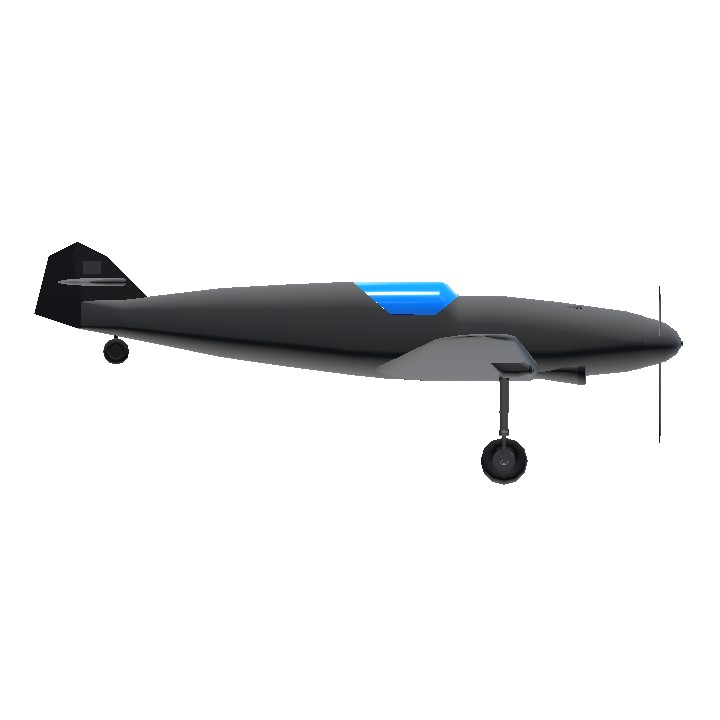
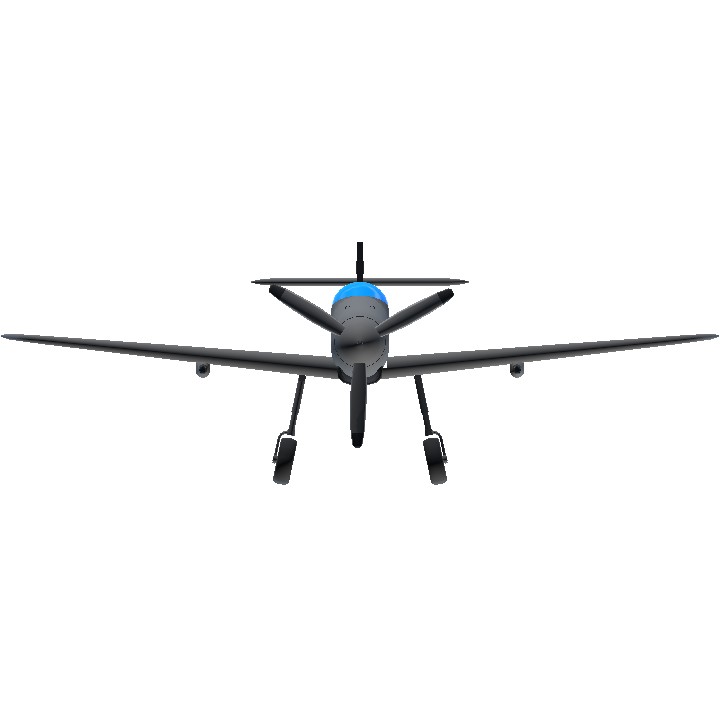
I think you don't like this plane for no reason
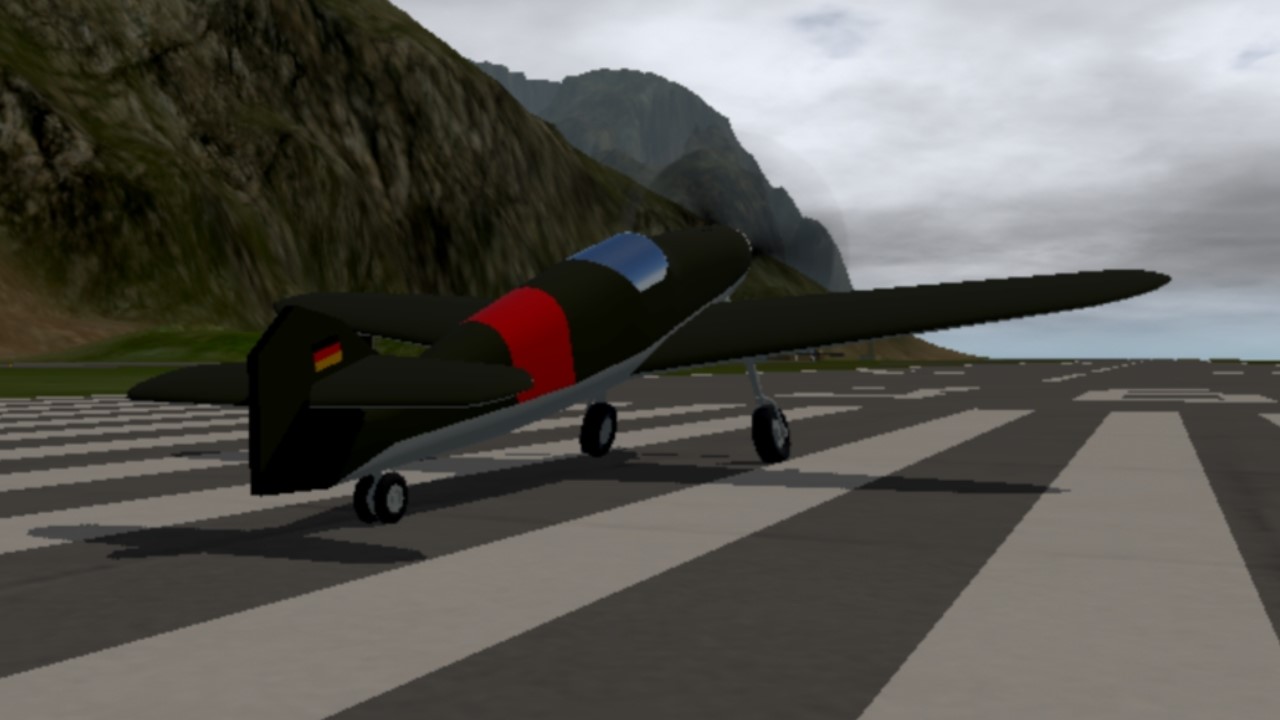
The Messerschmitt Bf 109 F-1 was a significant variant of the iconic German World War II fighter aircraft, designed by Willy Messerschmitt and first flown in 1935. The Bf 109 series was the backbone of the Luftwaffe's air superiority efforts throughout