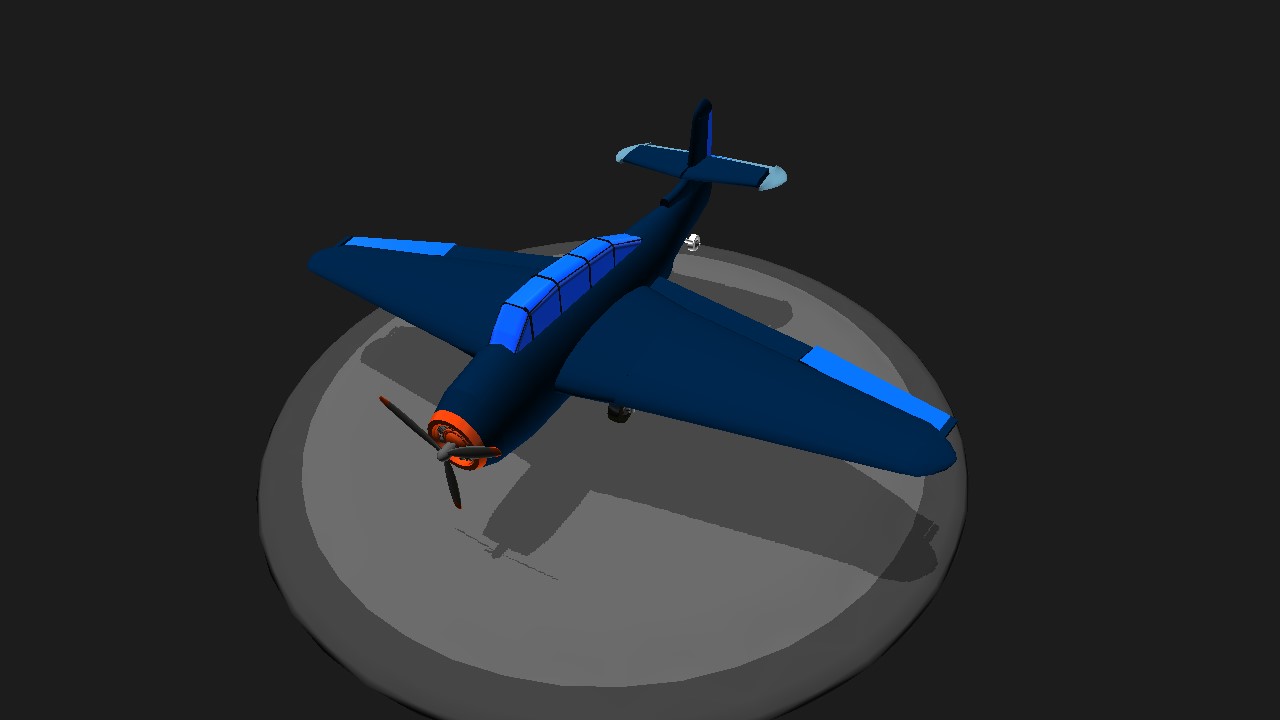
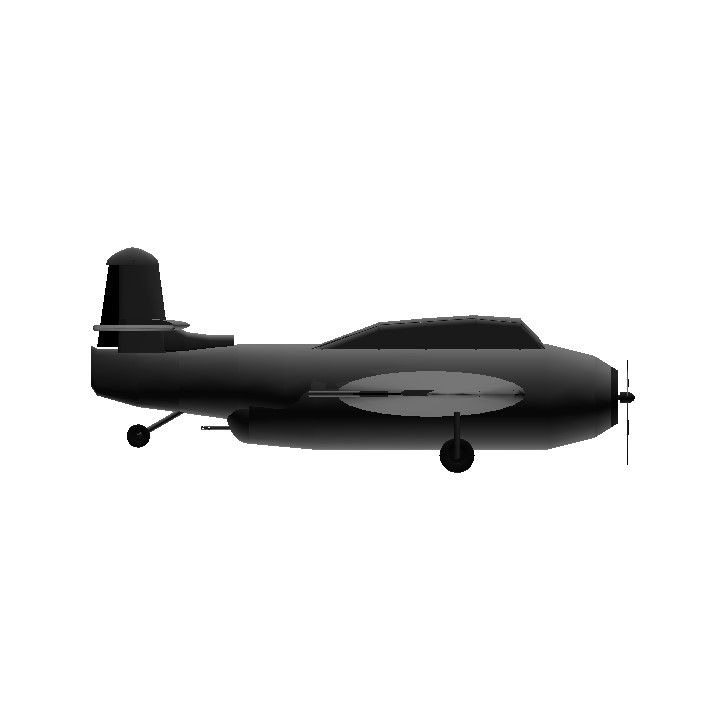
The U.S. TBF torpedo bomber is a new generation model used by Grumman to replace the old naval ship-borne attack aircraft TBD "Badger". It participated in the bidding in 1939, and received advance reservations in October 1940. August 7, 1941 Test flight of prototype XTBF-1. TBF is a single-engine multi-seat heavy-duty maritime attack aircraft equipped with a R2600 star-shaped high-power piston engine. To accommodate a torpedo or 900 kilogram bomb inside the belly, the TBF has a large fuselage with three cockpits arranged vertically. The lower part of the fuselage is a large bomb bay with a closed hatch. As a feature of the aircraft, the rear shooter has a spherical electric glass machine gun firing compartment that occupies the rear section of the cockpit. The TBF is equipped with a pair of cantilevered mid-wings with trapezoidal straps at opposite angles, and the outer section can be folded back to facilitate parking on the ship. The last three o'clock landing gear can all be included in the aircraft. TBF became the largest single-engine carrier aircraft in the US Navy.
Specifications
General Characteristics
- Created On Android
- Wingspan 50.4ft (15.4m)
- Length 37.7ft (11.5m)
- Height 15.8ft (4.8m)
- Empty Weight 12,454lbs (5,649kg)
- Loaded Weight 16,521lbs (7,493kg)
Performance
- Power/Weight Ratio 2.04
- Horse Power/Weight Ratio 0.121
- Wing Loading 37.6lbs/ft2 (183.6kg/m2)
- Wing Area 439.3ft2 (40.8m2)
- Drag Points 9507
Parts
- Number of Parts 108
- Control Surfaces 5
- Performance Cost 671