McDonnell Douglas DC-10
The McDonnell Douglas DC-10 is an American trijet wide-body aircraft manufactured by McDonnell Douglas. The DC-10 was intended to succeed the DC-8 for long-range flights. It first flew on August 29, 1970; it was introduced on August 5, 1971, by American Airlines.

A DC-10-30 of Continental Airlines
The trijet has two turbofans on underwing pylons and a third one at the base of the vertical stabilizer. The twin-aisle layout has a typical seating for 270 in two classes. The initial DC-10-10 had a 3,500-nautical-mile [nmi] (6,500 km; 4,000 mi) range for transcontinental flights. The DC-10-15 had more powerful engines for hot and high airports. The DC-10-30 and –40 models (with a third main landing gear leg to support higher weights) each had intercontinental ranges of up to 5,200 nmi (9,600 km; 6,000 mi). The KC-10 Extender (based on the DC-10-30) is a tanker aircraft operated primarily by the United States Air Force.
Early operations of the DC-10 were afflicted by its poor safety record, which was partially attributable to a design flaw in the original cargo doors that caused multiple incidents, including fatalities. Most notable was the crash of Turkish Airlines Flight 981 in Paris in 1974, the deadliest crash in aviation history up to that time. Following the crash of American Airlines Flight 191, the deadliest aviation accident in U.S. history, the U.S. Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) temporarily banned all DC-10s from American airspace in June 1979. In August 1983, McDonnell Douglas announced that production would end due to a lack of orders, as it had widespread public apprehension after the 1979 crash and a poor fuel economy reputation. As design flaws were rectified and fleet hours increased, the DC-10 achieved a long-term safety record comparable to those of similar-era passenger jets.
Production ended in 1989, with 386 delivered to airlines along with 60 KC-10 tankers. The DC-10 outsold the similar Lockheed L-1011 TriStar. It was succeeded by the lengthened, heavier McDonnell Douglas MD-11. After merging with McDonnell Douglas in 1997, Boeing upgraded many in-service DC-10s as the MD-10 with a glass cockpit that eliminated the need for a flight engineer. In February 2014, the DC-10 made its last commercial passenger flight. Cargo airlines continued to operate a small number as freighters. The Orbis Flying Eye Hospital is a DC-10 adapted for eye surgery. A few DC-10s have been converted for aerial firefighting use. Some DC-10s are on display, while other retired aircraft are in storage.
Garuda Indonesia
Garuda Indonesia is the flag carrier of Indonesia, headquartered at Soekarno–Hatta International Airport near Jakarta. A successor of KLM Interinsulair Bedrijf, it is a member of SkyTeam airline alliance and the second-largest airline of Indonesia after Lion Air, operating scheduled flights to a number of destinations across Asia, Europe, and Australia from its hubs, focus cities, as well as other cities for Hajj. It is the only Indonesian airline that flies to European airspace.