the war. The F-1 model, introduced in 1941, marked a major improvement in both performance and design over its predecessors, incorporating new technologies and modifications that enhanced its combat capabilities.
Design and Improvements:
Airframe & Aerodynamics:
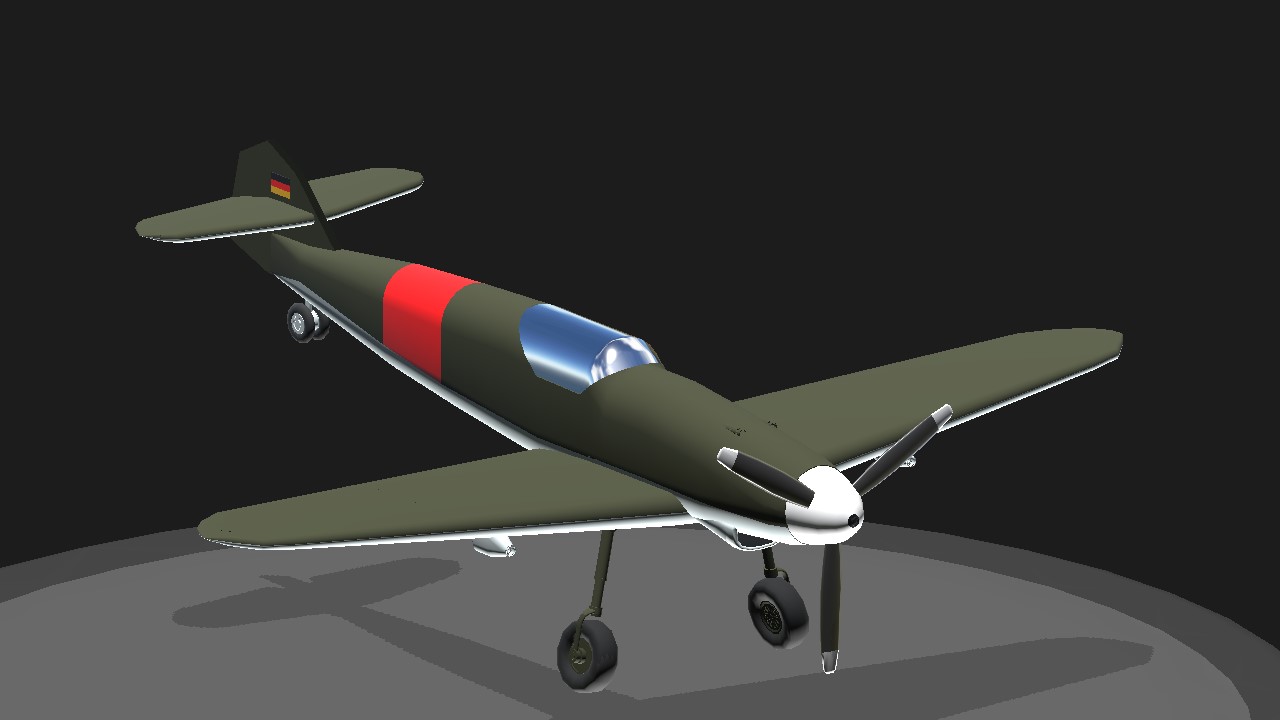
- The Bf 109 F-1 featured a redesigned, more aerodynamically efficient airframe compared to earlier versions (like the Bf 109 E, or "Emil").
