The Peacemaker :
BUT SIMPLE!
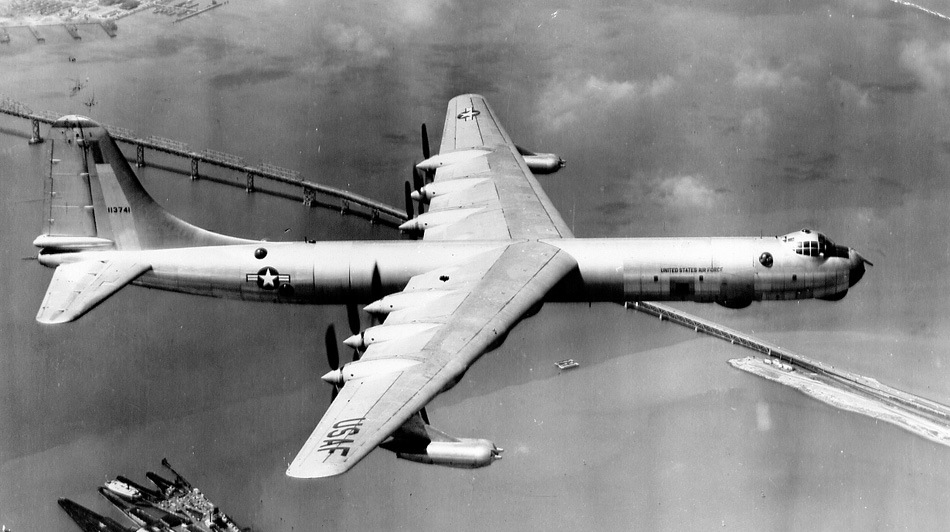

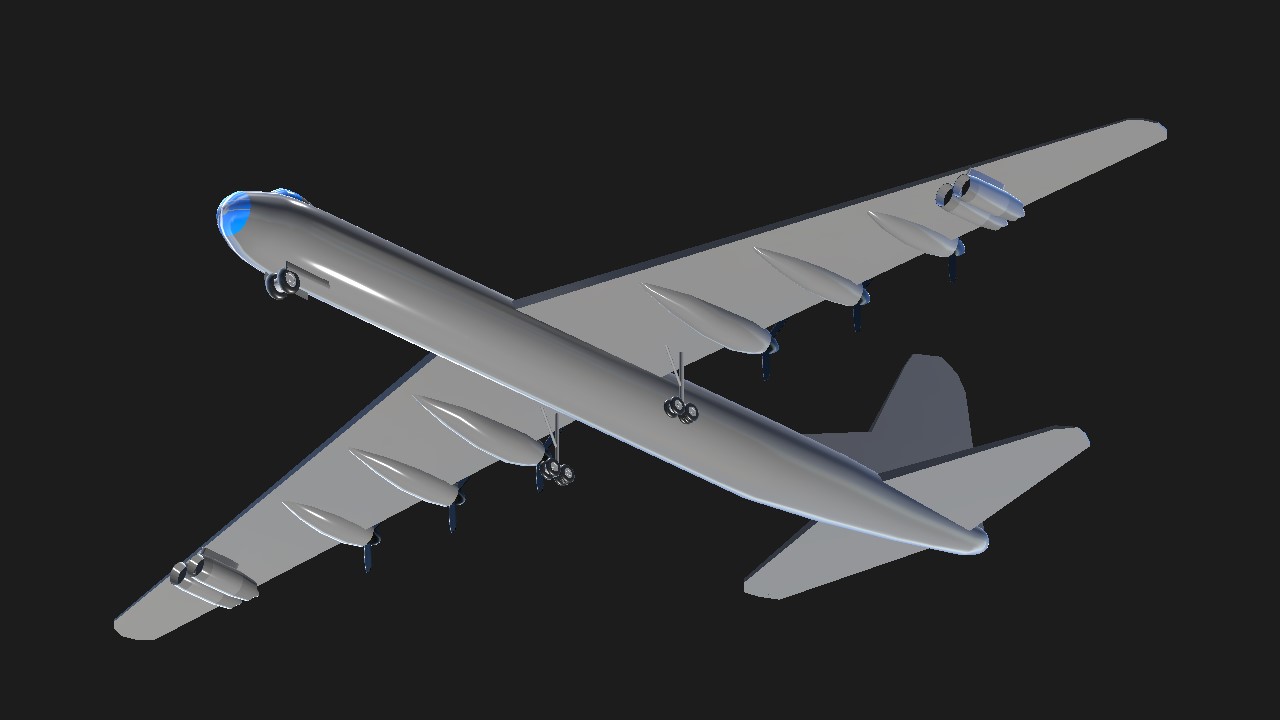
The Convair B-36 "Peacemaker"[N 1] is a strategic bomber built by Convair and operated by the United States Air Force (USAF) from 1949 to 1959. The B-36 is the largest mass-produced piston-engined aircraft ever built, although it was exceeded in span and weight by the one-off Hughes H-4 Hercules. It has the longest wingspan of any combat aircraft. The B-36 was capable of intercontinental flight without refueling.
