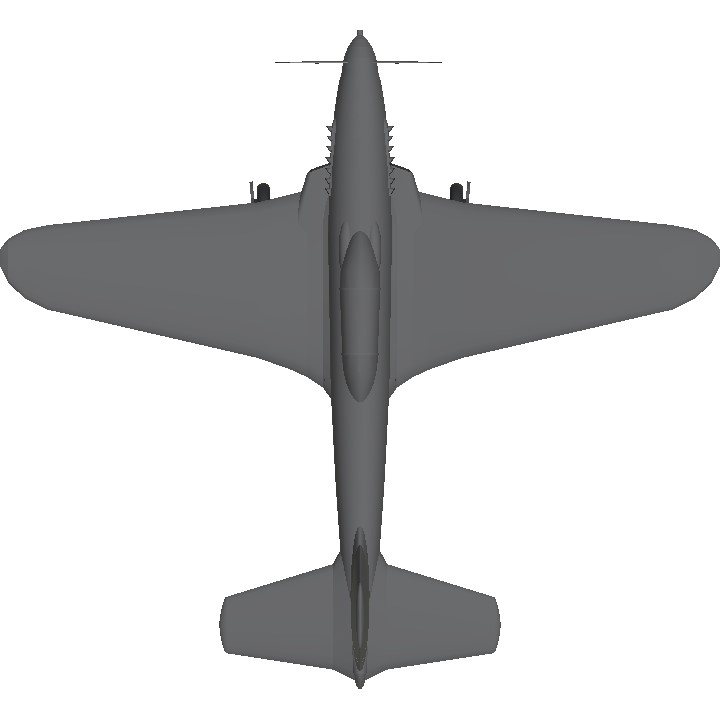
Description
Yak-3 went back to 1941 when the I-30 prototype was offered along with the I-26 (Yak-1) as an alternative design. The I-30, powered by a Klimov M-105P engine, was of all-metal construction, using a wing with dihedral on the outer panels. Like the early Yak-1, it had a 20 mm (0.79 in) ShVAK cannon firing through the hollow-driveshaft nose spinner as a motornaya pushka (???????? ????? - Literally: 'Motor Cannon'), twin 7.62 mm (0.300 in) synchronized ShKAS machine guns in cowling mounts and a ShVAK cannon in each wing.
During the Battle of Stalingrad, Luftwaffe fighters exhibited significant speed, climb rate, and armament