- The most noticeable change was the redesigned, shorter fuselage, which improved maneuverability. The cockpit was also streamlined to reduce drag, and the wings were more tapered, contributing to better overall flight performance.
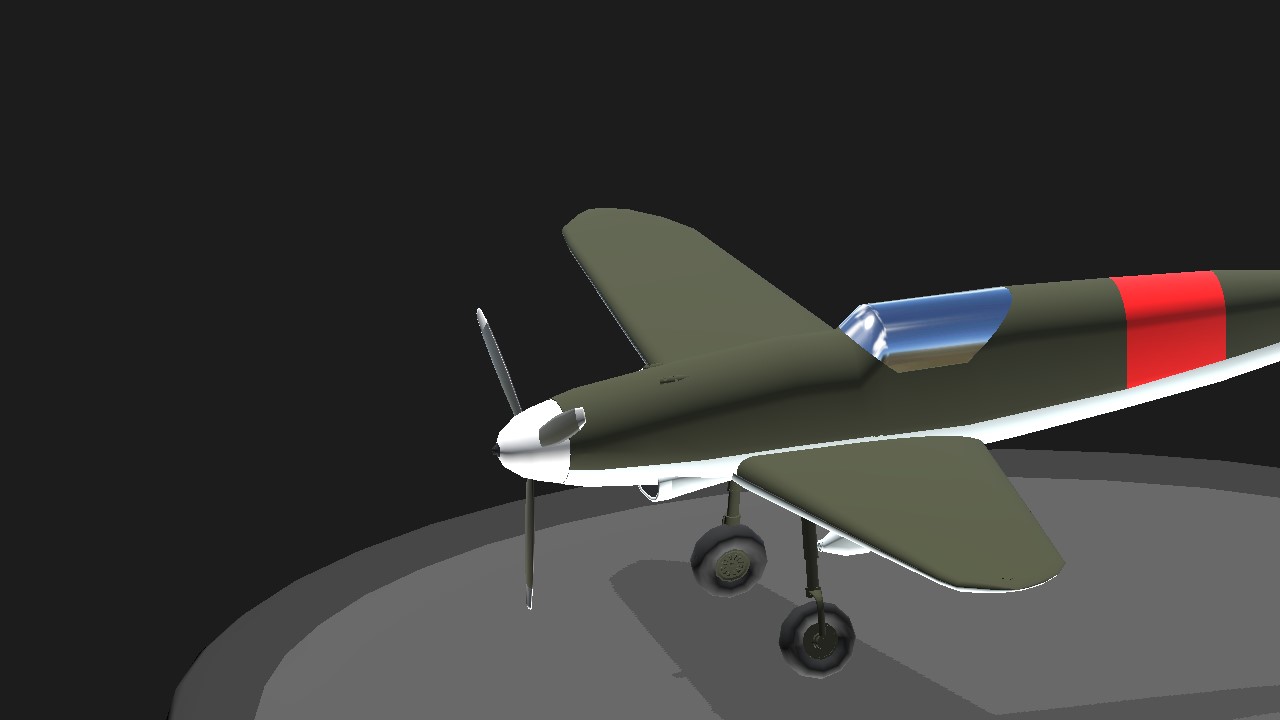
- The engine cowling was reworked to house the more powerful DB 601E engine, improving cooling efficiency and reducing drag.