Entering service in 1948, the B-36 was the primary nuclear weapons delivery vehicle of Strategic Air Command (SAC) until it was replaced by the jet-powered Boeing B-52 Stratofortress beginning in 1955. All but four aircraft have been scrapped.
Incidents:
Though the B-36 had a good overall safety record, well above average for the class and time, 10 B-36s were involved in accidents between 1949 and 1954 (three B-36Bs, three B-36Ds, and four B-36Hs).[61] A total of 32 B-36s were written off in accidents between 1949 and 1957 of 385 built.[22]:?238? When a crash occurred, the magnesium-rich airframe burned easily.[62]
On 14 February 1950 off the northwest coast of British Columbia on Princess Royal Island, 17 crew parachuted from their blazing B-36B; 12 crewmen were found with one injured, and five were missing.[63]
On Labor Day, Monday, 1 September 1952, a tornado hit Carswell Air Force Base, Fort Worth, damaging aircraft of the 7th and 11th Bomber Wings' complement of B-36s. Some two-thirds of the USAF's entire B-36 fleet was damaged, as well as six aircraft being built at that point at Convair's Fort Worth plant. The base was shut down and operations transferred to Meacham Field. Joint repairs by Convair and the USAF had repaired 18 of the 19 heavily damaged aircraft (and the six damaged and unfinished aircraft at Convair) by May 1953. One example was to be scrapped, but was used as a nuclear testing site ground target. Another heavily damaged aircraft was rebuilt as the NB-36H Nuclear Reactor Testbed aircraft
On February 2, 1953 Convair B-36H Serial No 51-5729 crashed 16 miles southwest of CFB Goose Bay, Labrador, following a transatlantic flight from RAF Fairford. The aircraft crashed in hilly wooded terrain. The investigation determined that a Ground-controlled approach failure was at fault. Two of the 17 crew perished.
On the night of 17 March 1953 RB-36H-25, 51-13721 departed the Canary Islands to test North American air defenses. Change in weather conditions drove the aircraft off course, and early in the morning on 18 March the aircraft collided with a mountain on the west side of Trinity Bay (48.184352°N 53.664271°W) just north of Burgoyne's Cove, Newfoundland, Canada. All 23 crew, including Brigadier General Richard Ellsworth, were killed.[65]
Specifications
General Characteristics
- Created On Android
- Wingspan 218.9ft (66.7m)
- Length 156.9ft (47.8m)
- Height 41.6ft (12.7m)
- Empty Weight 64,977lbs (29,473kg)
- Loaded Weight 124,047lbs (56,266kg)
Performance
- Power/Weight Ratio 0.724
- Horse Power/Weight Ratio 0.048
- Wing Loading 22.8lbs/ft2 (111.4kg/m2)
- Wing Area 5,439.1ft2 (505.3m2)
- Drag Points 32313
Parts
- Number of Parts 134
- Control Surfaces 5
- Performance Cost 745







Look very good, thk you bro