advantages over those of the VVS. The Yak-1 then in service was understood to be in urgent need of a modernization were it to fight on equal footing against the latest models of German fighters, as well as better energy retention and higher firepower.
Then, in 1943, a group of designers headed by Alexander Sergeyevich Yakovlev designed the Yak-3, a further development of the proven Yak-1 aimed at improving survivability, flight characteristics and firepower, which required a lower weight, a higher-power engine and therefore, faster speed.
Gallery

![]h(ttps://i.ibb.co/BLW26cQ/20240225-193435.jpg)<br />



Specifications
General Characteristics
- Predecessor WWII Challenge (Closed)
- Created On Android
- Wingspan 36.4ft (11.1m)
- Length 33.4ft (10.2m)
- Height 13.6ft (4.1m)
- Empty Weight N/A
- Loaded Weight 6,844lbs (3,104kg)
Performance
- Horse Power/Weight Ratio 0.438
- Wing Loading 16.2lbs/ft2 (78.9kg/m2)
- Wing Area 423.7ft2 (39.4m2)
- Drag Points 5606
Parts
- Number of Parts 186
- Control Surfaces 5
- Performance Cost 721
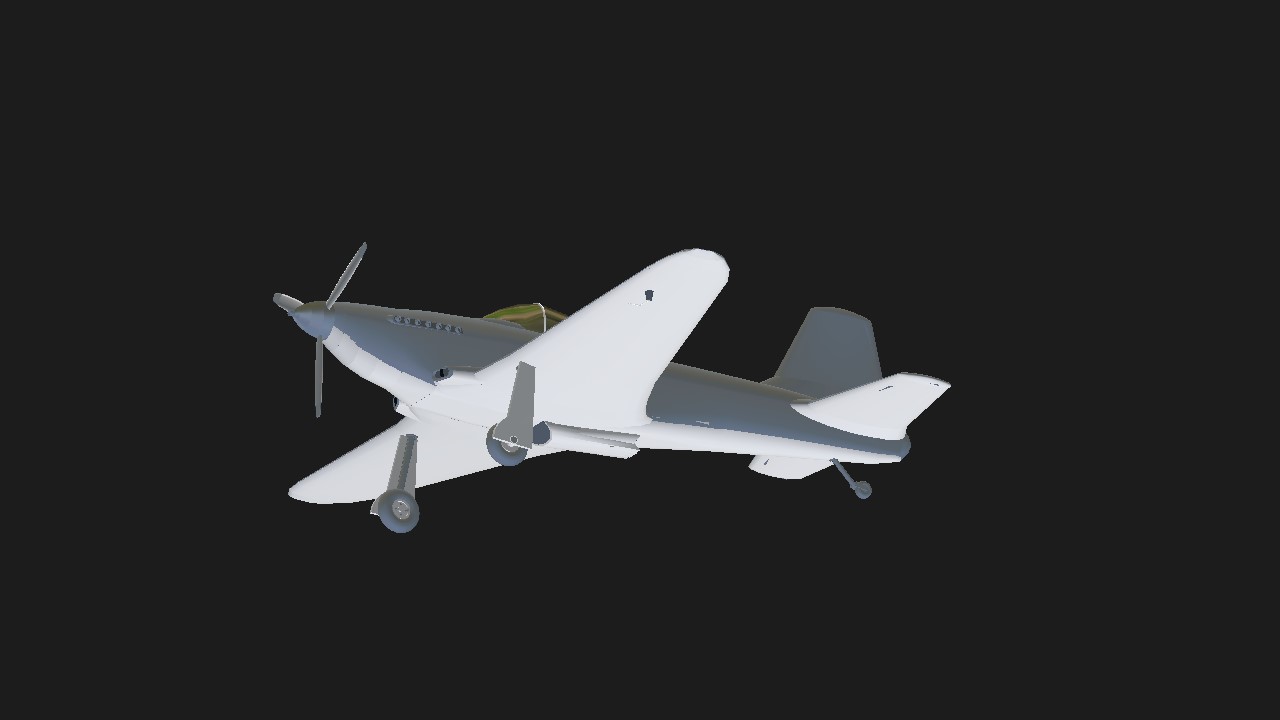
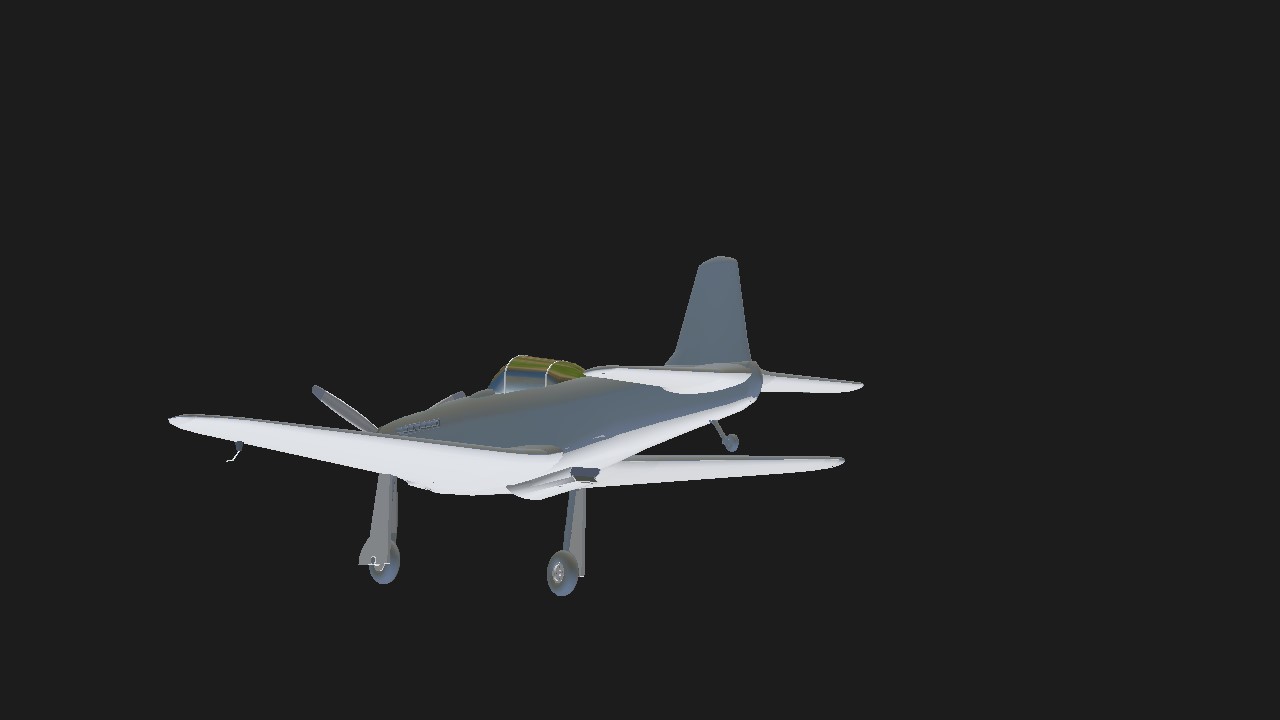
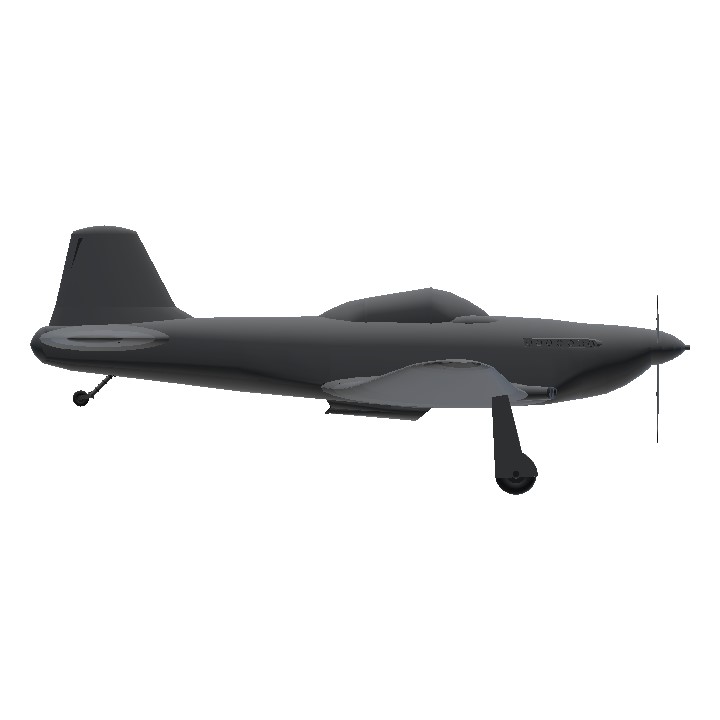
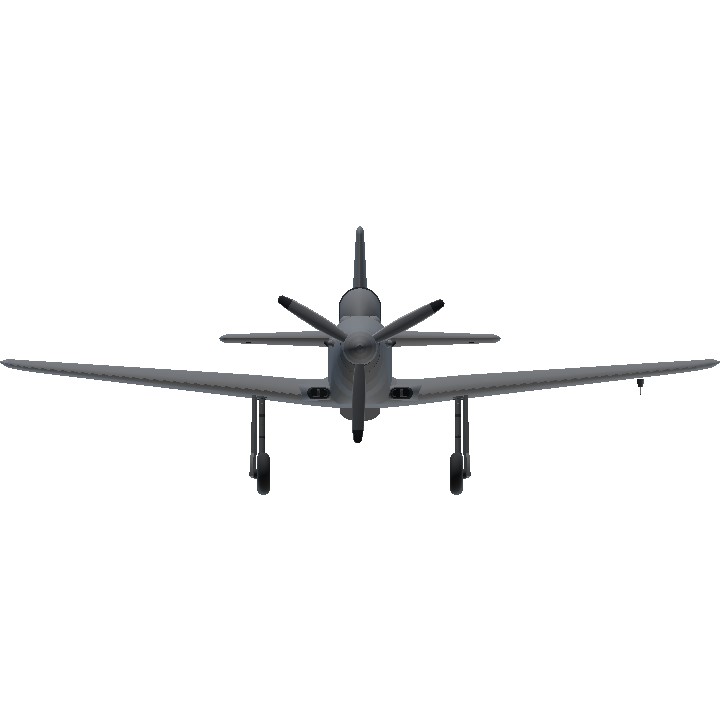






RATING
Looks : 6/10 pts.
Details : 4/10 pts.
Performance : 7.5/10 pts.
Weaponry : 9/10 pts.
Functionality : 6/10 pts.
OVERALL RATING : 6.5/10