Engine:
- The F-1 was powered by the Daimler-Benz DB 601E engine, a 1,175 hp liquid-cooled V12 engine. This represented an increase in power over earlier Bf 109 variants, allowing the aircraft to achieve higher speeds and better climb rates.
- The engine was equipped with an MW 50 (Methyl Hydrate) water-methanol injection system, which boosted power output for short durations, especially during combat.
Armament:
- The primary armament of the Bf 109 F-1 consisted of:
- Two 7.92mm MG 17 machine guns mounted in the engine cowling, synchronized to fire through the propeller arc.
- One 20mm MG FF/M cannon mounted in the nose, firing through the propeller hub.
- The armament was relatively standard for the time, offering a balance of rapid-fire machine guns and a heavy cannon for anti-aircraft and ground-attack roles.
- The primary armament of the Bf 109 F-1 consisted of:
Cockpit and Visibility:
- The F-1’s cockpit was redesigned for better pilot visibility and comfort. It had a canopy that provided improved rearward and downward visibility compared to earlier models, which helped with dogfighting tactics.
- The canopy was also semi-retractable, allowing for increased airflow over the pilot in high-speed flight.
Flight Performance:
- The Bf 109 F-1 was a highly agile and fast aircraft. Its maximum speed reached around 640 km/h (398 mph), which made it competitive with the best Allied fighters of the period.
- It had a climb rate of approximately 20 m/s (about 4,000 feet per minute), which allowed it to quickly reach combat altitudes.
- Its operational range was around 600 km (373 miles), giving it good reach for combat missions.
Handling and Combat:
- The F-1 was known for its excellent handling characteristics, particularly in high-speed dives and sharp turns. It could outmaneuver many Allied fighters of the early war period, including the British Spitfire Mk. V in certain conditions.
- The F-1 was well-suited for dogfighting, although pilots still had to be cautious during high-speed engagements to avoid overstressing the aircraft’s airframe, which could cause a loss of control.
- The improved aerodynamics and power-to-weight ratio made the F-1 an effective interceptor and a strong contender in the air superiority role.
Operational Use:
- The Bf 109 F-1 entered service in 1941, primarily in the Eastern Front, where it was used extensively against Soviet aircraft. It also saw service in the Mediterranean theater, particularly in North Africa, where it proved highly effective against Allied fighters.
- Jagdgeschwader (Fighter Wings), including JG 2 and JG 3, operated the F-1, and it was used in both Bodenplatte (Operation Bodenplate) and other major Luftwaffe operations during the early years of World War II.
- While it was eventually surpassed by newer Bf 109 variants (like the F-4, G-2, and G-6), the F-1's combination of speed, firepower, and agility made it one of the best fighters in the world at the time of its introduction.
Legacy:
- The Bf 109 F-1 was one of the key stepping stones in the evolution of the Bf 109 series, transitioning from the earlier, less refined models to the more powerful, heavily armed versions that would dominate the skies for the remainder of the war.
- It was considered a favorite of many Luftwaffe aces, and its performance remained competitive even as newer Allied aircraft came into service.
Conclusion:
The Messerschmitt Bf 109 F-1 was a pivotal fighter in the early years of World War II, combining excellent performance, innovative design features, and effective armament. Although it was eventually outclassed by later variants and newer Allied designs, its legacy as one of the most effective and versatile fighters of the war remains secure.
Specifications
Spotlights
- ACEOFFICERS one year ago
General Characteristics
- Created On Android
- Wingspan 41.0ft (12.5m)
- Length 36.8ft (11.2m)
- Height 13.2ft (4.0m)
- Empty Weight 2,417lbs (1,096kg)
- Loaded Weight 12,295lbs (5,577kg)
Performance
- Horse Power/Weight Ratio 0.121
- Wing Loading 47.2lbs/ft2 (230.6kg/m2)
- Wing Area 260.3ft2 (24.2m2)
- Drag Points 2248
Parts
- Number of Parts 119
- Control Surfaces 9
- Performance Cost 437