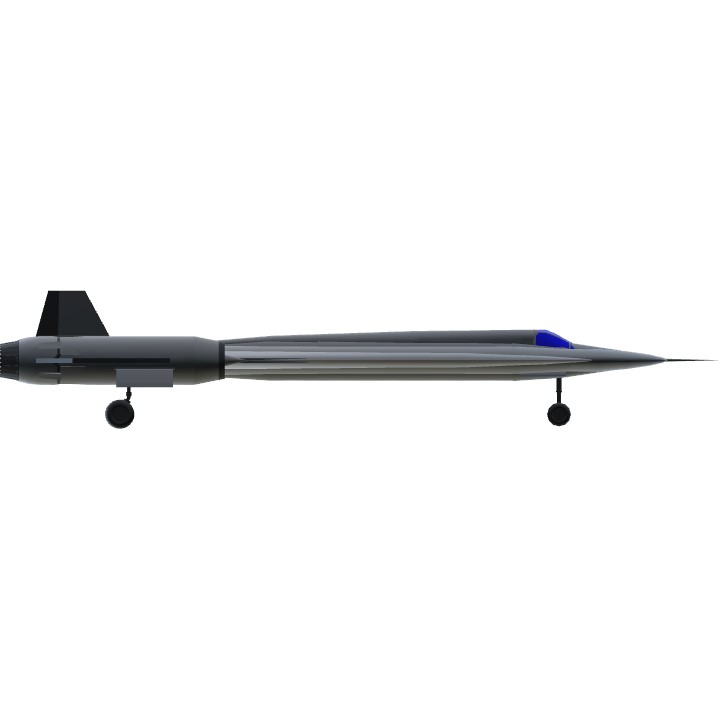
The Lockheed SR-71 "Blackbird" is a long-range, Mach 3+ strategic reconnaissance aircraft that was operated by the United States Air Force. It was developed as a black project from the Lockheed A-12 reconnaissance aircraft in the 1960s by Lockheed and its Skunk Works division. American aerospace engineer Clarence "Kelly" Johnson was responsible for many of the design's innovative concepts. During aerial reconnaissance missions, the SR-71 operated at high speeds and altitudes to allow it to outrace threats. If a surface-to-air missile launch were detected, the standard evasive action was simply to accelerate and outfly the missile. The shape of the SR-71 was based on the A-12 which was one of the first aircraft to be designed with a reduced radar cross-section
Specifications
General Characteristics
- Created On iOS
- Wingspan 36.4ft (11.1m)
- Length 48.5ft (14.8m)
- Height 9.0ft (2.7m)
- Empty Weight 16,245lbs (7,368kg)
- Loaded Weight 34,736lbs (15,756kg)
Performance
- Power/Weight Ratio 1.94
- Wing Loading 77.6lbs/ft2 (379.1kg/m2)
- Wing Area 447.4ft2 (41.6m2)
- Drag Points 4646
Parts
- Number of Parts 54
- Control Surfaces 6
- Performance Cost 363