At its peak from the late 1980s to the mid-1990s, Garuda operated an extensive network of flights all over the world, with regularly scheduled services to Adelaide, Cairo, Fukuoka, Johannesburg, Los Angeles, Paris, Rome, and other cities in Europe, Australia and Asia.[6] In the late 1990s and early 2000s, a series of financial and operational difficulties hit the airline hard, causing it to drastically cut back services. In 2009, the airline undertook a five-year modernization plan known as the Quantum Leap, which overhauled the airline's brand, livery, logo and uniforms, as well as acquiring a newer, more modern fleet and facilities and renewing focus on international markets. It earned Garuda awards such as Most Improved Airline, 5-Star Airline, and World's Best Cabin Crew by Skytrax. Garuda has since fallen back to financial difficulties exarcebated by dysfunctional management and corruption. However, it has maintained its service and safety standards. The top management was replaced in 2020 and a new restructuring programme is also underway.
Garuda also operated a budget subsidiary, Citilink, that provided low-cost flights to multiple Indonesian destinations and was spun-off in 2012. In November 2018, the airline took over operations as well as financial management of Sriwijaya Air by a cooperation agreement (KSO); the contract expired in December 2019.
Garuda Indonesia Flight 865
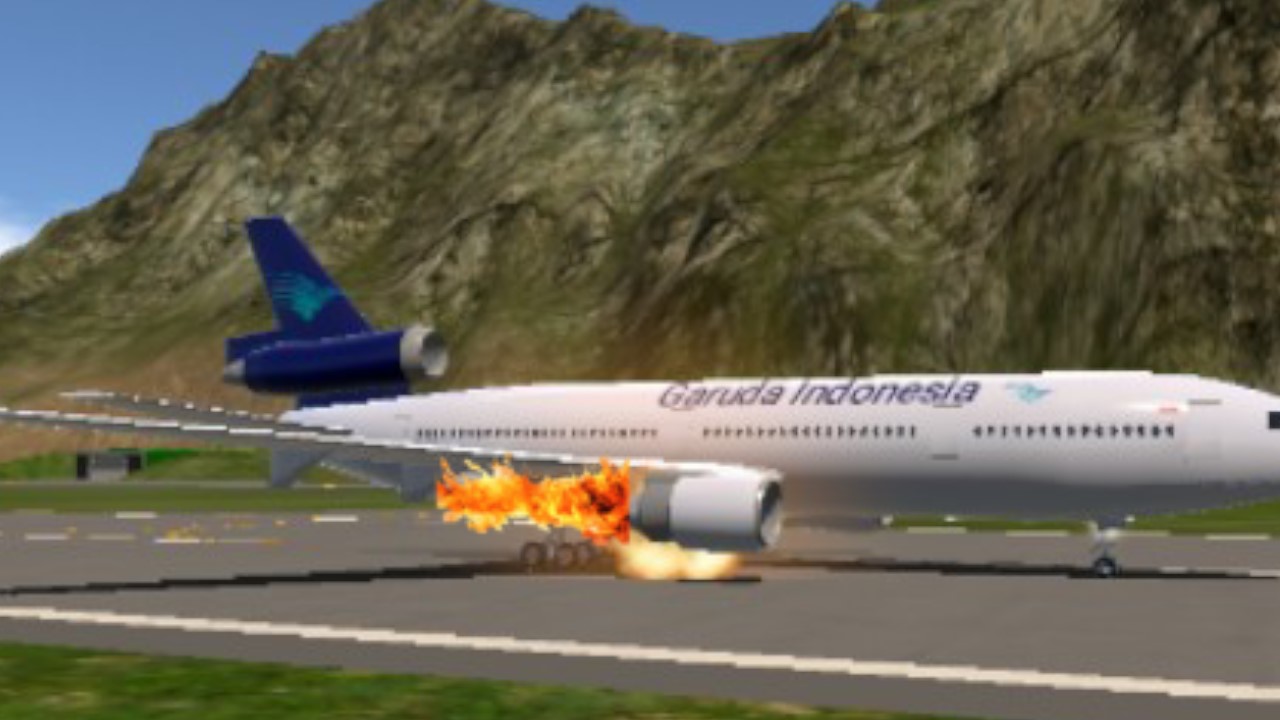
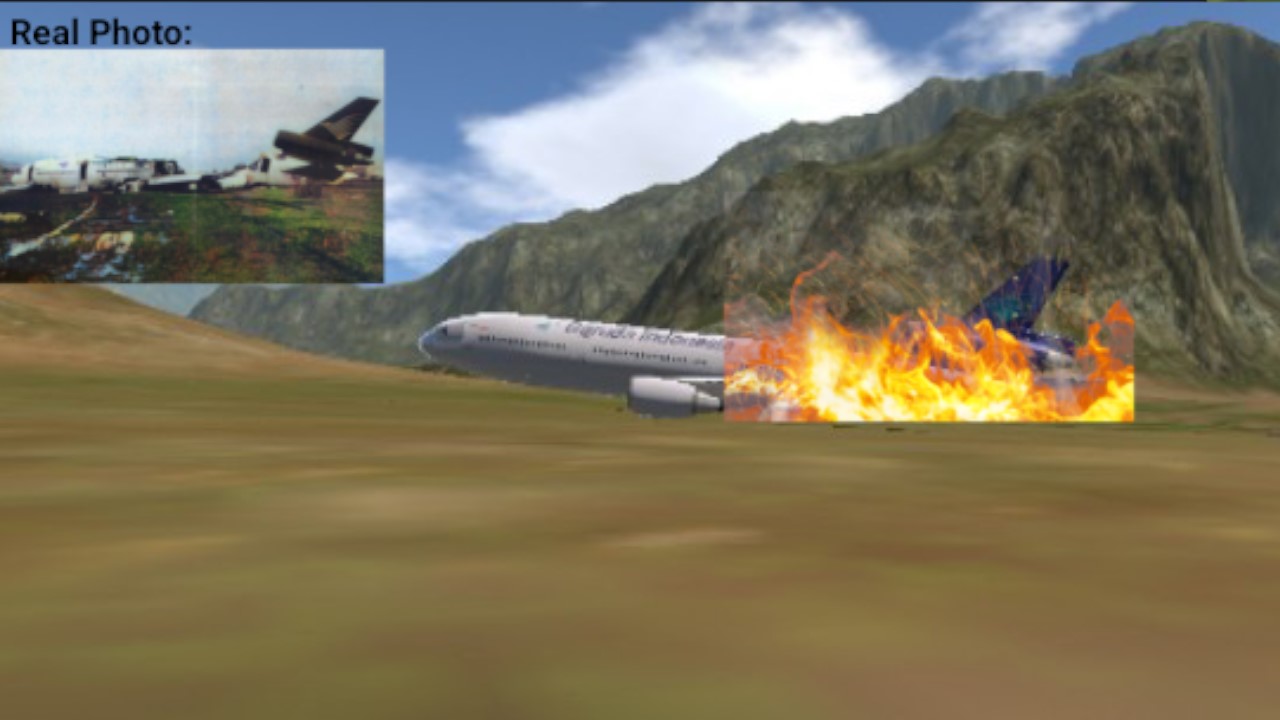
Garuda Indonesia Flight 865 (GA865/GIA865) was a scheduled international flight from Fukuoka, Japan, to Jakarta, Indonesia via Bali, Indonesia. On 13 June 1996, Flight 865 crashed on its takeoff from runway 16 at Fukuoka Airport. Three of the 275 on board were killed in the accident.
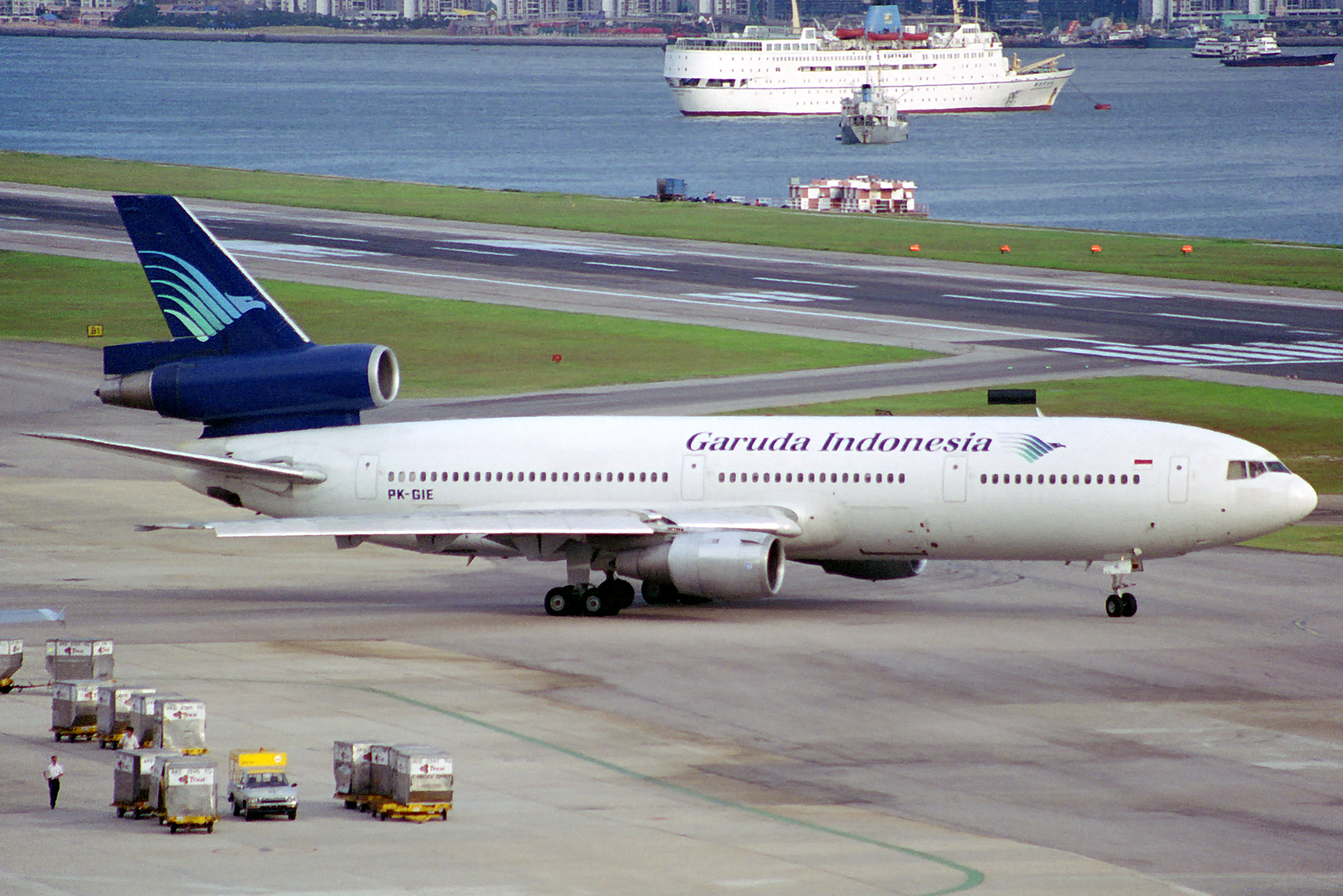

