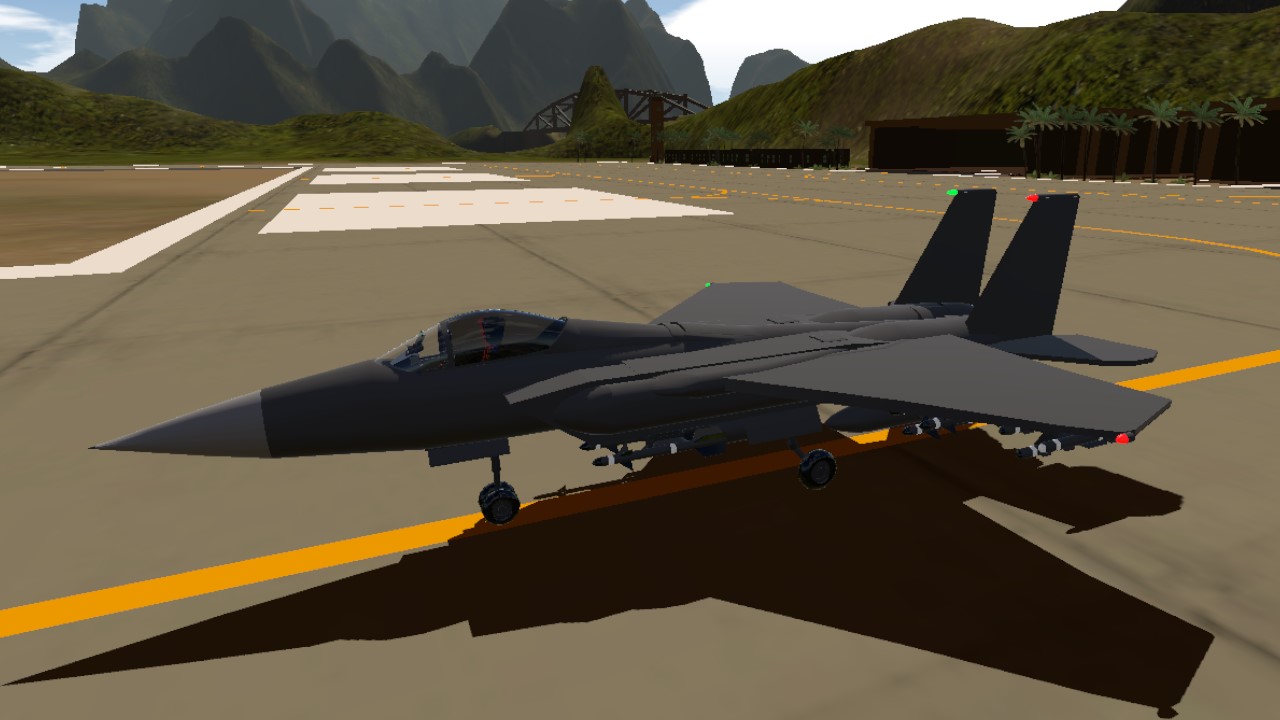
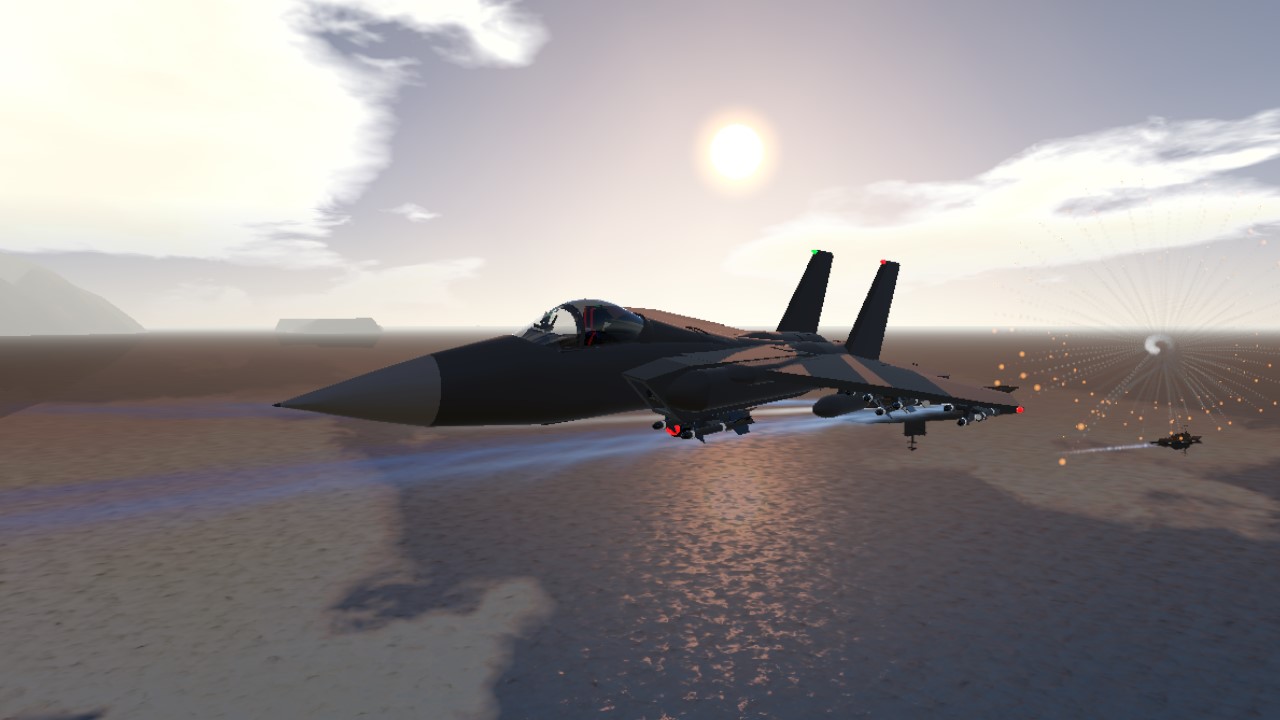
The McDonnell Douglas F-15 Eagle is an American twin-engine, all-weather tactical fighter aircraft designed by McDonnell Douglas (now part of Boeing). Following reviews of proposals, the United States Air Force selected McDonnell Douglas's design in 1969 to meet the service's need for a dedicated air superiority fighter. The Eagle first flew in July 1972, and entered service in 1976. It is among the most successful modern fighters, with over 100 victories and no losses in aerial combat, with the majority of the kills by the Israeli Air Force. The Eagle has been exported to Israel, Japan, and Saudi Arabia. The F-15 was originally envisioned as a pure air-superiority aircraft. Its design included a secondary ground-attack capability that was largely unused. The aircraft design proved flexible enough that an improved all-weather strike derivative, the F-15E Strike Eagle, was later developed, entered service in 1989 and has been exported to several nations. As of 2021, the aircraft is being produced in several variants
Specifications
General Characteristics
- Predecessor F-15 EAGLE
- Created On Windows
- Wingspan 38.1ft (11.6m)
- Length 54.5ft (16.6m)
- Height 16.3ft (5.0m)
- Empty Weight 9,217lbs (4,181kg)
- Loaded Weight 17,813lbs (8,080kg)
Performance
- Power/Weight Ratio 7.569
- Wing Loading 31.4lbs/ft2 (153.1kg/m2)
- Wing Area 568.1ft2 (52.8m2)
- Drag Points 5603
Parts
- Number of Parts 256
- Control Surfaces 8
- Performance Cost 1,338