachute soldiers. He was heavily involved in Afghanistan
in the 1980s, and several aircraft were lost due to Stinger missiles.
The An-12s were then equipped with decoy launchers (30 rounds). They were also used during the conflicts in Chechnya.
An-12 has since been largely replaced by the Il-76.
Takeoff with two notches of flaps. Level flight with a Trim screen.
I thank "BogdanX" for creating the front of the device.
- Engine: 1 2 3 4 button.
- Navigation lights: key 5.
- Landing light: key 6.
- Motor smoke: button 8.
- Shutter: vtol.
- Trim: Trim.



@XEPOH , Thanks for your upvote .
@agnanSatrio, thanks for you up vote.
@USSR , thanks for you upvote .
@Ruimtevaart , thank for you upvote .
@Trainzo np :)
@Minecraftpoweer , @CarsonG1017 , @Awsomur , @getorge , thanks for yours upvote .