PK-GIE, the aircraft involved in the accident, at Kai Tak Airport in July 1993.
Real Photo

PK-GIE, the aircraft involved in the accident, at Kai Tak Airport in October 1995.
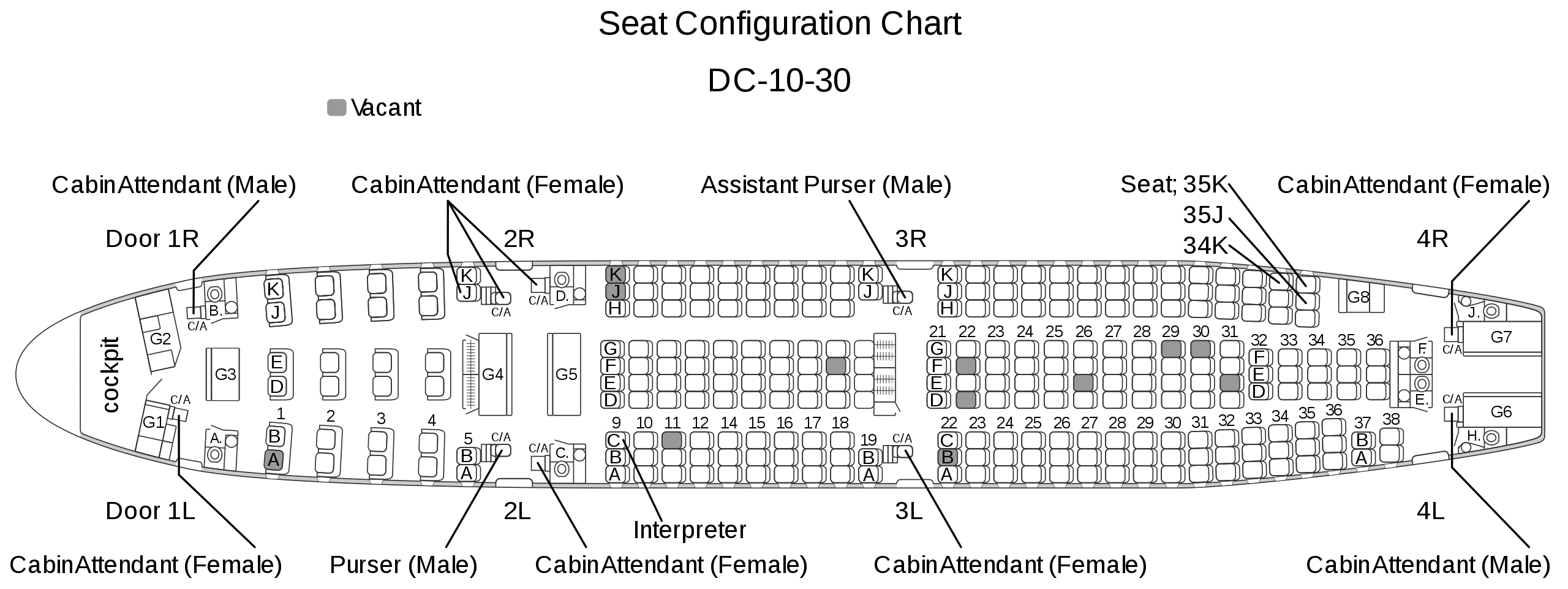
Seat map of Garuda Indonesia Flight 865 (the passengers in 34K, 35K, and 35J died)

Seat map of Garuda Indonesia Flight 865 (the passengers in 34K, 35K, and 35J died) [Note: Indonesian Version]

Seat map of Garuda Indonesia Flight 865 (the passengers in 34K, 35K, and 35J died) [Note: Japanese Version]

Wreckage of the landing gear after 6 days ago

Aftermath of the crash after 6 days ago

Wreckage of the landing gear after 6 days (another view)

Aftermath of the crash after 6 days ago (another view)

Aftermath of the crash after 6 days ago (third view)

Wreckage of the tail after 6 days ago
Specifications
Spotlights
- OldDaiBilibili 8 months ago
General Characteristics
- Predecessor DC 10 -30
- Created On Android
- Wingspan 165.4ft (50.4m)
- Length 181.7ft (55.4m)
- Height 59.0ft (18.0m)
- Empty Weight N/A
- Loaded Weight 132,731lbs (60,206kg)
Performance
- Power/Weight Ratio 1.147
- Horse Power/Weight Ratio 0.033
- Wing Loading 28.2lbs/ft2 (137.9kg/m2)
- Wing Area 4,700.5ft2 (436.7m2)
- Drag Points 10416
Parts
- Number of Parts 523
- Control Surfaces 9
- Performance Cost 3,482






